In an exploration of the rich diversity of aquatic flora, you find yourself intrigued by the Echinodorus Uruguayensis, an aquatic weed often misunderstood living beneath the surface of various water bodies. At first glance, the name may seem a mouthful, perhaps even vague and uninteresting but prepared to be captivated by this intricate plant life that thrives in the depths of water ecosystems. Dubbed the ‘aquatic weed’, the Echinodorus Uruguayensis boasts an intriguing existence, and it undeniably warrants your profound attention and understanding in the vast context of water-dwelling plants.
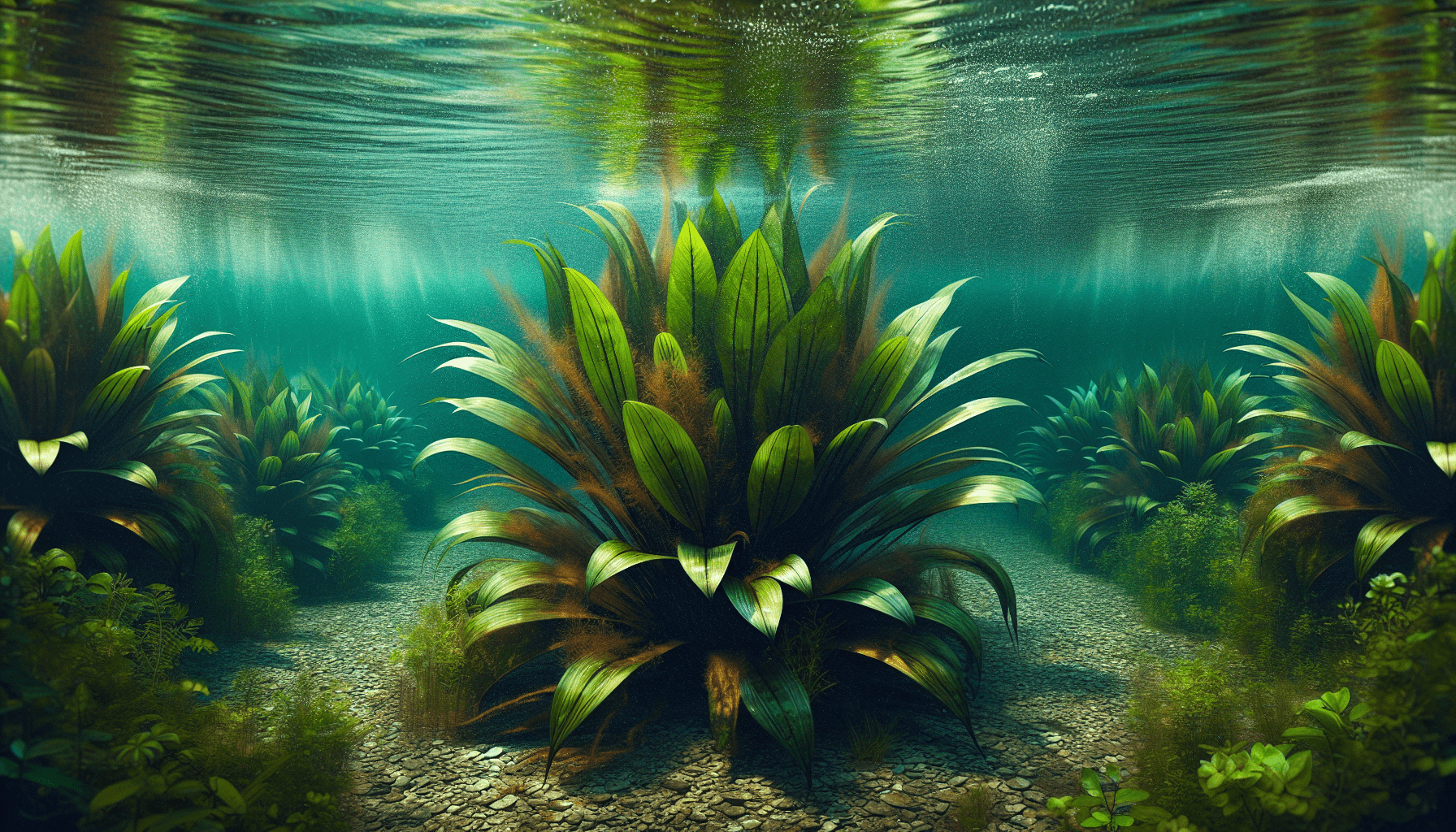
Identification of Echinodorus Uruguayensis
Echinodorus uruguayensis, known for its distinctive shape and size, is a prevalent aquatic plant native to South America. An essential member of the aquatic ecosystem, its identification is a crucial aspect of botanical study and care.
Physical Characteristics
A distinguishing characteristic of Echinodorus uruguayensis is its formation of broad green leaves that exhibit a ternate pattern. The leaves emerge from a centralized stalk, referred to as the rosette. This structural formation often results in a bushy foliage display. Mature leaves commonly reach a length of about 40-50 cm, providing a distinctive presence in the aquatic environment.
Color Variations
The color of Echinodorus uruguayensis is predominantly dark green, with the leaf blades displaying a glossy texture. In conditions of intense light exposure, a subtle maroon or reddish hue may appear along the margins or undersides of the leaves, enhancing its aesthetic.
Different Stages of Growth
The growth stages of Echinodorus uruguayensis transition from juvenile to mature size. The juvenile stage often displays a compact and straightforward leaf structure. As the plant matures, more widespread and intricate leaf formations arise. The mature stage is characterized by a robust combination of broad, long leaves that extend outwards from the rosette.
Taxonomy and Naming of Echinodorus Uruguayensis
Understanding the taxonomy and nomenclature of Echinodorus uruguayensis is essential to uncover its botanical story and relation to the ecosystem.
Etymology and Historical Background
Echinodorus is a genus name that stems from the Greek roots “Echinos,” meaning hedgehog, and “doron,” meaning gift. This name likely references the prickly look of the flower spikes when in seed. Uruguayensis, derived from Uruguay, denotes the plant’s geographic origin.
Scientific Classification
In hierarchical terms of scientific classification or taxonomy, Echinodorus uruguayensis belongs to the family Alismataceae. It holds close relationship with other aquatic plants bearing similar properties.
Habitat and Distribution
Information about the habitat and geographic distribution of this species provides insight into its ecological context and survival requirements.
Natural Habitat
As a water-loving plant, Echinodorus uruguayensis thrives in damp, marshy environments and generally poised along the fringes of freshwater bodies. This aquatic adaptation is conducive to its South American origins, where wet, swampy landscapes are prodigious.
Geographical Distribution
Echinodorus uruguayensis is indigenous to South America and is quite widespread across several countries, including Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, and Argentina. Today, their presence extends to other parts of the world due to their popularity in aquarium cultivation.

Growth Requirements
Specific growth requirements of Echinodorus uruguayensis involve critical factors such as light conditions, water parameters, and nutrition.
Light Conditions
While Echinodorus uruguayensis is a tolerant species, thriving in various lighting conditions, it exhibits a preference for bright, indirect light that encourages vigorous growth and a healthier foliage display.
Water Parameters
Being an aquatic plant, Echinodorus uruguayensis can adapt to a range of water conditions. Ideal water parameters include a pH range of 6.5-7.5, although it can tolerate slight variations.
Nutrition and Soil Type
Echinodorus uruguayensis draws most of its nourishment directly from the soil. A nutritionally rich substrate will fuel the plant’s growth and promote a healthy appearance. It is also known to assimilate nutrients from the water through its leaves.
Propagation and Reproduction
The reproduction mechanisms of E. uruguayensis include flower and seed production and vegetative propagation.
Flower and Seed Production
Under optimal conditions, Echinodorus uruguayensis produces white flowers on a long, thread-like stem that extends above the water surface, often leading to seed production. These seeds can further propagate when they fall into the substrate and sprout into new plants.
Vegetative Propagation Methods
In addition to seed production, Echinodorus uruguayensis can also reproduce vegetatively. New plants, or daughter plants, are formed from the mother plant along the stem, known as the rhizome. These daughter plants can be pruned and re-planted where they develop into mature plants.
Role in Aquatic Ecosystem
Echinodorus uruguayensis plays a significant role in the aquatic ecosystem due to its functional utility and interactions with other species.
Function in Aquatic Habitat
Primarily, this plant absorbs nutrients from the water, thus reducing algal bloom. It also provides shelter and nesting grounds for aquatic fauna, offering protection against predators.
Interactions with Other Species
Echinodorus uruguayensis is known to co-exist peacefully with other aquatic species, both plant, and animal. Its presence enhances biological diversity in the habitat while facilitating a balanced ecosystem.
Potential Threats and Preservation
Despite its resilience, Echinodorus uruguayensis also face potential threats, necessitating effective conservation strategies.
Threats to Survival
The survival of Echinodorus uruguayensis is threatened by environmental changes such as dwindling water levels, pollution, and changes in the water’s acidity or alkalinity. Moreover, invasive species can also pose a risk, competing for the same resources.
Conservation Strategies
Conserving Echinodorus uruguayensis involves preserving its natural habitats, enforcing stringent regulations against invasive species, and initiating measures to keep the water quality in check.
Echinodorus Uruguayensis as Aquatic Ornamental Plant
As an ornamental plant, Echinodorus uruguayensis brings beauty and vitality to aquariums and artificial aquatic habitats.
Use in Aquascaping
Their lush green leaves and robust growth make them a popular choice among aquascaping enthusiasts. They are often used as a background plant due to its size, providing a verdant backdrop to the aquatic scape.
Care and Maintenance in Aquariums
Echinodorus uruguayensis requires minimal maintenance in aquariums, which adds to its popularity. Regular pruning helps maintain its shape and size, while monitoring water parameters ensures its good health.
Research and Study on Echinodorus Uruguayensis
Scientists have conducted numerous studies to unravel the secrets of Echinodorus uruguayensis, yielding interesting findings and revealing areas of ongoing study.
Noteworthy Research Findings
Research on Echinodorus uruguayensis has uncovered its potential as a bioindicator of environmental changes, making it useful for monitoring water quality.
Areas of Ongoing Investigation
Studies continue to explore the plant’s capacity to absorb pollutants from water bodies, offering potential solutions for water purification.
Interesting Facts About Echinodorus Uruguayensis
Echinodorus uruguayensis holds a rich tapestry of unique properties and trivia that spark interest.
Unique Properties or Behaviors
An interesting trait of Echinodorus uruguayensis is its ability to flourish both submerged and emerged. This adaptive quality sets it apart from many other aquatic species.
Trivia and Miscellaneous Information
Did you know that Echinodorus uruguayensis is often mistaken for Echinodorus grandiflorus due to their similar appearance? Noteworthy differences, such as the plant size and location of flower spike emergence, are key identifiers.