In the broad and diverse sphere of aquatic flora, Azolla Mexicana stands out not merely as a typical water fern, but as a unique aquatic weed which encapsulates an array of intriguing characteristics. Perceived frequently in the waters of North and South America, this pervasive plant intricately intertwines scientific and ecological aspects. The forthcoming article elucidates the specified dynamics, growth conditions, ecological impacts, and potential uses of this aquatic marvel. Retaining its central focus on Azolla Mexicana, the article further explores its distinctive ability to adapt and thrive – painting a vivid narrative of the resilience and complexity inherent in the plant kingdom.
Identifying Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana is an aquatic fern commonly known for its symbiotic relationship with a nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium. This unique relationship allows it to inhabit environments that might otherwise prove challenging for other aquatic species.
A Brief Description of Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana is a species of aquatic fern which flourishes in freshwater environments with high nutrient content. This small, free-floating fern thrives on the water surface, contributing to its common moniker of ‘water fern.’
Common Physical Traits of Azolla Mexicana
Your observation of Azolla Mexicana will reveal some of its distinct physical traits. It boasts tiny, overlapping scale-like leaves, essentially forming two distinctive layers – an upper layer which remains dry and a submerged lower layer. The leaves are generally green but can exhibit shades of red under nutrient stress or high light. The fern also has a highly branched stem structure, which supports the development of numerous rootlets.
Various Names for Azolla Mexicana
While Azolla Mexicana is its formal nomenclature, this aquatic fern goes by a variety of common names in different regions. You might hear it referred to as ‘Mexican water fern,’ ‘mosquito fern,’ or ‘nitrogen-fixing fern,’ which is a nod to its nitrogen-fixation property.
Habitat and Distribution of Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana displays an impressive adaptability to various environments, which contributes to its broad distribution.
Natural Habitats of Azolla Mexicana
The natural habitats of Azolla Mexicana are largely freshwater environments. In these settings, you can find extensive mats of Azolla Mexicana covering water surfaces, especially in slow-moving or stagnant water bodies like ponds, lakes, ditches, and rice fields.
Geographical Range of Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana is a native of North and Central America. However, its adaptability has seen this species now established in parts of South America and North Africa.
Types of Water Bodies that Support Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana thrives primarily in freshwater bodies. These range from slow-flowing rivers and streams to rice fields, ponds, and ditches.

Life Cycle and Growth of Azolla Mexicana
The life-cycle and growth habits of Azolla Mexicana are fascinating and contribute to its unique ability to colonize diverse aquatic habitats.
Growth Habits of Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana multiplies through a form of budding, wherein new plants form from the branches of existing specimens. This fern’s growth is remarkably fast, doubling its biomass within two to three days under favorable conditions.
Reproductive Mechanism of Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana reproduces both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction involves the growth of male and female reproductive organs on the lower surface of the leaf. Meanwhile, asexual reproduction takes place through fragmentation, where sections of the fern break off and grow into separate plants.
Stages of Azolla Mexicana’s Life Cycle
Azolla Mexicana’s life cycle includes a free-floating vegetative growth phase, sexual reproduction phase, and a dormant phase where the plant forms a dense mat of overlapping leaves able to survive adverse conditions such as dry spells.
Nutritional Requirements of Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana has precise nutritional requirements necessary for its growth, reproduction, and survival.
Light Requirements of Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana requires ample sunlight for its photosynthetic processes. However, it can also adapt to grow in shaded conditions.
Water and Temperature Requirements of Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana needs a considerably stable water environment and prefers water temperatures between 20-30°C. That said, this hardy fern can endure adverse conditions like waterlogged environments or brief periods of desiccation.
Nutrient Needs of Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana can live in nutrient-poor conditions due to its nitrogen-fixing ability. But for optima growth, it requires a supply of phosphorus and trace minerals.
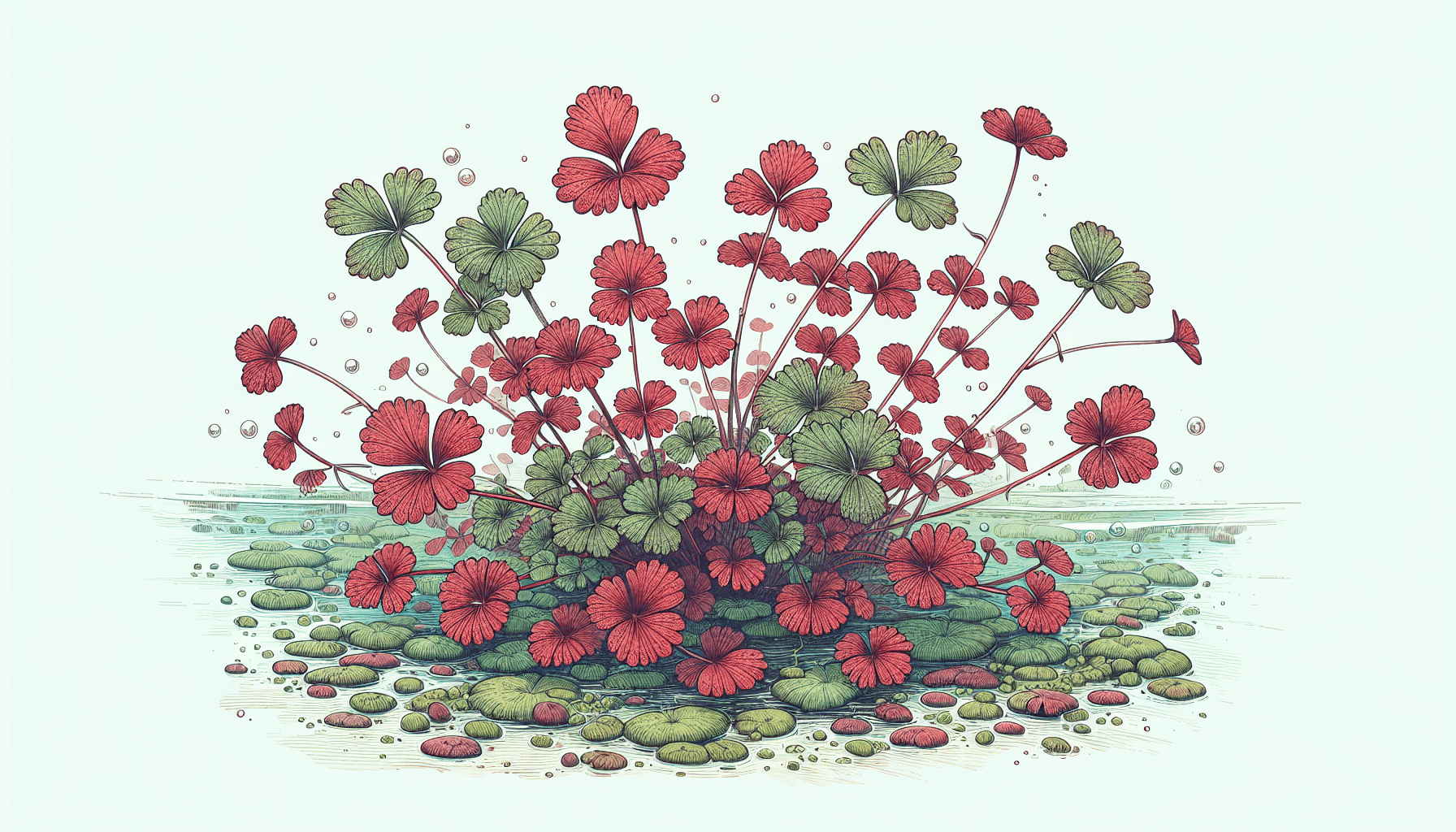
Use of Azolla Mexicana in Agriculture
Azolla Mexicana’s valuable properties lend themselves useful in agricultural applications.
Azolla Mexicana as a Biofertilizer
Azolla Mexicana can enhance soil fertility due to its nitrogen-fixing capability, making it an effective biofertilizer, particularly in rice cultivation.
Azolla Mexicana in Pest Control
Azolla Mexicana’s dense growth can prevent mosquito breeding by obstructing the water surface, thus contributing to biological pest control.
Azolla Mexicana in Nutrient Cycling
Azolla Mexicana plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling in freshwater ecosystems. As it dies and decomposes, it releases nutrients back into the water, making them available to other organisms.
Azolla Mexicana and the Environment
Azolla Mexicana’s relationship with its environment is varied. It can have both positive and negative impacts on the water quality, carbon sequestration, and biodiversity.
Impacts of Azolla Mexicana on Water Quality
While Azolla Mexicana can improve water quality by absorbing pollutants and excessive nutrients, its overgrowth can have the opposite effect, depleting oxygen levels and endangering aquatic life.
Azolla Mexicana in Carbon Sequestration
Azolla Mexicana contributes to carbon sequestration. As it photosynthesizes, it absorbs carbon dioxide and releases oxygen, thereby reducing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Biodiversity Implications of Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana can both enhance and threaten biodiversity. While its dense mats provide a food source and habitat for certain fauna, its uncontrolled growth can disrupt local ecosystems and outcompete native species.
Potential Hazards of Azolla Mexicana
A certain degree of caution is required when dealing with Azolla Mexicana due to its potential to become an invasive species.
Invasive Nature of Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana’s fast growth rate and high reproductive capability make it a potential invasive species. In areas where it’s non-native, it can spread quickly and cause significant ecological disruption.
Damage Caused by Azolla Mexicana
Uncontrolled growth of Azolla Mexicana can block sunlight, deplete oxygen, and affect water quality, endangering the survival of other aquatic life forms.
Management and Control of Azolla Mexicana
Proper management and control methods are necessary to keep the Azolla Mexicana population in check. This includes biological control through the introduction of specific insects that feed on the fern and manual or mechanical removal if infestations occur.
Azolla Mexicana in Research and Science
Azolla Mexicana has attracted the interest of scientists given its fascinating biological characteristics and potential applications.
Uses of Azolla Mexicana in Scientific Studies
Azolla Mexicana is used in studies of plant-microbe symbiosis, water pollution control, and the development of biofuels, among others.
Potential Applications of Azolla Mexicana
The fern’s nitrogen-fixation property sparks interest in its potential application as a biofertilizer in sustainable agriculture. Additionally, it’s explored for its role in bioenergy, carbon sequestration, and environmental remediation.
Role of Azolla Mexicana in Climate Science
Azolla Mexicana’s critical contribution to carbon sequestration presents significant research opportunities in climate science, potentially playing a role in climate change mitigation strategies.
Cultural and Historical Significance of Azolla Mexicana
Beyond its biological and ecological properties, Azolla Mexicana holds historical and cultural significance.
Historical Uses of Azolla Mexicana
Historically, Azolla Mexicana has been used in agriculture—for hundreds of years—in Asia as a biofertilizer, particularly in rice cultivation. This practice helped to boost crop yields remarkably.
Azolla Mexicana in Folklore and Traditional Culture
In certain cultures, Azolla Mexicana features in folklore and traditional practices—as a symbol of fertility and abundance.
Modern Cultural Significance of Azolla Mexicana
In modern times, Azolla Mexicana’s interesting biology and potential ecological benefits have earned it recognition in the scientific and agricultural communities.
Future Outlook on Azolla Mexicana
As we continue to learn more about Azolla Mexicana, new insights and potential applications are likely to come to light.
Foreseen Impacts of Climate Change on Azolla Mexicana
Climate change could impact the distribution and growth of Azolla Mexicana. Predictions and management strategies need to account for this possibility.
Potential Uses and Developments of Azolla Mexicana
Azolla Mexicana’s potential uses in sustainable agriculture, bioenergy, and carbon sequestration are subjects of ongoing research, with promising developments expected in these areas.
Concerns and Management Strategies for Azolla Mexicana
Management strategies to control the invasive risk of Azolla Mexicana, while maximizing its benefits, will need careful development. Vigilance and a measured approach will guide Azolla Mexicana’s role in the future.
In conclusion, Azolla Mexicana is a fascinating fern that offers much potential in various fields—from sustainable agriculture and environmental remediation to combating climate change. However, its possible destructive propensity as an invasive species cannot be overlooked. Therefore, thoughtful research and management will dictate the future role of this versatile fern.