In this comprehensive article, your understanding of the aquatic ecosystem stands to be significantly enriched as we explore the nuances of Aponogeton Madagascariensis, an intriguing aquatic weed. Often referred to as Madagascar Laceleaf, this plant is a fascinating topic due not only to its distinctive leaf structure but also its intricate role in aquatic environments. Understanding such an intriguing and complex species requires a comprehensive exploration into its botanical characteristics, habitat and overall ecological role, which this article promises to deliver. With regard to your understanding of aquatic ecology, this in-depth presentation of Aponogeton Madagascariensis aims to be a valuable addition.
General Overview of Aponogeton Madagascariensis
Aponogeton Madagascariensis, a fascinating species of aquatic flora, showcases an array of botanical and ecological characteristics that make it a subject of interest for scientists, environmentalists, and aqua culturists alike. Its unusual diaphanous foliage and adaptive growth norms have prompted extensive exploration into various facets of its lifecycle, reproductive strategies, and ecological impact.
Origins of the plant
Aponogeton Madagascariensis is honored with its name due to its origin: the island of Madagascar. This unique aquatic plant has since found a home across different regions of the globe, primarily due to its adaptability and aesthetic appeal.
Other names for the plant
It is known by several names, reflecting its distinctive appearance and nature. In many circles, it is referred to as the Madagascar Lace plant, due to the beautifully intricate ‘lace-like’ patterns seen in its mature leaves.
General appearance
The Aponogeton Madagascariensis is possessed of an appealing overall appearance, characterized by long, slender leaves that showcase a distinct lace-like perforation once matured. Bearing a semi-transparent green hue, these leaves fan out over the water surface, providing a delicate and aesthetically pleasing contrast to other aquatic plants.
Botanical Description of Aponogeton Madagascariensis
The botanical structure of Aponogeton Madagascariensis, articulated by root, leaf, and rosette growth, presents a unique blend of beauty and resilience.
Plant structure
The Aponogeton Madagascariensis plant structure can be described as rosette-like. The large and protruding leaves emerge from a central hub, giving it a distinctive, fan-like appearance that is both pleasing to the eye and functionally formidable in an aquatic setting.
Leaf structure and appearance
The Aponogeton Madagascariensis leaf is the most distinguishing feature of the plant. Each mature leaf displays a symmetric pattern of perforations, giving them a lace-like appearance. They often span 50-70 cm in length, with the average leaf width reaching around 5-8cm.
Root structure and growth pattern
Aponogeton Madagascariensis has a tuberous, rhizomatic root system. These subterranean stems sprout laterally, providing stable grounding and facilitating nutrient absorption from the surrounding water and substrate.
Habitat Preferences of Aponogeton Madagascariensis
Aponogeton Madagascariensis thrives under specific conditions falling within certain parametric thresholds. It is primarily an aquatic plant, but its adaptability allows it to survive in a variety of environments.
Preferred environments
Aponogeton Madagascariensis prefers warm, slightly alkaline aquatic environments. It can endure varying water depths, but it thrives where there is abundant sunlight availability, which is necessary for photosynthesis.
Geographical distribution
The geographical reach of Aponogeton Madagascariensis extends from its home in Madagascar to different continents, including Africa, Asia, and the Americas. This wide distribution can be attributed to its adaptive flexibility and its popularity in aquaculture.
Adaptations to aquatic environments
The adaptability of Aponogeton Madagascariensis to aquatic environments is seen in its structural and physiological components. The plant showcases a symbiotic relationship with the aquatic ecosystem around it, be it in the form of nutrient absorption or symbiotic relationships with aquatic fauna.
Life Cycle and Growth Patterns of Aponogeton Madagascariensis
The life cycle of Aponogeton Madagascariensis comprises four stages: seed germination, juvenile stage, reproductive phase, and lifecycle duration.
Seed germination
Aponogeton Madagascariensis seeds are initially dormant. It takes a suitable water temperature and right water depth to initiate the germination process. Once the optimal conditions are met, the seed begins absorbing water and the germination process commences.
Juvenile stage
During the juvenile stage, the plant begins to develop roots and small leaves. Growth at this stage is fairly slow, as the plant needs time to acclimate to the aquatic environment and to expand its root system for nutrient and hydration purposes.
Reproductive phase
Once Aponogeton Madagascariensis reaches maturity, the reproductive phase commences. This is characterized by the plant blossoming flowers, which proves to be a crucial factor in the pollination process. The pollination process can take place underwater, being another illustration of the plant’s adaptability.
Lifecycle duration
The entire lifecycle of Aponogeton Madagascariensis can span multiple years, though the exact duration varies depending on environmental factors.
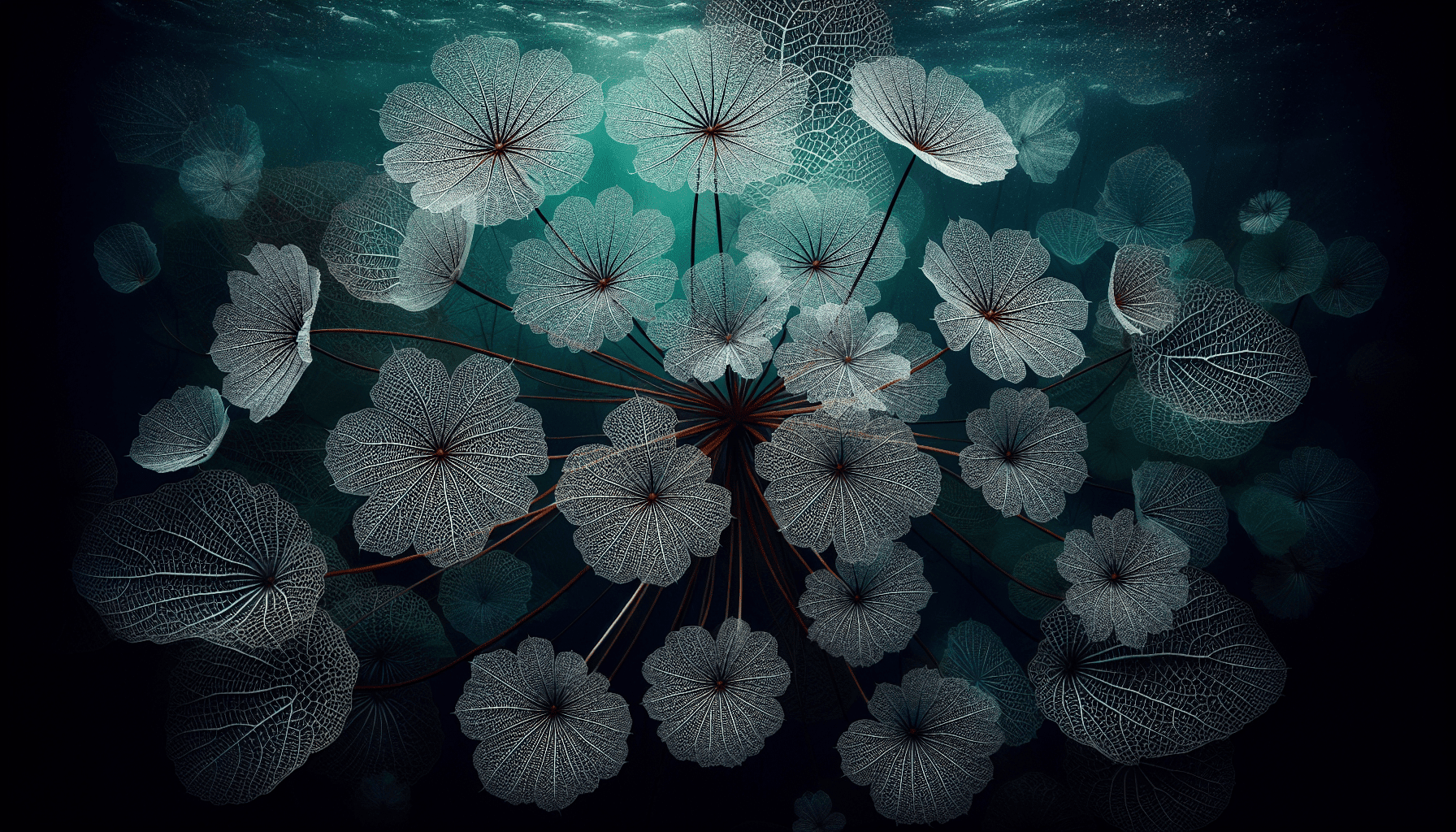

Reproductive Strategies of Aponogeton Madagascariensis
Aponogeton Madagascariensis showcases interesting patterns related to its reproductive process.
Flowering patterns
The onset of flowering is a determinant of the plant’s maturity. The flowers, which appear on long erect stalks rising above the water, are white or light green in color and display the plant’s elegance in full measure.
Pollination mechanisms
The peculiar submerged-life of Aponogeton Madagascariensis introduces an enthralling approach to pollination. Here, the floral structures undergo self-pollination, where the flower can produce seeds even without any pollination agent.
Seed dispersal methods
The seeds of Aponogeton Madagascariensis are dispersed through the water with the help of currents and aquatic creatures. They can also be dispersed externally, through human intervention or through migratory birds.
Adaptive strategies for reproduction
To ensure propagation in the aquatic environment, Aponogeton Madagascariensis has evolved several adaptive mechanisms. It is theorized that its flowering time is seasonally adjusted to maximize its reproductive chances.
Aponogeton Madagascariensis in Aquaculture
Aponogeton Madagascariensis is widely revered in the world of aquaculture, both for its mesmeric beauty and its striking adaptability to different aquatic environments.
Rationale for use in aquariums
Aponogeton Madagascariensis brings a distinctive look to aquariums with its lace-like leaves, making it a favorite among aquatic enthusiasts. In addition, it’s a robust plant, adaptable to different environmental parameters like temperature, pH, and light.
Ideal settings for growth in aquaculture
Aponogeton Madagascariensis prefers warm, brightly lit aquariums with a slightly alkaline pH balance. The plant requires a stable nutrient substrate for healthy root growth, as well as regular trimming to maintain its shape.
Tips for maintenance in aquariums
While Aponogeton Madagascariensis is generally low-maintenance, it’s important to regularly monitor water temperature and pH levels. Also, occasional pruning of dead leaves helps to prevent algal infections and maintain the health and aesthetic appeal of the plant.
Ecological Impact of Aponogeton Madagascariensis
Aponogeton Madagascariensis, being a native of Madagascar, has a far-reaching ecological impact. It plays multiple roles in the ecosystems it inhabits.
Role in aquatic ecosystems
Aponogeton Madagascariensis acts as a source of food and shade for various aquatic creatures. Its root network serves as a haven for various microorganisms and its foliage offers a habitat for small aquatic species.
Interactions with other species
By providing both food and shelter, Aponogeton Madagascariensis encourages species diversity in its immediate vicinity, promoting a healthy ecosystem balance.
Potential ecosystem benefits and detriments
Aponogeton Madagascariensis plays a significant role in maintaining a balanced ecosystem, chiefly through nutrient cycling. However, its rapid propagation, when unchecked, can lead to a destabilization of the local ecosystem due to overcrowding.
Potential Uses of Aponogeton Madagascariensis
Beyond its ornamental significance, Aponogeton Madagascariensis offers considerable potential for culinary, medicinal, and pharmaceutical use.
Culinary uses
Although Aponogeton Madagascariensis is mostly renowned for its ornamental value, some parts of the plant can indeed be eaten, utilized in traditional culinary practices in certain regions.
Medical and pharmaceutical uses
While the medicinal and pharmaceutical uses of Aponogeton Madagascariensis have not been extensively studied, initial research indicates potential uses in herbal remedies, given the plant’s rich composition of beneficial compounds.
Ornamental uses
The ornamental use of Aponogeton Madagascariensis is by far the most acknowledged and widespread, given its unique, attractive foliage that adds beauty and intrigue to both natural bodies of water and domestic aquariums.
Conservation Status and Threats to Aponogeton Madagascariensis
While the Aponogeton Madagascariensis has displayed considerable adaptability, it faces potential threats to its survival.
Current conservation status
As of now, the Aponogeton Madagascariensis is not classified under any particular conservation status. It enjoys a wide global distribution, suggesting a healthy population in its natural and adopted habitats.
Environmental threats
The greatest environmental threat to Aponogeton Madagascariensis is habitat loss or degradation, primarily arising from human activities such as dredging, pollution, or waterway modifications. Climate change also presents a potential threat by altering the preferred environmental parameters of the plant.
Anthropogenic threats
Direct human activities, such as over-collection for the aquarium trade or habitat modification, present considerable threats. Without regulation or cultivation practices, these activities can significantly deteriorate the natural populations of Aponogeton Madagascariensis.
Research and Studies on Aponogeton Madagascariensis
Considering the unique characteristics of Aponogeton Madagascariensis, it has been a subject of various research studies.
Notable past research
Past research has mainly focused on understanding the botanical and ecological characteristics of Aponogeton Madagascariensis. These studies have offered valuable insights into the plant’s growth patterns, reproductive strategies, and habitat preferences, laying the groundwork for further detailed research.
Ongoing studies
Current research endeavors are more geared towards the plant’s conservation, potential uses in medicine and pharmacology, as well as its role and adaptation in non-native habitats.
Potential areas for future investigation
Given the broad range of attributes that Aponogeton Madagascariensis presents, future investigations can focus on uncovering its full potential, such as its medicinal and pharmaceutical properties. Conservation-focused exploration is also necessary, to ensure the survival and maintenance of balanced ecosystems involving this fascinating aquatic species.