Perceiving the array of flora populating our water bodies, you may not often distinguish between the benign and the invasive. One such potentially harmful infiltrator, camouflaged in the familiar green tapestry is the aquatic weed Cyperus eragrostis. Commonly referred to as the Tall Flat Sedge, it not only poses significant threats to the aquatic ecosystem balance but also jeopardizes terrestrial cultivation efforts. In the ensuing discourse, you will gain insights into the nature, characteristics, and consequences of this aquatic adversary and equip yourself with the knowledge to identify, manage and potentially control its rapid proliferation.
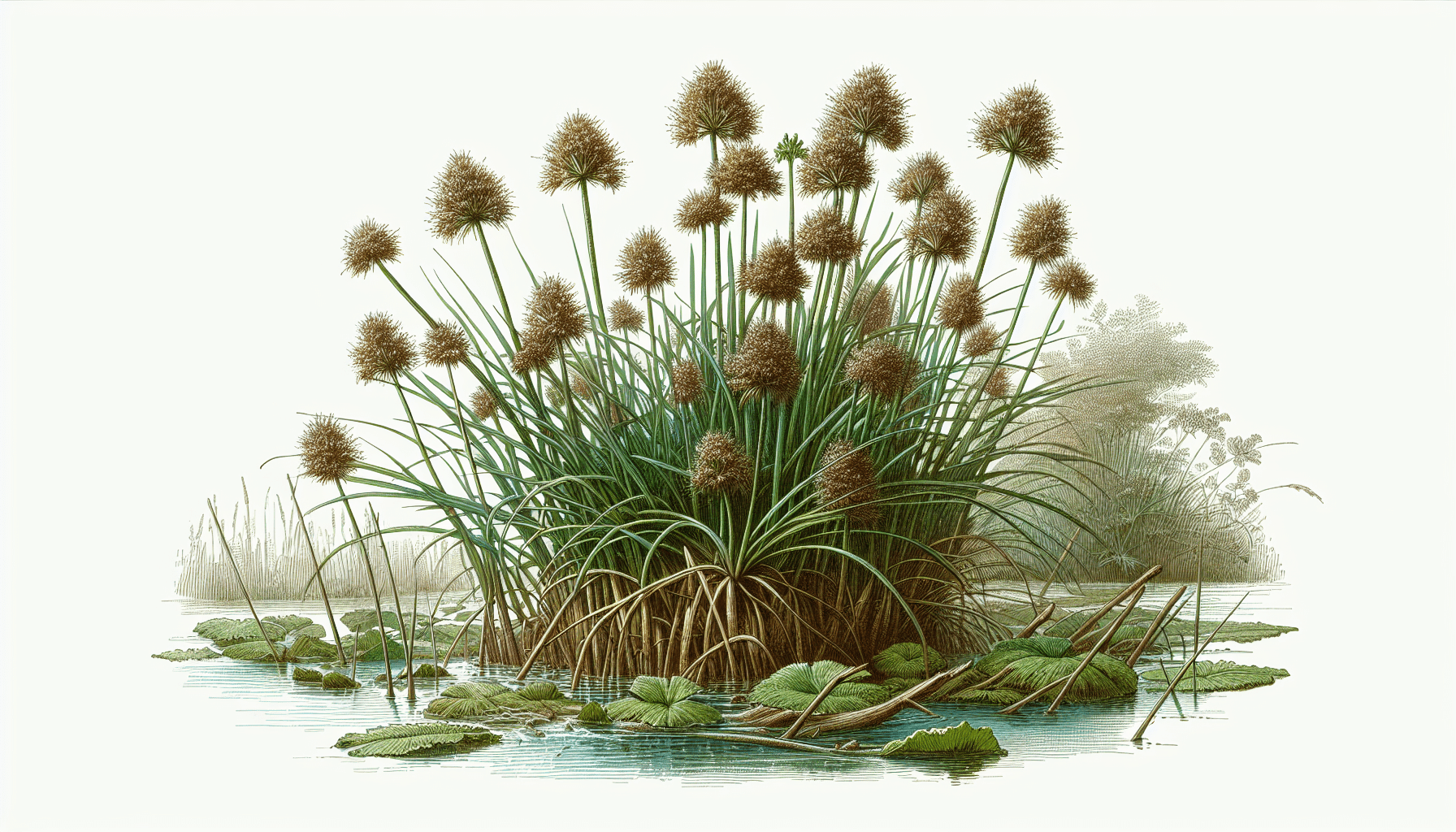
Definition of Cyperus Eragrostis
Cyperus Eragrostis, commonly known as Nutgrass or Tall Cyperus, is a perennial species from the Cyperaceae family. Known for its adaptability and resilience, this aquatic weed is well recognized in the world of botany.
Scientific classification
In scientific terms, Cyperus Eragrostis classifies under the Plantae kingdom and following the hierarchy, this specie finds its heredity in the class of Monocots, order of Poales, family of Cyperaceae, and genus of Cyperus. Eragrostis, which translates to love grass, is the specific epithet bestowed upon this very species.
Common names
Over the course of history, Cyperus Eragrostis has been given various names including Tall Cyperus, Pale Galingale, Nutgrass, and Common Umbrella-sedge. Notably, Nutgrass references this species ability to thrive in high moisture environments.
Morphological features
Cyperus Eragrostis boasts an array of distinctive morphological features. It possesses triangular cross-sectional, erect stems that can grow between 10 to 100 cm tall. Its leaves, narrow and grass-like, extend from the base. It also showcases clusters of greenish to pale brown flowers at the top of the stems. Its fruit, a trigonous achene, is brown in color and about 2 mm long.
Habitat and Geographic Distribution
Cyperus Eragrostis is remarkably adaptable, flourishing in a variety of natural habitats across the globe.
Regions of prevalence
This specie is widely prevalent in various tropical, subtropical and temperate regions. Notably, in North, Central and South America, it is found intensively. It is also found in large numbers in the Australasia region, from India to New Zealand.
Preferred natural conditions for growth
Cyperus Eragrostis favours high moisture environment. Thus it is found in abundance around water bodies, wetlands, damp grasslands and even roadside ditches. It is also found in disturbed sites including cultivated fields and waste land.
Migration patterns
This plant species has shown remarkable ability to disperse and colonize a variety of geographic locations, often due to human activities. Its seeds, vehicle to its migration, are dispersed through water, wind and maybe accidentally through human intervention.
Life Cycle of Cyperus Eragrostis
This resilient plant species follows a somewhat predictable cycle of growth, reproduction, and adaptation to seasonal changes.
Growth stages
Seeds of Cyperus Eragrostis germinate in warm temperatures, enhancing the growth of both root and shoot. Upon attaining maturity, it forms clumps of erect stems, showcasing its stark flowering heads.
Reproductive methods
Reproduction predominantly occurs through seeds. However, vegetative reproduction through rhizomes or stolons is also prominent. This capability enables the plant to create a new individual even from a small piece of root or stem.
Seasonal changes in the plant
Due to its hardy nature, Cyperus Eragrostis continues to grow and reproduce until the first frost of the year. However, it takes a dormant state in colder seasons, resuming its cycle with the advent of warmer temperatures.
Ecological Role
Despite being treated as a weed, Cyperus Eragrostis plays a substantial ecological role, particularly in aquatic ecosystems.
Interaction with aquatic ecosystem
Cyperus Eragrostis creates a vital protective habitat for various aquatic organisms. Additionally, it also assists in preserving the water quality by filtering out pollutants and preventing soil erosion.
Impacts on other aquatic organisms
The dense root system of Cyperus Eragrostis provides shelter for different water-borne organisms and its leaf litter serves as food for a diverse set of insects.
Function in nutrient exchange
Cyperus Eragrostis plays a notable role in nutrient exchange within its environment. It absorbs nutrients from the soil and releases them into the water through leaf decay, thereby supporting the overall nutrient dynamics of the ecosystem.

Cultural and Historical Significance
Though often portrayed as a nuisance, Cyperus Eragrostis holds certain cultural and historical significance.
Utilization by indigenous cultures
Cyperus Eragrostis was used by indigenous cultures in diverse ways. The plant’s strong fibers were employed in making artifacts like baskets and mats, and its aromatic tubers were utilized for culinary purposes.
Symbolic representation
While its symbolic representation differs among cultures, in Egyptian mythology, it is often associated with the life-giving Nile river and was sometimes used in religious rituals.
Archaeological findings related to Cyperus Eragrostis
Several archeological findings reveal the past use of Cyperus Eragrostis. Its seeds have been discovered at ancient roman sites, suggesting its utility as an ancient crop.
Human Impact and Control Measures
Unfortunately, the rapid growth and resilience of Cyperus Eragrostis often leads to detrimental effects on human activities.
Detrimental effects on human activities
A notorious weed, Cyperus Eragrostis, can invade crops, causing significant yield losses. It is also known to obstruct waterways, leading to increased maintenance costs for irrigation and drainage systems.
Methods for control and eradication
Despite its resilience, there are several ways to control the growth of Cyperus Eragrostis. These include mechanical measures, such as uprooting the weed before seed set, and chemical control through the carefully timed use of herbicides.
Compliance and regulation policies
Certain compliance and regulations are in place in different regions to prevent the spread of invasive plants like Cyperus Eragrostis, urging landowners to control the growth of such weeds on their property.
The Influence of Climate Change on Cyperus Eragrostis
As a highly adaptable species, Cyperus Eragrostis shows significant resilience and adaptation to the impacts of climate change.
Impact of rising temperatures
Rising temperatures due to climate change have the potential to favour the germination and growth of Cyperus Eragrostis, as it thrives in warm conditions.
Response to changing water levels
Cyperus Eragrostis shows extraordinary adaptability to varying water levels, able to survive both in wet and dry conditions, thereby ensuring its survival in changing environments.
Resilience and adaptation to new climates
As a highly resilient species, Cyperus Eragrostis possesses the ability to adapt to a variety of new climates, indicating its potential to continue spreading under future climate change scenarios.
Role in the Aquatic Food Chain
While deemed a nuisance by humans, Cyperus Eragrostis holds a crucial role in the aquatic food chain.
Nutritional benefits for aquatic animals
The plant acts as a vital food source and habitat for many aquatic creatures. The decomposing leaves and stems are rich in nutrients, providing a valuable food source.
Predators of Cyperus Eragrostis
Numerous insects and herbivores, like fish and geese, are known to feed on Cyperus Eragrostis. Interestingly, some humans also consume its tubers, treating it as a sort of popcorn.
Importance for biodiversity
By providing food and habitat to a variety of aquatic organisms, Cyperus Eragrostis plays a key role in maintaining biodiversity in aquatic ecosystems.
Health Risks Associated with Cyperus Eragrostis
Despite playing a vital ecological role, Cyperus Eragrostis can potentially pose health risks.
Potential allergenic properties
As with other members of the sedge family, Cyperus Eragrostis can trigger allergies in certain individuals due to its pollen.
Contribution to water pollution
While the plant contributes to filtering pollutants, when it dies and decomposes, it releases these accumulated pollutants back into the water bodies.
Posology of ingestion or exposure
Ingestion or exposure to Cyperus Eragrostis doesn’t typically pose a health risk unless one is allergic to it. However, consuming water tainted by its residual toxins from decomposed parts could potentially cause mild to moderate health issues.
Biotechnological Applications and Research
Interestingly, Cyperus Eragrostis is subjected to numerous biotechnological research and applications due to its unique characteristics.
Use in biofuels production
Cyperus Eragrostis has drawn attention as a promising bioenergy crop. This is due to its high biomass productivity, broad ecological adaptation, and potential to grow on marginal lands, making it a suitable candidate for biofuel production.
Genetic studies and plant breeding
Owing to its extensive genetic diversity, researchers are increasingly focused on Cyperus Eragrostis for studies related to plant breeding and genetics.
Potential medicinal applications
Though still in exploratory stages, Cyperus Eragrostis is being investigated for potential medicinal applications. Its tubers exhibit certain antibacterial and antifungal properties, sparking interest in the pharmaceutical world.
In sum, despite its notorious reputation as a weed, Cyperus Eragrostis commands significant scientific interest. Be it its ecological role, resilience to climate change, or potential in biotechnology, the specie undeniably possesses multifaceted significance in the contemporary world.