In this scholarly discourse, the focus is on the exploration of Aponogeton distachyos, otherwise known as the aquatic weed. This plant found often in freshwater bodies, hides an incredible wealth of information, concerning its ecology, cultivation, and uses. The article sheds light on its peculiar characteristics, its invasion history and impact on its environment, as well as its potential for use. Endeavor to immerse yourself in what promises to be an engaging analysis of this extraordinary aquatic plant.
Overview of Aponogeton distachyos
Definition of Aponogeton distachyos
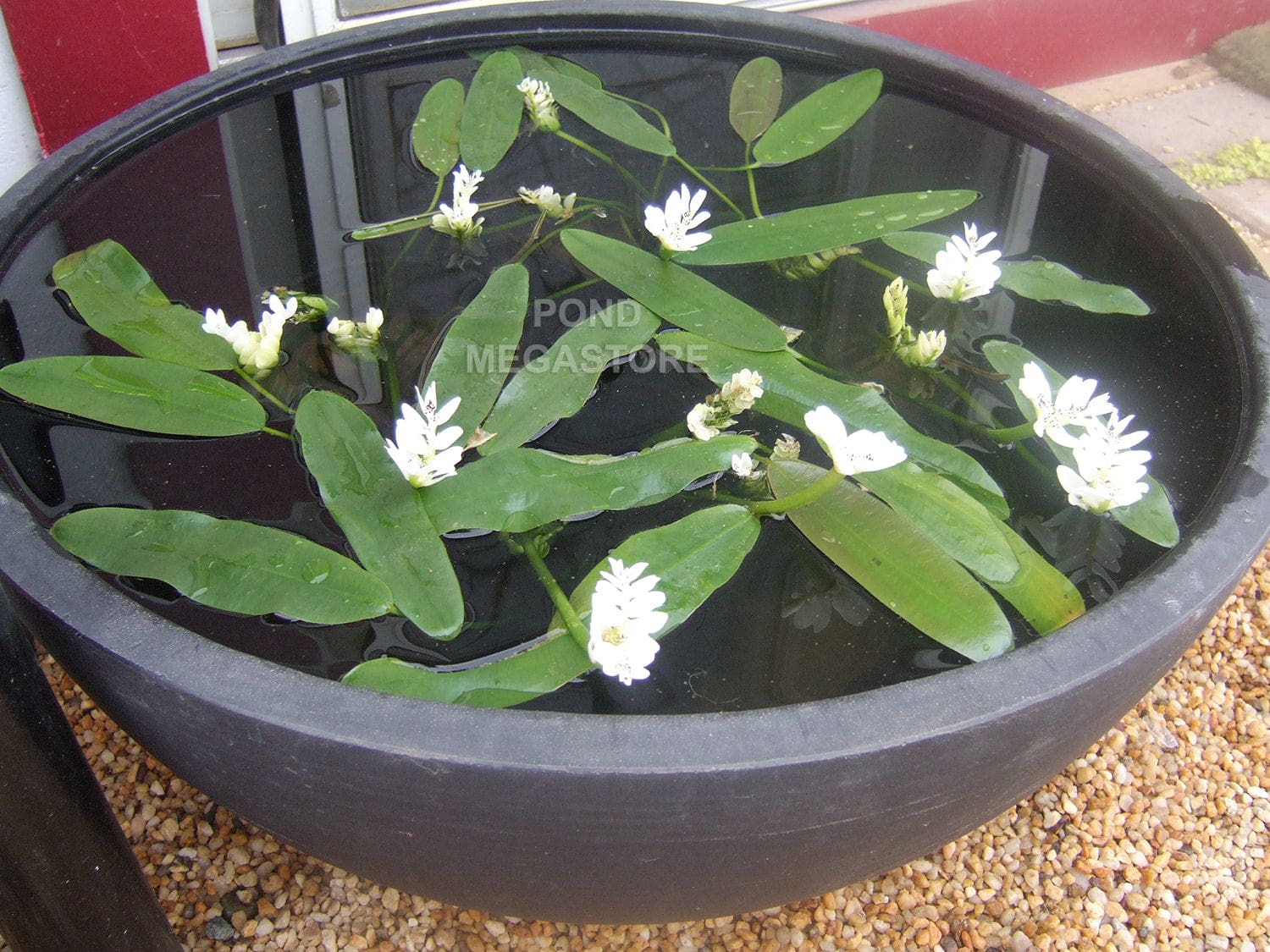
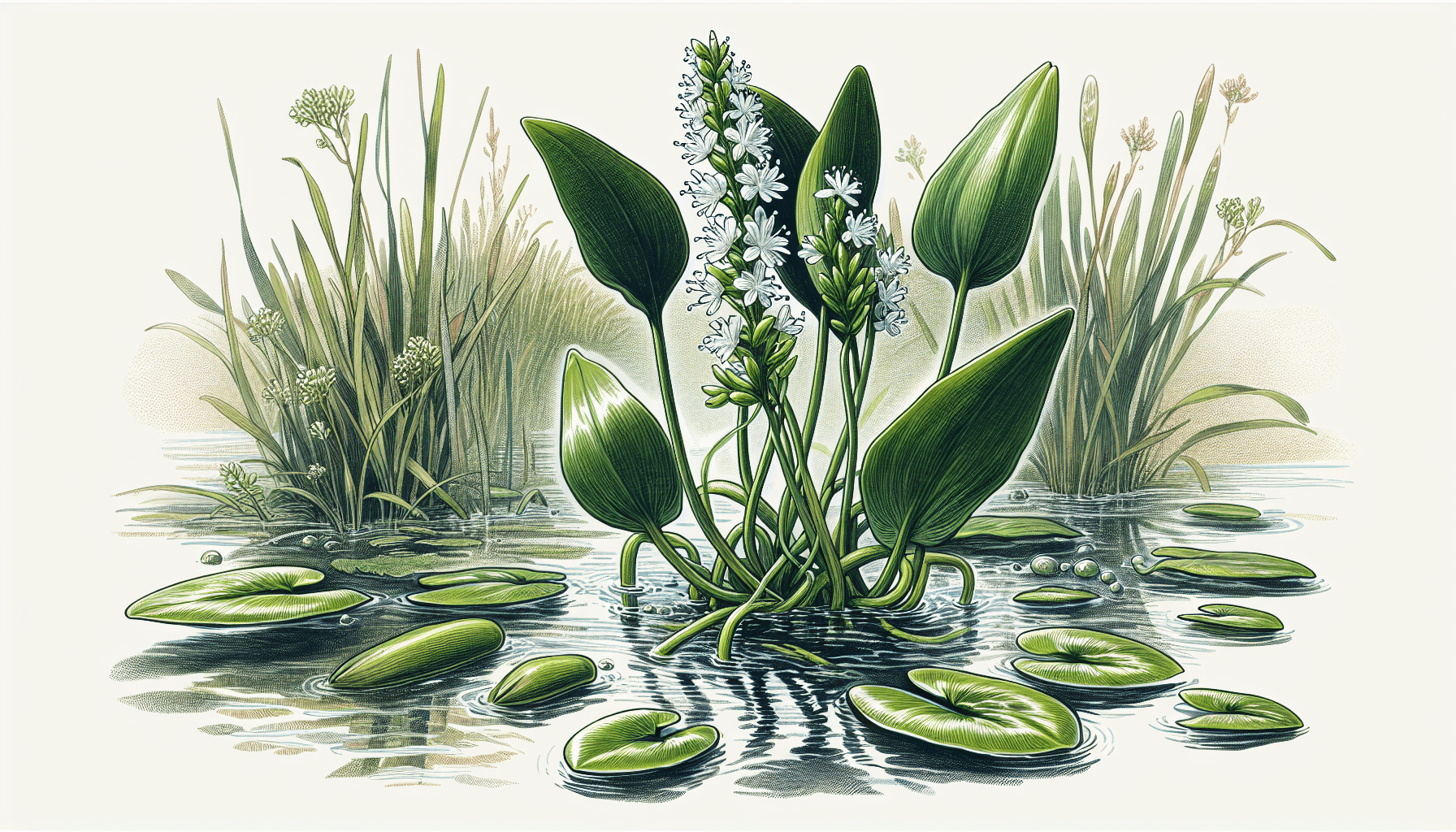
Aponogeton distachyos, more commonly known as waterblommetjie, aquatic weed, or Cape-pond weed, is a fast-growing, freshwater, aquatic plant species. It falls under the Aponogetonaceae family and is noted for its distinctly fragrant, small, white flowers that float above the water surface on elongated stalks.
Origins and natural habitat
Aponogeton distachyos is native to the southern regions of Africa. This extends from the southwestern Cape of South Africa up to Mozambique. In its natural habitat, it thrives in freshwater ponds, streams, and vleis.
Basic characteristics and appearance
Aponogeton distachyos is a perennial plant that has floating and submersed leaves. The floating leaves are oblong, glossy, dark green in color, and can reach up to 30 cm in length. The underwater leaves are thin, ribbon-like, and transparent. It produces small, white, fragrant flowers that bloom in two rows on a single stalk, which gives it the name ‘distachyos’ meaning two-spikelet.
Common names and terminology
Aponogeton distachyos is commonly known by a number of different names based on its geographical location and characteristics. In South Africa, it is known as ‘waterblommetjie’. Internationally, it’s referred to as ‘water hawthorn’, ‘Cape-pond weed’, or ‘two-bract pondweed’.
Identification of Aponogeton distachyos
Physical attributes for identification
You can identify Aponogeton distachyos by its oblong floating leaves, ribbon-like underwater leaves, and small, sweet-smelling, white flowers that emerge on a stalk above the water surface. Each flower stalk carries two rows of flower spikes, a distinguishing characteristic of the species.
Difference with other similar species
While there are other species within the Aponogeton genus, Aponogeton distachyos can be distinguished by its fragrant, white flowers and the two rows on each flower spike. Moreover, many Aponogeton species do not have the oblong floating leaves characteristic of A. distachyos.
Seasonal changes in appearance
Aponogeton distachyos is deciduous in nature and undergoes changes with seasons. During autumn and winter, the floating leaves and flowers are prominently visible. However, in warmer spring and summer months, the plant largely retreats underwater, with its submerged leaves being the primary feature visible.

The ecological role of Aponogeton distachyos
Contribution to the ecosystem
Aponogeton distachyos plays a vital role in water ecosystems. It provides a habitat for various aquatic organisms such as mollusks and insect larvae. It also contributes to oxygenating water bodies and it forms an integral part of the food chain‚ contributing organic matter that feeds microorganisms and insects.
Interactions with other organisms
This aquatic plant interacts with various organisms within its ecosystem. The flowers attract pollinators, while the leaves and young seedlings are often eaten by waterfowl. In its natural habitat, the plant also serves as a breeding ground for numerous species of frogs. Its rhizomes are known to be a food source for otters.
Impact on biodiversity
By providing food, shelter, and breeding grounds for various aquatic organisms, Aponogeton distachyos plays a significant role in maintaining and promoting biodiversity.
Distribution of Aponogeton distachyos
Geographical regions where it is found
Originating in Southern Africa, Aponogeton distachyos is broadly distributed there, particularly in the Western Cape. The species has also spread to other parts of the world including Europe, Australia, and North America.
Factors affecting its spread
Aponogeton distachyos spreads by both seed dispersal and vegetative reproduction from portions of the rhizome. Factors such as water clarity, temperature, light levels and soil fertility affect its spread within a water body.
Effect of climate and environment on its distribution
Though the plant can adapt to a range of water conditions, it prefers mild, temperate climates and thus, finds suitability in cooler regions over hotter ones.
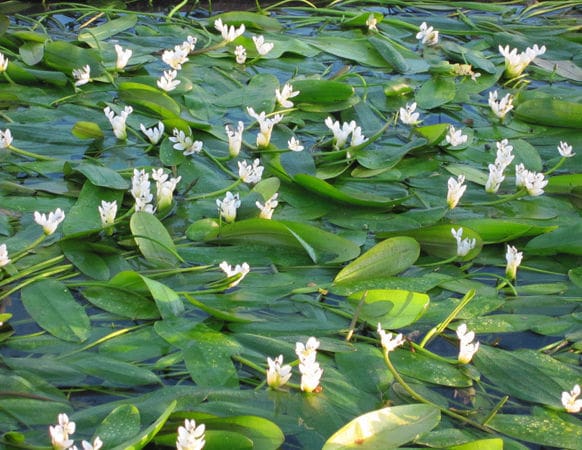

Cultivation and Propagation of Aponogeton distachyos
Preferred growing conditions
Aponogeton distachyos is best grown in ponds, water gardens or containers submerged in water. It prefers sunny to partially shaded conditions and requires a water depth of between 30 cm to 60 cm. It is tolerant to a range of pH levels.
Reproduction and propagation methods
Reproduction can occur through seed dispersal but most common is vegetative propagation, where pieces of the rhizome grow into new plants. Additionally, mature plants produce ‘daughter’ plants which can be separated and grown independently.
Gardening and landscape uses
Due to its attractive flowers, the plant is often utilized in aquatic gardening and is sought after for ornamental water features.
The effects and uses of Aponogeton distachyos
Culinary uses
In some cultures, particularly in the Western Cape of South Africa, the flower buds and seed pods of Aponogeton distachyos are harvested as a seasonal delicacy and used in traditional dishes like waterblommetjiebredie.
Medicinal properties and uses
While Aponogeton distachyos has no known specific medicinal uses, in general, Aponogetons have been suggested to possess antiviral properties.
Potential hazards and problems
When not properly managed, Aponogeton distachyos can become invasive and obstruct waterways, which can cause problems in irrigation and drainage systems.
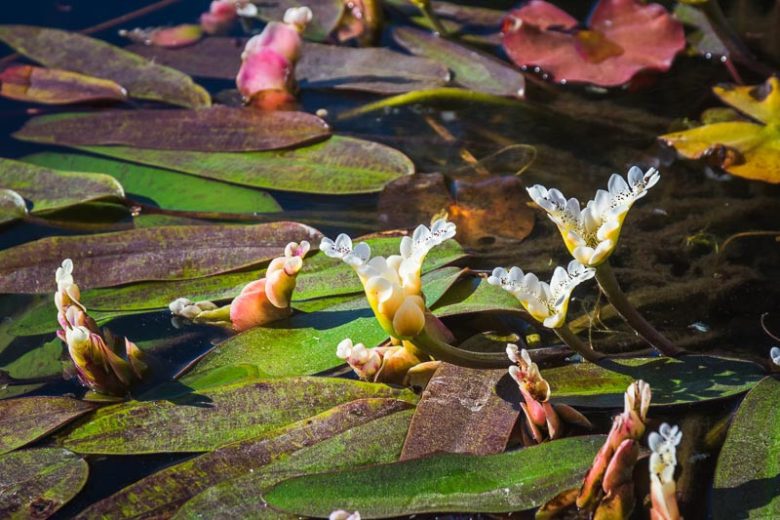

The life cycle of Aponogeton distachyos
Stages in the life cycle
Like many aquatic plants, Aponogeton distachyos has a life cycle that consists of germination, growth, flowering, and seed production stages. This cycle is influenced by seasonal changes.
Length and timing of life cycle phases
The flowers of Aponogeton distachyos appear from late autumn through winter, which is also when seeding typically occurs. The seed then germinates and grows during the following spring and summer.
The impact of external factors on the life cycle
External factors such as temperature, light levels, and water conditions can significantly affect the life cycle stages and growth of Aponogeton distachyos.
Rules and regulations regarding Aponogeton distachyos
Legal status and regulations in different countries
In some countries where Aponogeton distachyos is considered invasive, regulations have been put in place to control its spread. For instance, in Australia, it has been declared a weed of national significance and its cultivation and trade are restricted.
Implications for trade and transportation
Due to its potential to become invasive, the trade and transport of Aponogeton distachyos are often subject to strict regulations. This is to prevent its accidental introduction to non-native water bodies.
Conservation efforts and status
While Aponogeton distachyos does not have any specific conservation status, general efforts are made to conserve all species within the Aponogeton genus. This mainly involves habitat preservation and controlled cultivation.
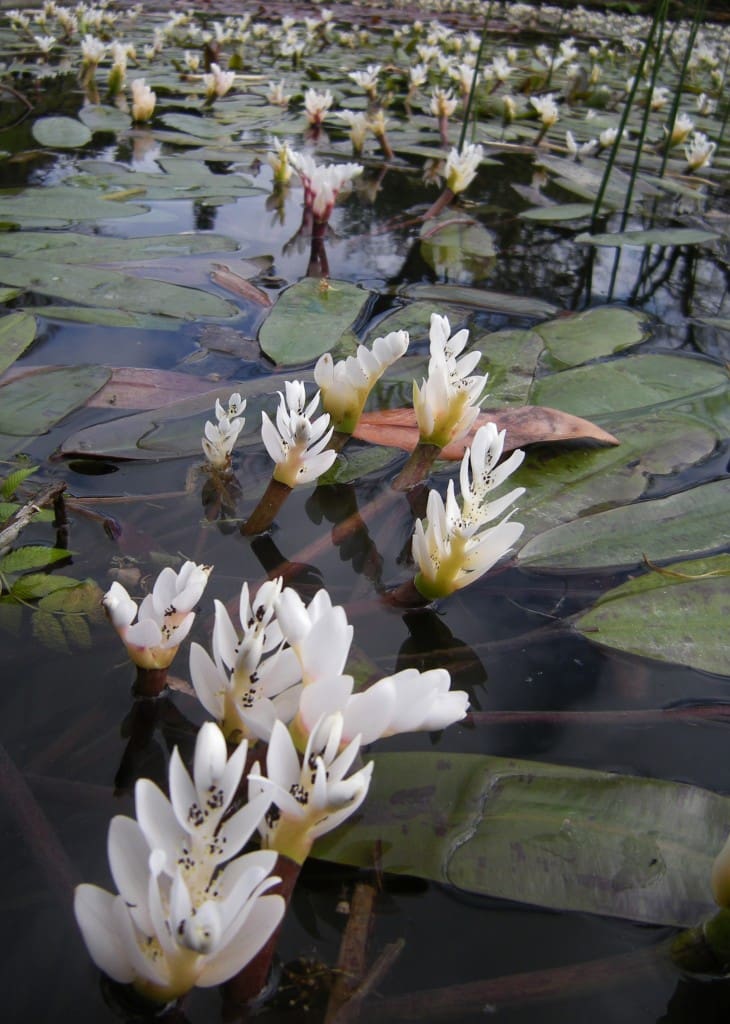

Threats to Aponogeton distachyos
Common pests and diseases
Aponogeton distachyos does not have many significant pests or diseases. However, it can occasionally be affected by general aquatic plant issues such as algae, snails, and aphids.
Environmental threats and challenges
Environmental changes such as water pollution, water level changes, and extreme temperatures can pose threats to Aponogeton distachyos.
Impact of human activity
Factors such as over-harvesting for culinary purposes and destruction of natural habitats can threaten the populations of this species.
Research on Aponogeton distachyos
Recent scientific studies and findings
Recent studies have focused on the species’ potential for phytoremediation – using the plant to remove pollutants from water bodies. However, more research in this area is needed.
Research gaps and future directions
There is still considerable scope for research on the ecological benefits, potential medicinal properties and improved cultivation methods of Aponogeton distachyos.
Contributions to science and understanding of biodiversity
Aponogeton distachyos, like many aquatic plants, plays a crucial role in understanding aquatic biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. It helps scientists understand habitat dynamics, nutrient cycling, and species interactions in various freshwater ecosystems.