In your pursuit to deepen your knowledge of aquatic plants, you may stumble upon the enigmatic species known as Aponogeton. Standing as a testament to the complex biodiversity of the water world, Aponogeton holds the unique distinction of being both aesthetically captivating and ecologically significant. This compelling article endeavours to shed light on this curious aquatic weed, seeking to unravel its characteristics, its habitat, and the role it plays in the ecosystem’s balance. By the end of your reading, your understanding of this underwater inhabitant will be significantly expanded and enhanced.
Overview of Aponogeton
Within a serene aquatic landscape, you may encounter a particular genus of aquatic plants that intriguingly intertwines beauty and complexity within its morphology – the Aponogeton. Prominent within the flourishing water plant flora, their verdant elegance enhances aquatic environments and creates enticing ecosystems for a variety of water beasts.
Definition of Aponogeton
As you delved deeper, Aponogeton refers to a genus of fascinating aquatic plants, primarily known for its role in water garden aesthetics and as a habitat for aquatic life. With its origin in the Greek language, the term ‘Aponogeton’ is a congregation of ‘apono’, which means ‘away from’, and ‘geton’, signifying ‘neighbor’. This curious name shows the evolutionary adaptation of these plants to distant themselves from terrestrial plants, embracing their true aquatic nature.
Distribution and habitat
You won’t be surprised by the vast geographical distribution of Aponogeton, as it inhabits diverse ecosystems worldwide. Native to Asia, Africa, and Australasia, these plants thrive in freshwater habitats such as rivers, streams, and ponds and could stretch their boundaries from the familiar tropical regions to the largely unexplored subtropical areas.
Ecology and conservation status
The intricate connection of Aponogeton to its ecological surroundings contributes to varied conservation statuses. Some of its species are known to be colonizers and inhabit environments deemed harsh and unsuitable to other aquatic species. However, human activities, such as over-harvesting and habitat destruction, contribute to many species’ risk status. Apart from a few listed as threatened, many Aponogeton species lack enough data for proper conservation classification.
Classification of Aponogeton
Taxonomic hierarchy
Aponogeton is systematically categorized under the order of Alismatales and the family Aponogetonaceae. The genus currently includes over 50 accepted species.
Species of Aponogeton
There are different species of Aponogeton differing in their geographical distribution and morphological characteristics. Some prominent species include Aponogeton ulvaceus, Aponogeton boivinianus, and Aponogeton crispus.
Notable variations and hybrids
The beauty of nature, indeed, lies in diversity and variations. In some locations, you come across remarkable natural hybrids, such as Aponogeton x satarensis, which is a product of inter-species cross-pollination.
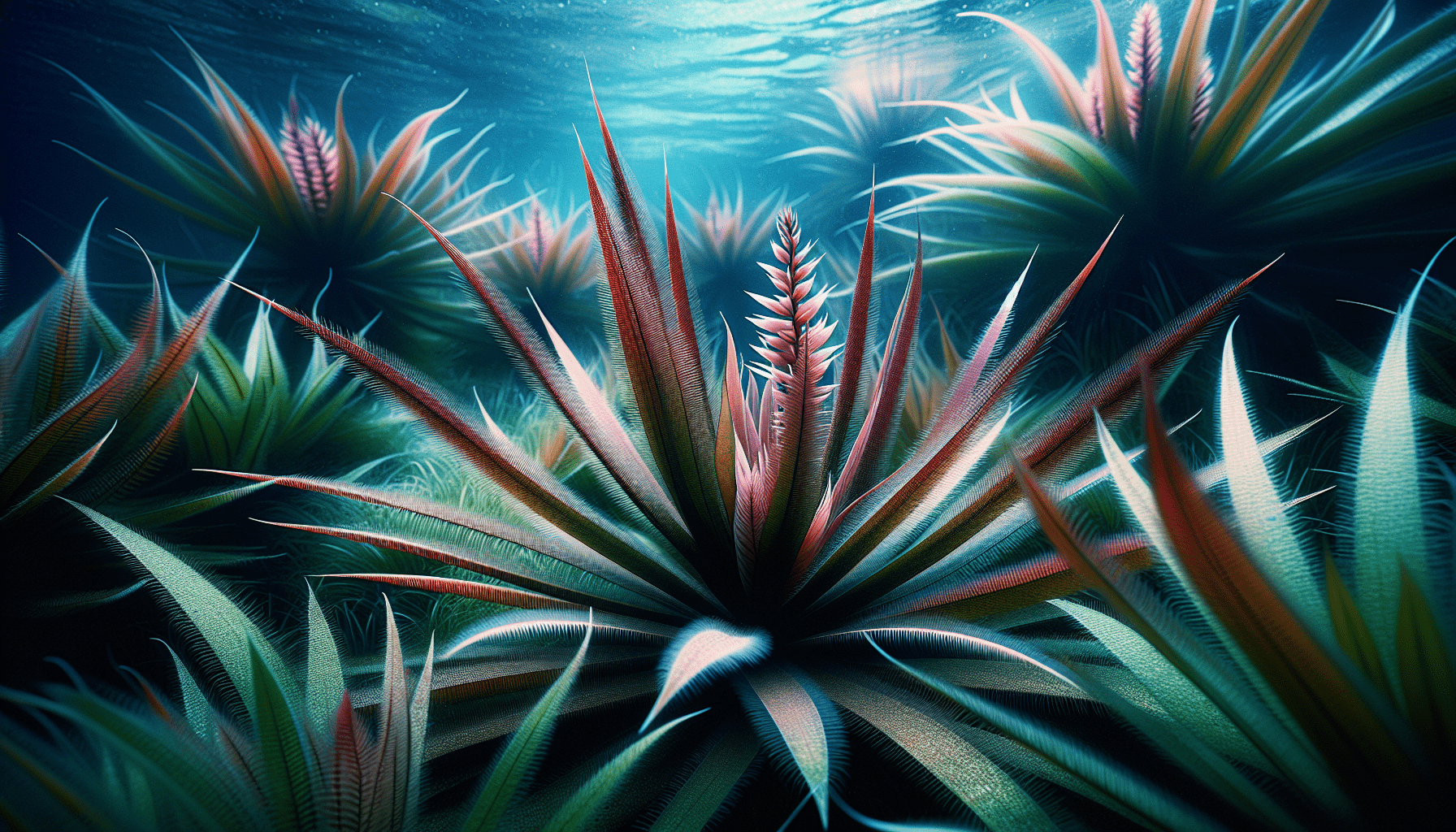

Morphological Features of Aponogeton
Root and stem characteristics
Aponogeton possesses a tuber or an enlarged underground rhizome, functioning as a food storage organ. In most species, an elongated stem, called the peduncle, arises from the base, reaching out towards the water surface.
Leaf structure and appearance
The captivating feature of Aponogeton is indeed the leaves surfacing above the water, often displaying a range of colors from green to brown or red. The leaf forms vary across species, from delicate and feathery to broad and flattened.
Flower and fruit
Emerging from the peduncle are the fragrant flowers of Aponogeton. After successful pollination, these flowers produce fruits that are best described as a small, spherical capsule housing the precious seeds.
Seeds
The seeds of Aponogeton serve as the key for its survival for the next generation, exhibiting diverse shapes and sizes ranging from spherical to sometimes wrinkled forms.
Growth Requirements and Life Cycle
Propagation: sexual and asexual
Both sexual and asexual methods are employed by Aponogeton for propagation. While asexual propagation happens through the division of its tuber, the sexual method involves seed germination, which occurs once the fruit dehisces and releases the seeds.
Seasonal variations
As with most plants, seasonal changes impact the growth and reproduction of Aponogeton. Many species show a well-marked rest period during the dryer and colder months, shedding their leaves and remaining as a dormant tuber till favorable conditions return.
Light, temperature, and water conditions
Light, temperature, and water parameters are crucial for the successful growth of Aponogeton. While most species prefer bright light conditions, a few can withstand lower light levels. Optimal temperature ranges and profoundly aquatic environments contribute to their growth and reproduction success.
Nutrient requirements
Nutrients availability can remarkably influence the growth of Aponogeton. Usually, they derive their primary nutritional needs from the water through their roots, but additional fertilization might be necessary in nutrient-poor waters.
Role of Aponogeton in Ecosystem
Aquatic wildlife habitat
Aponogeton plays an indispensable role in supporting aquatic biodiversity by providing necessary nesting and hiding spaces to diverse fauna.
Contribution to water quality
By oxygenating the water and assimilating nutrients, Aponogeton has a positive impact on water quality improvement.
Food source
Its leaves, flowers, fruits, and roots are food options for various fish, waterfowl, and other aquatic animals thus augmenting their survival.
Impact on biodiversity
By attracting pollinators, providing shelter and food to aquatic fauna, and stabilizing aquatic ecosystems, Aponogeton rightly serves as a keystone species, supporting and boosting biodiversity.
Positive Aspects of Aponogeton
Economic benefits
Aponogeton species are commercially important, especially in the aquarium plant industry, thereby contributing to the economy.
Aesthetical value in aquascaping
With their unique leaf forms and colors, Aponogeton species are aesthetically appealing and are extensively used in aquariums and water garden landscaping.
Cultural and historical importance
In many cultures, Aponogeton species are revered, linked with mythology, and possess historical significance.
Potential medicinal properties
While there is not enough scientific evidence yet, many traditional cultures utilize Aponogeton species in folk medicine, ascribing diverse health benefits to them.
Negative Impacts of Aponogeton
Potential to become invasive
Due to their fast growth and prolific reproduction, some species of Aponogeton can colonize areas rapidly, causing a threat to local biodiversity by becoming invasive.
Interspecific competition
Their growth vigor can lead to competition with other native plant species for resources, thereby affecting their survival.
Biomagnification of pollutants
Like other aquatic plants, Aponogeton can accumulate pollutants from the water, and when consumed by fish and other organisms, can lead to biomagnification, posing threats to ecosystem health.
Impact on man-made structures and navigation
Their propensity to form dense clumps can interfere with water conveyance systems, fishing activities, and navigation, causing economic loss and inconvenience.
Eradication and Management of Aponogeton
Preventive measures
Regular monitoring and early detection of any Aponogeton invasion are essential preventive strategies.
Chemical, mechanical, and biological control methods
Various control methods can be adopted for managing the growth of Aponogeton. Chemical controls involve the use of aquatic herbicides, while mechanical methods include physical removal. Biological control methods may also be applied, nevertheless, their effectiveness and associated risks must be thoroughly evaluated before usage.
Restoration and rehabilitation of affected areas
After successful control and removal of invasive Aponogeton species, the rehabilitation of the affected areas by reintroducing native plant species is necessary for ecosystem recovery.
Current Research and Innovations
Recent studies on Aponogeton
Scientific studies being carried out on different aspects of Aponogeton, including its taxonomy, ecology, and reproduction, are tweaking its understanding and use.
Key findings and discoveries
Recently, new species of Aponogeton are being discovered, and their growth requirements, reproduction, and interaction with aquatic fauna are being extensively studied.
Potential future uses and applications
The versatile characteristics of Aponogeton open up the possibility of its diverse future uses, such as in phytoremediation and pharmaceuticals.
Frequently Asked Questions about Aponogeton
How to grow and care for Aponogeton?
Aponogeton can be grown ideally from tuber or seeds and requires suitable light, temperature, and nutrition for successful establishment and growth.
Can Aponogeton harm fish or other aquatic animals?
Aponogeton does not inherently harm fish or other aquatic animals unless it grows invasively and affects the ecosystem balance.
What to do if Aponogeton becomes invasive?
If Aponogeton turns invasive, it must be promptly controlled and eradicated to prevent ecosystem disruptions, and the area should be restored with suitable native species. Consult with a local environmental or aquatic management authority for specific instructions.