The exploration of “What Is The Aquatic Weed Alisma Gramineum” initiates with a comprehensive discussion of this particular aquatic species, its nature, and characteristics. This article provides a rich understanding of Alisma Gramineum, a prevalent water plant that exhibits unique adaptations to thrive in its aquatic environment. Your quest to discover more about this intriguing aquatic weed is bound to be fulfilled as you unearth pertinent facts and insightful details about its habitat, biological traits and its significance in the ecosystem.
What is Alisma Gramineum?
Alisma Gramineum, a member of the Alismataceae family, is a perennial plant native to several regions around the world. It is commonly identified as an aquatic weed due to its preference for marshy, water-soaked environments. It thrives in shallow water and riparian edge habitats, often surfacing in ponds and drainage ditches.
Definition of Alisma Gramineum
The Alisma Gramineum is an herbaceous plant characterized by its long, slender leaves and small whitish-pink flowers arranged in an umbellate pattern. As a symbolic element in folklore, medical applications, and even culinary art, it plays various roles in different cultures.
Other names for Alisma Gramineum
Several common names, such as ribbon-leaf water-plantain, slimleaf water-plantain, and gramineous water-plantain, identify Alisma Gramineum. Its popularity across cultures has earned it several vernacular names, reflecting its significant presence in traditional customs and folklore.
Alisma Gramineum in different languages
In the global flora environment, Alisma Gramineum goes by different names across various languages. For instance, in French, it’s identified as ‘Alisma Grêle,’ while it is called ‘Zebrina Blanca’ in Spanish.
Characteristics of Alisma Gramineum
Morphology of Alisma Gramineum
The Alisma Gramineum displays a rosette arrangement, with its leaves protruding from a corm-like base. Most notable are its inflorescences, which are conical and contain small, delicate white to pale pink flowers, typically blooming from June to August.
Adaptive features of Alisma Gramineum
This plant shows a remarkable adaptation to its environment. Its submerged leaves take on a different form from the aerial leaves, a characteristic that enables the Alisma Gramineum to thrive both subaqueously and in well-drained terrains.
Lifespan and growth pattern
Alisma Gramineum is a perennial plant, marking it with a lifespan that exceeds more than two years. For growth, it propagates primarily through seed production, with an adult plant capable of producing numerous flowering heads, which contain many small seeds.
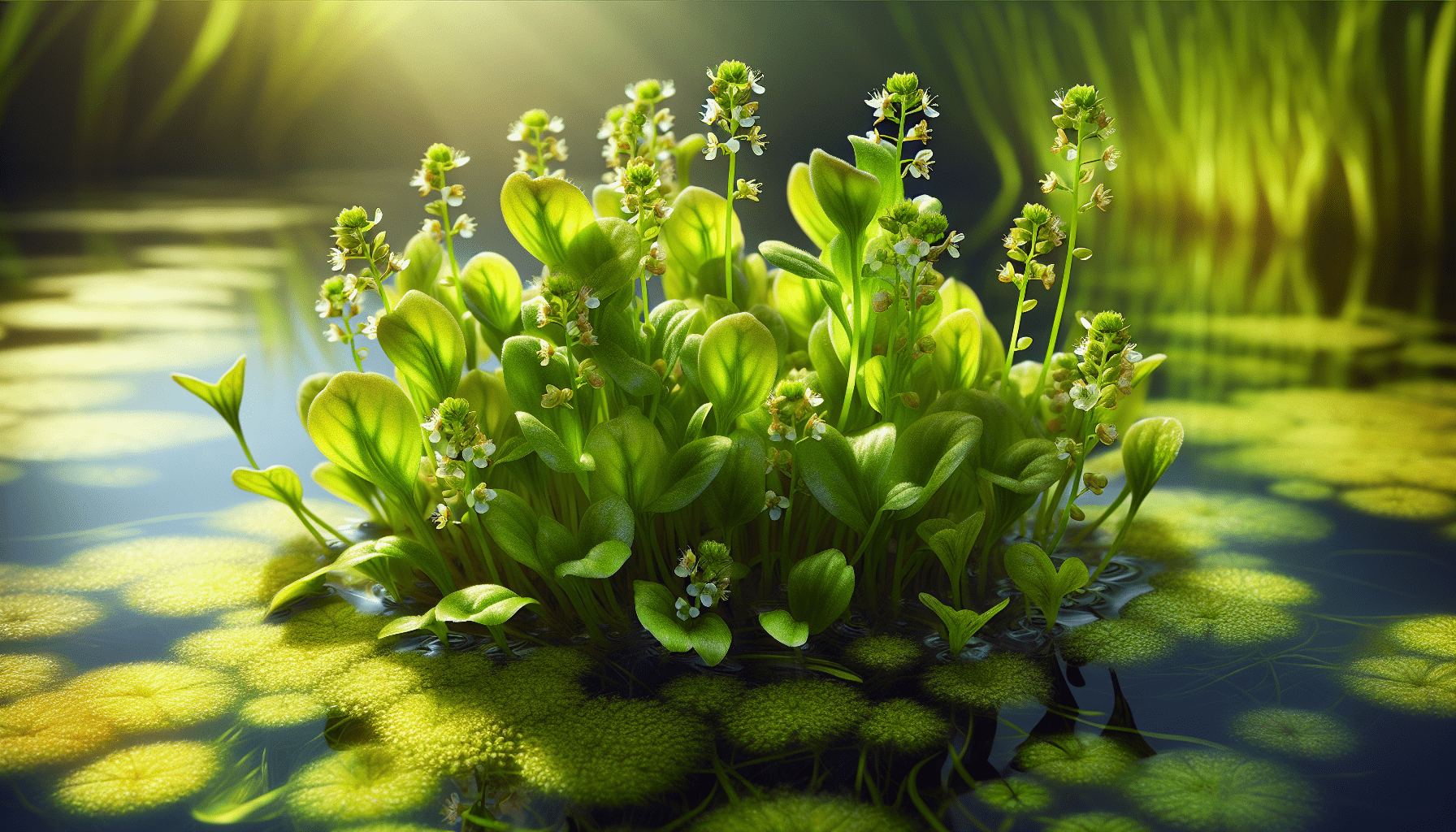
Habitat of Alisma Gramineum
Geographical distribution of Alisma Gramineum
The aquatic weed has a wide global distribution. It is indigenous to regions traversing Europe, Asia, and North America.
Ideal environmental conditions for growth
This hardy plant thrives in shallow, slow-moving, or stagnant water bodies, such as ponds, lake edges, and stream banks. It prefers silty or clayey loamy soils but can grow in less favorable conditions, too.
Man-made environments favouring Alisma Gramineum
In man-made environments, Alisma Gramineum can often be found flourishing in drainage ditches or in the stagnant waters of rice fields, owing to their similarity with natural, stagnant habitats.
Role in Aquatic Ecosystem
Importance in aquatic food chains
As a primary producer in the food chain, Alisma Gramineum provides an essential food source for various herbivorous insects and small mammals while its underwater structures offer shelter and breeding grounds for aquatic life.
Contribution to biodiversity
This aquatic plant plays a significant role in supporting biodiversity. Birds, insects, and other small mammals use the Alisma Gramineum as a food source, nest-building material, and habitat, thus increasing the diversity of the ecosystem.
Ecosystem services provided by Alisma Gramineum
Among other functions, Alisma Gramineum helps stabilize the environment it occupies, lessening soil erosion and regulating water flow. It also contributes to water purification by absorbing surplus nutrients present in the water bodies, curbing water pollution.

Reproduction and Dispersion
Alisma Gramineum’s reproductive system
Alisma Gramineum primarily reproduces through seeds. The flowers, which are hermaphroditic (contain both male and female reproductive organs), are typically pollinated by insects.
Reproductive season and lifecycle
The blossoming period typically takes place from June to August. The plant sheds its seeds once the flower wilts, and these seeds remain dormant through the winter, germinating the following spring.
Mechanisms for seed dispersion
The seeds are dispersed using hydrochory, i.e., the transportation of dispersal units by water. The seed casing allows for floatation, enabling their spread across various aquatic environments.
Culinary and Medicinal Use
Usage in traditional medicine
In traditional medicines, especially within East Asia, Alisma Gramineum is often used to treat various ailments, including kidney stones, edema, and urinary tract infections.
Nutritional value of Alisma Gramineum
Although not widely employed for culinary purposes, the roots of Alisma Gramineum are edible. After careful processing to remove toxicity, they are packed with nutrients, namely starch, fiber, and vitamins.
Potential risks and side effects
If ingested raw, Alisma Gramineum can cause severe stomach aches due to its high sapogenin content. However, correct processing can make it safe for consumption.
Alisma Gramineum as an Invasive Species
Impact on local biodiversity
In areas where it’s not native, Alisma Gramineum can outcompete local plant species, threatening biodiversity. Its prolific reproduction and rapid growth can overwhelm existing plant communities, causing drastic shifts in ecological dynamics.
Prevention and control measures
Mechanical control, including manual removal, is the most common prevention method. However, in cases of severe infestation, herbicide application may be necessary to control the spread.
Studies on its invasiveness
Given Alisma Gramineum’s potential to be invasive, it has been the subject of several studies seeking to understand its proliferation mechanisms, impacts, and control measures, aiming to maintain ecological balance and support biodiversity.
Conservation Status
Current conservation status
Despite its potential to become invasive in some niches, Alisma Gramineum is not currently identified as a globally threatened or endangered species.
Threats to the species
Changes to the hydrological cycles could pose a significant threat to the persistence of Alisma Gramineum. Additionally, pollution and the introduction of invasive species that outcompete this water-plantain species could influence its survival negatively.
Conservation efforts
As of now, specific conservation measures for Alisma Gramineum are not widely reported. However, efforts to conserve aquatic habitats, in general, can potentially benefit this species as well.
Research and Studies on Alisma Gramineum
Historical and recent studies
From early pharmacological research to more recent studies investigating Alisma Gramineum’s ecological dynamics, multiple scientific papers have shed light on this plant.
Findings related to medical and dietary use
Research findings have shown Alisma Gramineum to possess diuretic, antimicrobial, and antifungal properties. Additionally, some studies suggest potential properties that could make it a candidate for treating diabetes and obesity.
Future research directions
Future research should focus on comprehensively understanding the plant’s potential impacts on non-native environments, its phytochemical composition, and pharmacological properties to exploit its use beneficially.
Alisma Gramineum in Culture and Folklore
Role in local cultures and traditions
In various cultures, Alisma Gramineum has been historically significant. It’s used in Asian traditional medicine, crafted into trinkets in certain tribal communities, and often included in folktales.
Symbolic meanings of Alisma Gramineum
Different cultures attribute numerous symbolic meanings to Alisma Gramineum, associating it with wellness, longevity, and good fortune.
Stories and myths featuring Alisma Gramineum
Various folklores and myths incorporate Alisma Gramineum. For instance, some ancient tales mention this aquatic weed as a remedy bestowed by the Gods themselves, further emphasizing its cultural importance.