In the exploration of aquatic plant life, you will undoubtedly come across varying subspecies, each with their unique features and ecological significance. Among these myriad species, one plant that stands out is the aquatic weed ‘Callitriche Verna.’ Often undermining its importance due to its label as a ‘weed,’ the ecology gives this plant a role far more substantial than mere nuisance to body of water’s aesthetics. This article will guide you through an enlightening discussion about this unique underwater plant, its properties, and its ecological implications.
Understanding Callitriche Verna
Callitriche Verna, often referred to as water starwort or vernal water-starwort, is a species of aquatic plant native to various parts of the world. Herein, you’ll learn about the plat’s origin, botanical classification, physical characteristics, and more.
Definition of Callitriche Verna
Callitriche Verna is a perennial aquatic plant known for its ability to colonize bodies of water in various ecological regions. This species belongs to the Callitrichaceae family and is primarily characterized by its distinctive small white flowers and floating leaves.
Origination and geographical distribution
Callitriche Verna originates mainly from Europe, stretching from the Mediterranean region to northern Europe. It has, however, managed to colonize other parts of the globe, including North America and Asia, due to its adaptability to a range of freshwater habitats.
Botanical classification
Taxonomically, Callitriche Verna belongs to the Plantae Kingdom and the Tracheophyta Division. It falls within the Order of Plantaginales, and the Callitrichaceae Family. As previously outlined, the plant’s Genus is Callitriche, and the species is Verna.
Physical Characteristics of Callitriche Verna
Callitriche Verna exhibits a delicate aesthetic but possesses hardy characteristics that allow it to thrive in varying aquatic environments.
Aesthetics and appearance
The plant’s aesthetic appeals lie in its simplistic yet charming visual display. The presence of tiny white flowers nestled amidst vibrant floating leaves overlooking the surface of the water enhances any aquatic landscape’s visual appeal.
Root system and growth pattern
Callitriche Verna exhibits a taproot system that anchors it to the pond, lake, or riverbed, allowing it to effectively absorb nutrients. The plant grows rapidly under suitable conditions, with the ability to form dense colonies covering water surfaces.
Leaf and flower structure
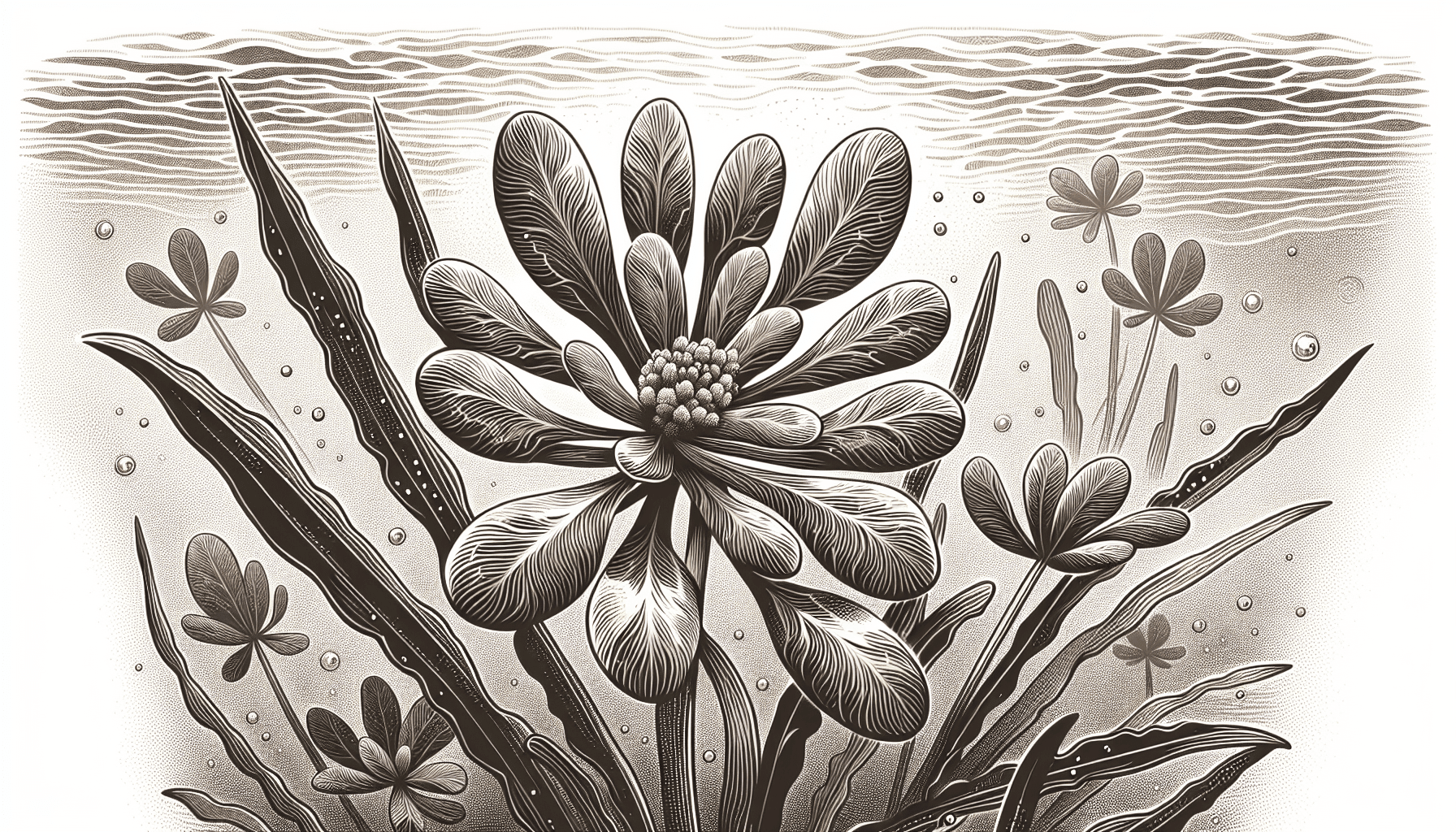
The leaves of Callitriche Verna are arranged oppositely along the stem, with underwater leaves generally linear and narrower than those floating on the surface. It exhibits petite white flowers, typically blooming from late spring to early summer.
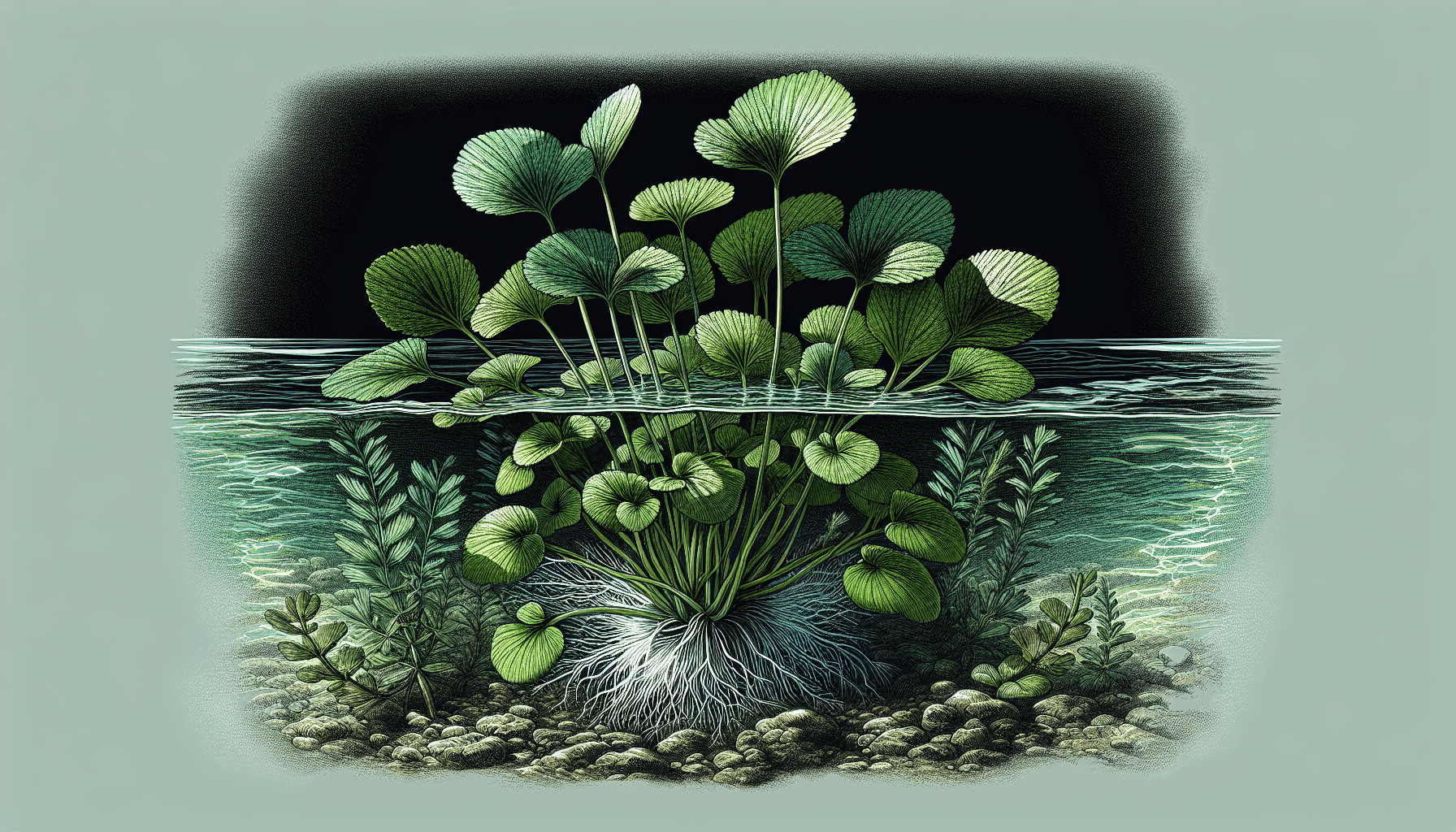
Ecological Roles of Callitriche Verna
Callitriche Verna plays vital roles in the ecological system, facilitating habitat establishment, functioning within the food web, and contributing significantly to environmental health.
Habitat establishment
The species provides a suitable habitat for numerous aquatic creatures, including insects, amphibians, and small fishes. Its underwater root system offers shelter, while its floating leaves provide shade and food resources for many organisms.
Niche in food web
The broad spread of Callitriche Verna on water surfaces provides sustenance to various herbivorous organisms. This directly impacts the food web by supporting a diverse group of predators that rely on these herbivores for sustenance.
Contributions to environmental health
Callitriche Verna contributes to improving water quality by absorbing harmful nutrients, reducing algal blooms, and oxygenating water bodies, which benefits all aquatic life forms.
Life Cycle and Reproduction
Understanding the life cycle and reproductive processes of Callitriche Verna reveals the species’ adaptability and longevity implications.
Lifecycle stages
The plant’s lifecycle initiates from seeds that establish roots upon reaching a suitable aquatic habitat. Subsequently, it exhibits vegetative growth evidenced by the expansion of foliage and eventually, flowering and fruiting stages.
Reproductive processes
Reproduction in Callitriche Verna is primarily through seeds, though vegetative propagation also happens via fragmentation. The flowers are monoecious, meaning each plant has both male and female flowers, facilitating self-fertilization.
Species longevity
The species’ perennial life habit contributes to its long-lived nature. If the aquatic conditions are conducive, Callitriche Verna can thrive year after year, endlessly adding splendor to the aquatic ecosystem.

Callitriche Verna in Aquatic Systems
In freshwater and marine systems, Callitriche Verna has pronounced impacts based on its roles and interaction with other aquatic species.
Roles and impacts in freshwater systems
In freshwater systems, Callitriche Verna acts as a primary producer, contributing to the ecosystem’s energy flow. Its presence significantly enhances biodiversity by offering food resources, oxygenation, and shelter for different organisms.
Roles and impacts in marine systems
Though Callitriche Verna is generally a freshwater dweller, it can tolerate brackish water conditions in marine systems. Its dense mat offers a favorable substrate for marine organisms during their different life stages.
Interactions with other aquatic species
The interactions of Callitriche Verna with other species are multifaceted, ranging from competitive to symbiotic. Its dominance may overshadow other species that require light. Conversely, various species depend on the plant for food and habitat.
Management and Control of Callitriche Verna
Management and control of Callitriche Verna become necessary in cases where the plant becomes overly dominant, posing risks to biodiversity and impacting human activities.
Reasons for management
Over-proliferation of Callitriche Verna can create dense mats obstructing light and impacting other species. Its rapid growth might also interfere with fishing, boating, and other aquatic activities necessitating management interventions.
Physical control methods
Physical control of Callitriche Verna involves manual or mechanical extraction. Hand-pulling is effective for small infestations, while larger-scale invasions may require mechanical equipment like weed cutters.
Chemical control methods
Chemical control is another option, where herbicides particularly effective against aquatic weeds are utilized. However, this should be a last resort due to possible impacts on non-target species and water quality.
Research on Callitriche Verna
Research focusing on Callitriche Verna has been conducted historically, currently, and will continue into the future, aiming to understand and effectively manage this valuable aquatic plant.
Historical research studies
Historical research on the species mainly focused on its basic biology and ecology, including morphological descriptions, lifecycle studies, and its interaction with different biotic components of the aquatic ecosystem.
Current research trends
Current research is often centered on its management, focusing primarily on understanding its rapid growth and propagation patterns and exploring ecological friendly control methods.
Future projections for research
Future research projections point towards advanced genetic studies, understanding its adaptive mechanisms, and exploring its potential in bioremediation and other ecological services.
Callitriche Verna in Human Contexts
Also, beyond its ecological significance, Callitriche Verna holds meaningful aspects that impact human lifestyles and industries.
Cultural significances
In some cultures, Callitriche Verna has been associated with folk legends and used in traditional herbal medicine, drawing attention to its cultural importance.
Role in landscape design and aquascaping
The unique aesthetic features of the plant make it a natural choice in aquatic landscape design and aquascaping. Its vibrant foliage and spreading habit accentuate the beauty of ponds, lakes, and aquariums.
Impacts on human activities and industries
The species can impact human activities positively or negatively. While its uncontrolled growth can interfere with fishing and boating, its potential use in wastewater treatment plants is a positive impact.
Threats and Challenges to Callitriche Verna
Like any other species, Callitriche Verna endures threats and challenges that affect its survival, among which habitat loss and degradation are significant.
Major threats to populations
Major threats to the plant are generally anthropogenic, ranging from water pollution to water course modifications and invasive species that can outcompete it.
Habitat loss and degradation
Habitat loss and degradation due to human activities pose significant challenges to Callitriche Verna. Wetland draining, water pollution, and aggressive agricultural practices are primary contributors to this issue.
Challenges in conservation efforts
Major challenges for conservation include the difficulty of restoring degraded habitats, the lack of awareness about the species’ value, and the complex nature of aquatic ecosystems.
Conservation of Callitriche Verna
Despite potential threats, numerous conservation efforts are in place, given the significance of Callitriche Verna in maintaining aquatic ecosystem health.
Conservation status and regulations
Its conservation status varies worldwide, but it is often listed as of Least Concern. Regulations to protect this species generally fall under broader freshwater habitat protection laws.
Conservation strategies
Conservation strategies for the species largely involve preventing habitat degradation, controlling invasive species, and educating the public about the plant’s ecological importance.
Recovery efforts and success stories
Numerous success stories demonstrate how management and restoration efforts, combined with community participation, have resulted in the recovery of Callitrich Verna populations in certain aquatic systems.
In conclusion, Callitriche Verna, notwithstanding its modest appearance, proves to be a strategic player in the functioning and aesthetic appeal of various freshwater and brackish aquatic systems. Its management, research, and conservation get the due importance considering its ecological significance and potential impacts on human activities and industries.