As an esteemed reader, your attention is drawn to a detailed exploration of the aquatic weed known as Callitriche Stagnalis. Not only will you gain an in-depth understanding of its ecological role, but you will also equip yourself with knowledge regarding the evolutionary traits and adaptations that enable this plant species to thrive in diverse aquatic environments. This compendium will serve as an intricate portrait of this often overlooked organism, blending scientific data and biological analysis for an academic yet accessible discourse on Callitriche Stagnalis.
Definition of Callitriche Stagnalis
Callitriche Stagnalis, commonly referred to as water starwort or pond water starwort, is a perennial aquatic plant renowned for its ubiquity in still and slow-flowing freshwaters. This species belongs to the plant family Callitrichaceae and is considered both an integral part of freshwater ecosystems and a potential weed under certain conditions.
Scientific classification
Belonging to the kingdom Plantae, Callitriche Stagnalis falls under the order Lamiales, which includes a wide range of flowering plants. Within this order, it is classified under the family Callitrichaceae, known for its aquatic or semi-aquatic species. Callitriche is the genus to which this plant belongs, a group characterized by its star-shaped flowers.
Common names
In addition to the scientific name Callitriche Stagnalis, this plant is commonly known by several different monikers such as: ‘water starwort’, ‘pond water starwort’, ‘common water starwort’, and ‘stagnant water starwort’. These names highlight the aquatic nature of the plant.
Description and physical attributes
Callitriche Stagnalis is a perennial plant, which means it lives for more than two years, often flowering and producing seeds over a long period. This plant is notable for its submerged leaves which are elongated and ribbon-like in shape, but become broader and ovate as they reach the water surface. The starwort possesses small, pale flowers found in the leaf axils, blooming from late spring to early autumn.
Habitat and Geographic Distribution
Freshwater habitats
The Callitriche Stagnalis thrives in still or slow-moving freshwaters, including the edges of ponds, lakes, ditches, and slow-flowing streams. They often create dense vegetative mats underwater and on the water surface, providing shelter and food for various aquatic organisms.
Geographical regions
Callitriche Stagnalis is most prevalent in the Northern Hemisphere, specifically in Europe, Asia, and North America. However, due to its invasive potential, it has managed to spread to other parts of the world, including Australia and South America.
Seasonal variations in distribution
While Callitriche Stagnalis is a hardy plant that can persist throughout the year, it particularly thrives in warmer months, rapidly expanding its presence during spring and summer. In contrast, during colder months, the plants often reduce in size and number.
Life Cycle of Callitriche Stagnalis
Seed germination
The water starwort’s life cycle begins with the germination of seeds, which typically happens in the spring. These seeds can either be dispersed by water or can germinate directly on the parent plant.
Vegetative growth
Following germination, the water starworts will begin to produce both submerged and emergent leaves, forming a dense vegetative mat in the water.
Propagation and reproduction
The Callitriche Stagnalis reproduces either vegetatively or through sexual means. The flowering period is generally from late spring to early autumn.
Ecological Role
Role in aquatic ecosystems
In freshwater ecosystems, Callitriche Stagnalis plays an essential role, providing shelter for various aquatic creatures, including insects, snails, and fish. It also contributes to the quality of the water by filtering pollutants and absorbing excess nutrients.
Interactions with wildlife
Callitriche Stagnalis acts as a food source for numerous herbivorous aquatic organisms. Certain bird species, such as ducks and geese, occasionally feed on the plant.
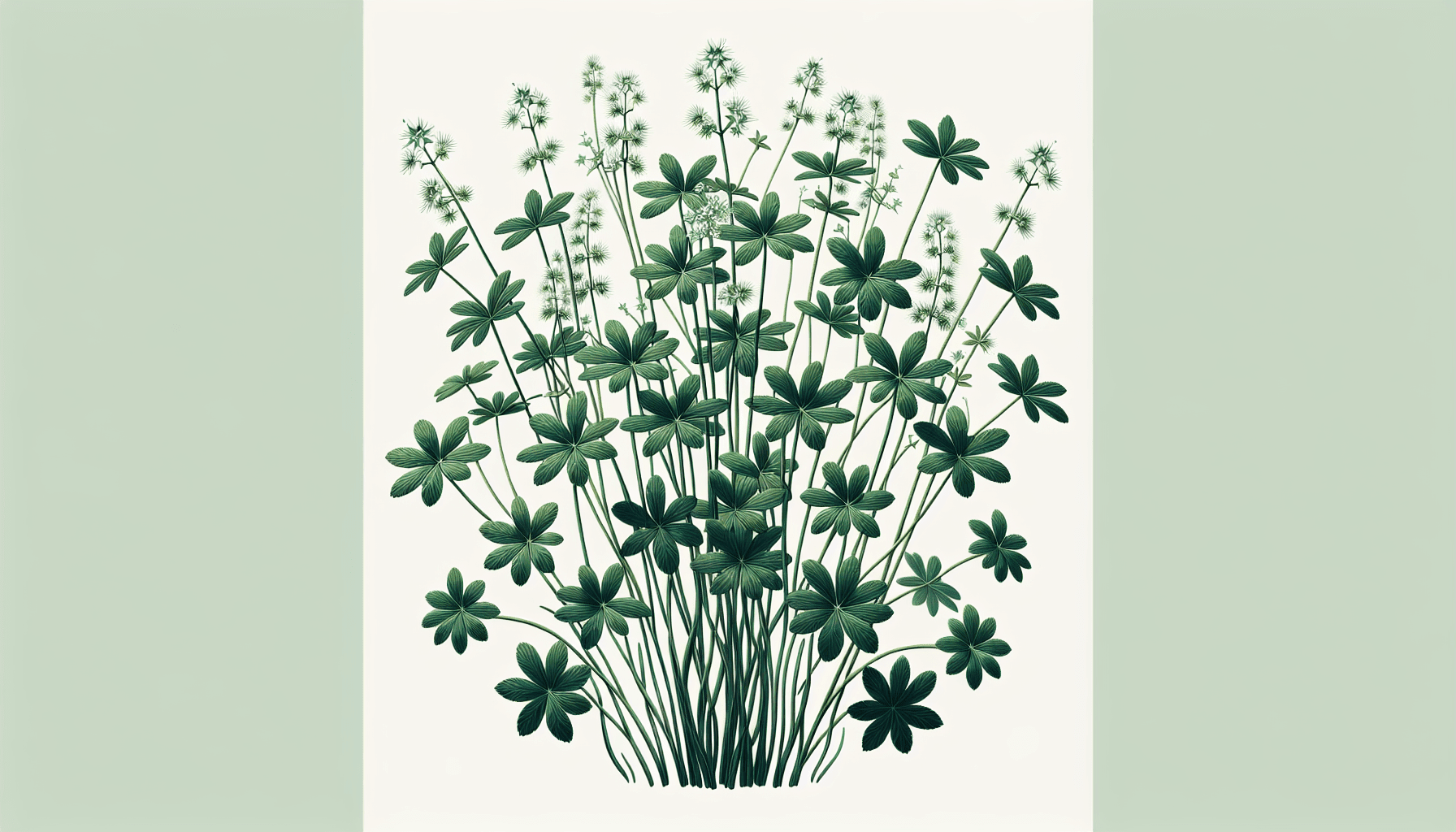

Callitriche Stagnalis as a Weed
Definition of a weed
The term ‘weed’ is used to describe any plant that grows excessively in an area where it’s not wanted, causing potential harm to the intended vegetation, infringing on biodiversity, or impacting human activities.
Issues caused by overgrowth
When left unchecked, Callitriche Stagnalis can grow excessively, causing issues such as blockages in waterways, reducing the water flow, and negatively impacting aquatic biodiversity by outcompeting native plant species. Its overgrowth can also affect recreational activities like boating and fishing.
How Callitriche Stagnalis becomes invasive
Callitriche Stagnalis becomes an invasive species when its growth exceeds the carrying capacity of its ecosystem, primarily through vegetative propagation and a lack of natural predators or competition. Its prolific growth and ability to adapt to different water conditions add to its invasive capability.
Control and Management of Callitriche Stagnalis
Preventative measures
The first line of defense against the overgrowth of Callitriche Stagnalis is prevention. This can be achieved through regular monitoring and swift removal upon detection.
Mechanical control methods
Mechanical methods include physical removal of the plants from the water bodies. However, it is essential to ensure that all plant parts are removed, as the plant can regenerate from fragments.
Chemical treatment
In cases of severe infestation, herbicides can be used to control the growth of the water starwort. However, one must consider the potential impact on non-target organisms and the environment as a whole.
Biological control
Certain organisms feed on Callitriche Stagnalis and can be used as a biological control method. This includes certain species of ducks and insects.
Effects on Aquatic biodiversity
Impact on aquatic flora
In its overgrowth state, Callitriche Stagnalis can outcompete native plants for nutrients, light, and space, leading to a decline in local plant diversity.
Impact on aquatic fauna
Despite providing a habitat and food to some species, the overgrowth can create an imbalanced ecosystem, negatively impacting some animal species.
Effect on overall biodiversity
Overall, while Callitriche Stagnalis plays an integral role in aquatic ecosystems, its invasive nature can threaten overall biodiversity, necessitating periodic monitoring and control measures.
Use in Aquaculture
Use in fish farming
Callitriche Stagnalis forms a crucial part in some aquaculture systems, providing shelter and nutrition to fish, and helping maintain water quality.
Use in wetland restoration
The root system of Callitriche Stagnalis aids in soil binding and prevention of erosion, making the plant useful in wetland restoration projects.
Nutritional and Medicinal Value
Nutrient content
Callitriche Stagnalis has a decent nutritional profile, with a high content of vitamins and minerals.
Medicinal uses and benefits
Traditional medicine systems have used different parts of Callitriche Stagnalis due to its known medicinal properties.
Current Research and Future Directions
Recent developments in control strategies
Recent studies have suggested taking a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to control the plant, focusing on developing biological control strategies.
Areas of future research
Current research gaps exist in understanding the long-term impact of Callitriche Stagnalis on freshwater ecosystems and in improving the efficiency of sustainable control strategies.