In your quest to understand freshwater ecosystems, you may come across a variety of plant species, one of which is the aquatic weed, Alisma Wahlenbergii. This article will provide you with an in-depth analysis of this aquatic plant, highlighting its physical characteristics, origins, ecological roles and impacts. It will give you insight into why this particular plant, despite its deceptively simple appearance, holds considerable importance within the realm of limnology, the study of inland waters.
Overview of Alisma Wahlenbergii
Definition of Alisma Wahlenbergii
Alisma Wahlenbergii is a perennial aquatic plant species belonging to the Alismataceae family. It shares its genus with not less than 11 other species. This plant species is primarily distinguished by its preferred watery habitat, unique structure, and functional traits that equip it for survival in its ecosystem.
Common Names and Synonyms
While Alisma Wahlenbergii is the scientific name given to this plant species, it is known by several common names in different regions. Being an aquatic species, common names are often derived from its water-loving nature. In addition, the plant has been categorized under varied synonyms due to its botanical history.
Regional Distribution
The regional distribution of Alisma Wahlenbergii is diverse, showing presence across various continents and within numerous aquatic ecosystems. Its adaptive qualities enable it to thrive across various climates and environmental conditions.
Scientific Classification of Alisma Wahlenbergii
Kingdom, Phylum, and Class of Alisma Wahlenbergii
From a scientific perspective, the classification of Alisma Wahlenbergii begins with its categorization under the Plantae kingdom. The plant belongs to the Angiosperms phylum (flowering plants) and is further classified under the class of Monocotyledonous. These classifications denote its phylogenetic placement in the botanical tree of life.
Order and Family
Guided by the infrastructure established by the phylogenetic kingdom and class, Alisma Wahlenbergii is further grouped in the Alismatales order and the Alismataceae family. This series of categorizations essentially defines the general structure, lifecycle, habitat and functional behavior this plant species presents.
Genus and Species Details
In its ultimate categorization, Alisma Wahlenbergii belongs to the Alisma genus, sharing its group with many other water-loving species. The species name, Wahlenbergii, is a tribute to the botanist who first classified it, thus embedding a piece of botanical history into its nomenclature.
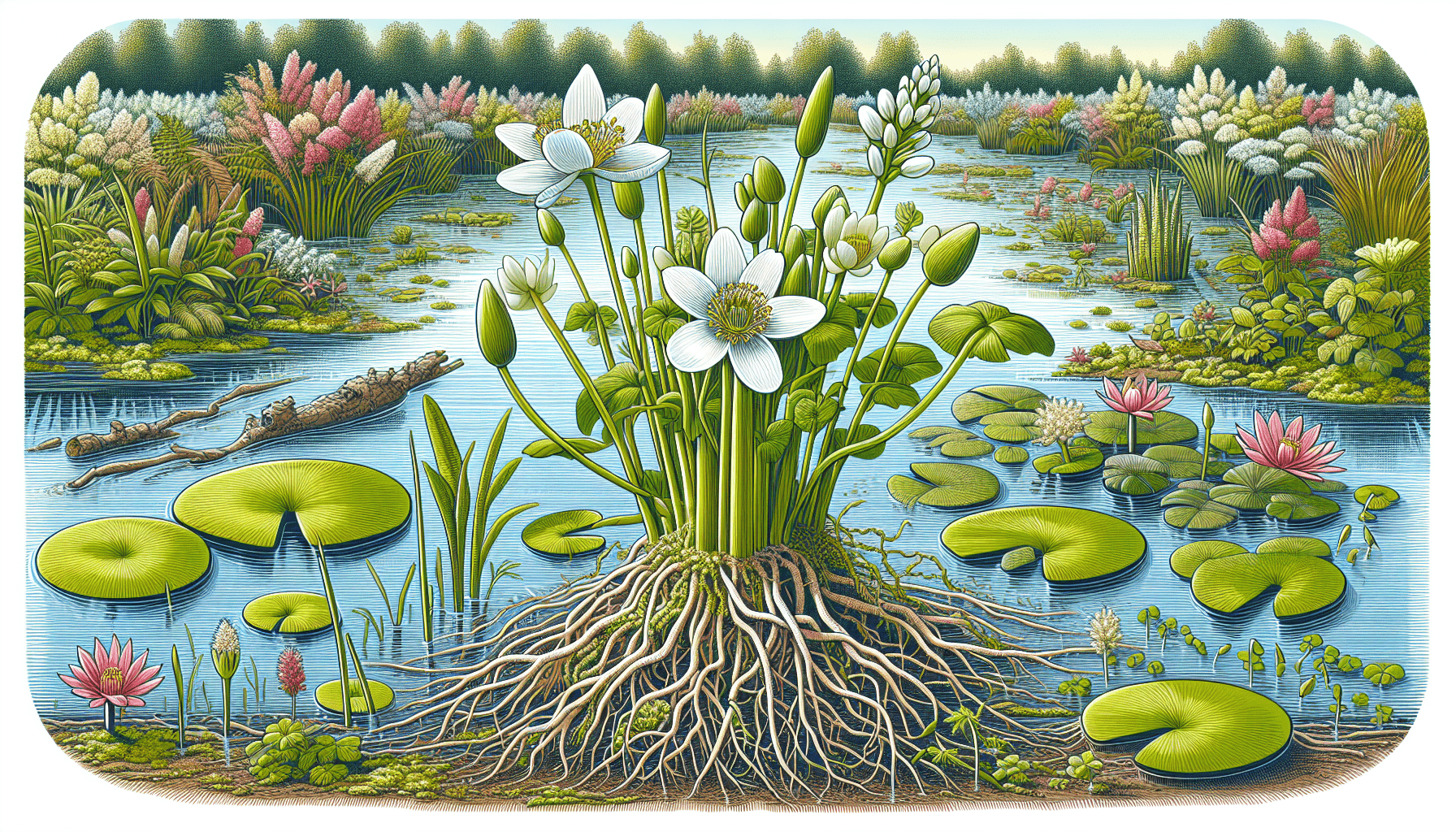
Physical Characteristics of Alisma Wahlenbergii
Size and Shape
Alisma Wahlenbergii is identifiable by its prominent size and irregular shape. The plant commonly reaches sizable dimensions due to its aggressive growing nature, an attribute that becomes more noticeable in its preferred habitat.
Leaf and Stem Description
The leaf and stem structure of Alisma Wahlenbergii is highly distinctive, characterized by elongated petioles and alternately arranged leaves. Its stem and leaves exhibit a coarse texture and a deep green color that aids in photosynthesis beneath the water surface.
Flower Description
The flowers of the Alisma Wahlenbergii are a hallmark of its beauty. Blooming from the ends of tall stalks, the flowers are composed of three symmetrical petals, displaying a uniform white color with subtle pink undertones.
Habitat and Ecological Niche
Preferred Aquatic Ecosystems
As an aquatic herb, Alisma Wahlenbergii favors watery ecosystems. Lakes, slow-moving rivers, and even marshes and swamps are common habitats for this plant, as these settings provide ample water and nutrients for its growth.
Regional Climates
The plant’s resilience allows it to adapt to differing climates depending on the region of distribution. However, it reveals a particular affinity towards temperate climates.
Interactions with Other Aquatic Life
Alisma Wahlenbergii interacts with other aquatic life forms in a complex way. It provides shelter and feeding grounds to various water-dwelling creatures and thus contributes significantly to biodiversity in its habitat.
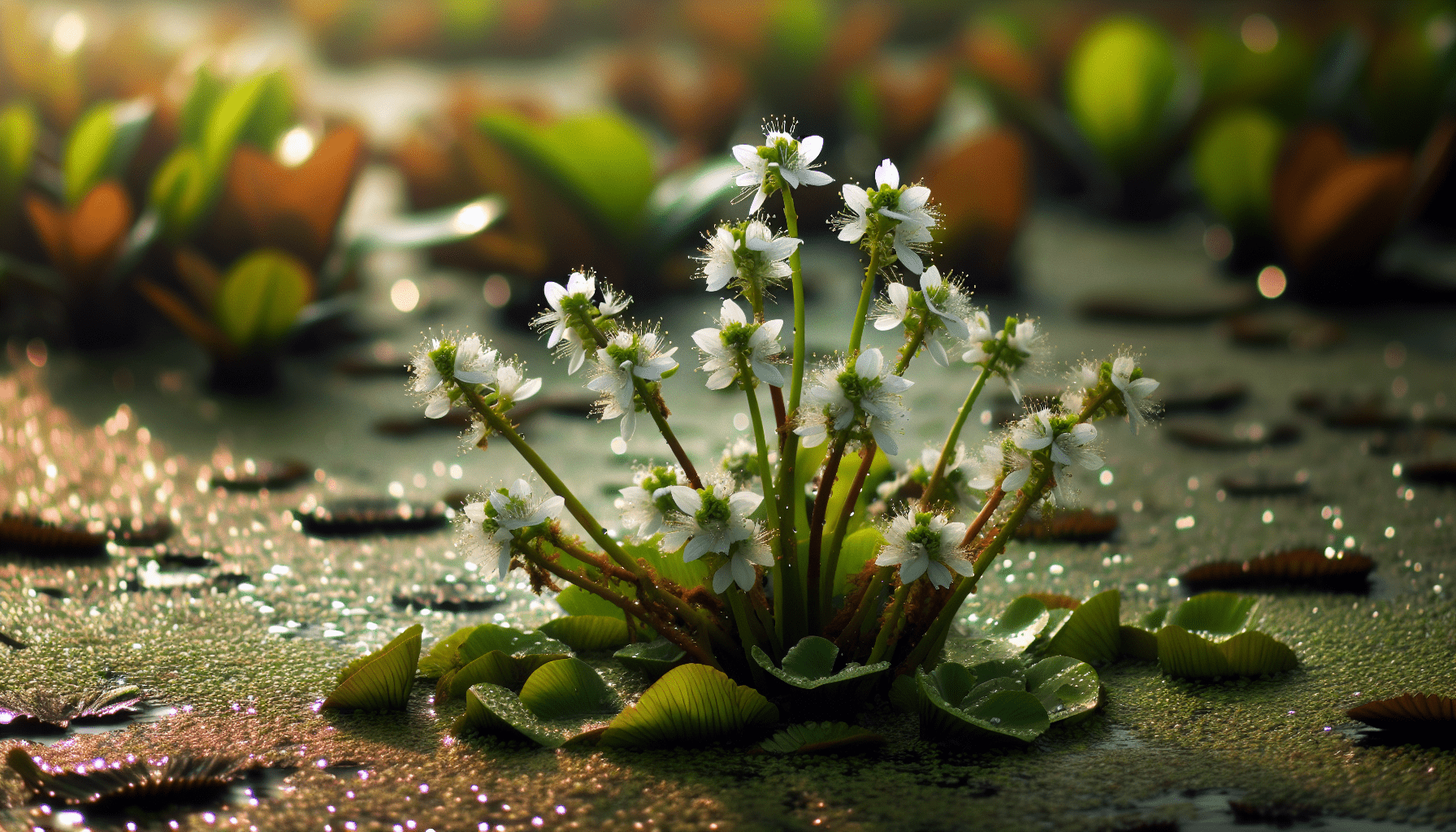

Reproductive Cycle and Growth Patterns
Reproduction Methods
Alisma Wahlenbergii primarily reproduces through its seeds, which float on the water surface and thus guarantee wide dispersal. In addition, vegetative reproduction is also common in this species.
Growth Cycle throughout the Year
The growth cycle of Alisma Wahlenbergii spreads throughout the year, with peak rates of growth observed during warmer months which are most favorable for flowering and seed production.
Lifespan of Alisma Wahlenbergii
As a perennial aquatic plant, Alisma Wahlenbergii exhibits a multi-year lifespan. This enables it to establish sturdy, long-term populations in its preferred habitats.
Role in the Ecosystem
Benefits to the Ecosystem
Despite its classification as an aquatic weed, Alisma Wahlenbergii offers substantial benefits to its ecosystem. It serves as an essential food source for various aquatic organisms and provides crucial nesting sites for water-borne insects and birds.
Potential Adverse Impacts
Despite associated benefits, Alisma Wahlenbergii can have adverse impacts when there is an overgrowth or if it invades alien territories. It may affect water quality and drainage, and also outcompete native species, threatening local biodiversity.
Cultivation and Care of Alisma Wahlenbergii
Ideal Growing Conditions
The ideal conditions for growing Alisma Wahlenbergii involve a watery environment with sufficient sunlight. Rich, loamy soils offer ideal root growth and nutrients.
Potential Pests and Diseases
Like any plant species, Alisma Wahlenbergii is susceptible to common aquatic plant pests and diseases, including insects, fungi, and bacteria that can adversely affect its growth and productivity.
Cultivation Methods
Cultivation requires strategic planning. Proper seed dispersion and ensuring the right environmental conditions such as water quality, temperature, and nutrient supply are key to thriving growth.
Application and Uses
Edible Uses
Although being an aquatic weed, certain parts of Alisma Wahlenbergii are edible and incorporated into local diets in some regions, keeping in mind proper preparation methods.
Medicinal Uses
The plant also finds uses in traditional medicine for treating various ailments, leveraging its potentially beneficial bioactive compounds.
Ornamental Uses
Alisma Wahlenbergii’s lush foliage and beautiful white flowers make it a preferred choice for water gardens, backyard ponds and tanks in various regions.
Conservation Status and Threats
Current Conservation Status
The current conservation status of Alisma Wahlenbergii varies by region. However, its perennial nature and ability for aggressive growth often prevent it from being threatened.
Threats to Survival
Despite its adaptability, Alisma Wahlenbergii faces threats from habitat destruction, climate change, and pollution. In addition, invasive control measures can also put pressure on local populations of this plant.
Conservation and Protection Measures
Formulating and implementing effective conservation strategies are crucial for ensuring the survival of Alisma Wahlenbergii, mainly focused on maintaining its natural habitats and controlling invasive practices.
Alisma Wahlenbergii: Invasive Weed Aspect
Overview of Invasive Species
Alisma Wahlenbergii, along with many of its relatives, is often classified as an invasive aquatic weed. This attribute is primarily due to its aggressive growth and wide reproductive dispersion capabilities that allow it to easily colonize new territories.
Adverse Effects of Invasive Alisma Wahlenbergii
The invasive growth of Alisma Wahlenbergii can disrupt local ecosystems, leading to a loss in biodiversity, impeding water movement and impacting local livelihoods associated with the water bodies it inhabits.
Control Measures and Management
Effective management of Alisma Wahlenbergii as an invasive species may include physical removal, chemical control, and biological control methods. Awareness and education about invasive species and their effects are also instrumental in their management.