“You are about to embark on an enlightening journey into the underwater world of Elodea Canadensis, a pervasive aquatic weed. As you traverse this intellectual landscape, you will be enlightened on the plant’s phylogenetic placement, growth attributes, ecological implications, and its role within its ecological niche. This article illuminates the inherent complexities and intriguing facets of Elodea Canadensis, offering an in-depth exploration of its various aspects from a biological and ecological perspective.”
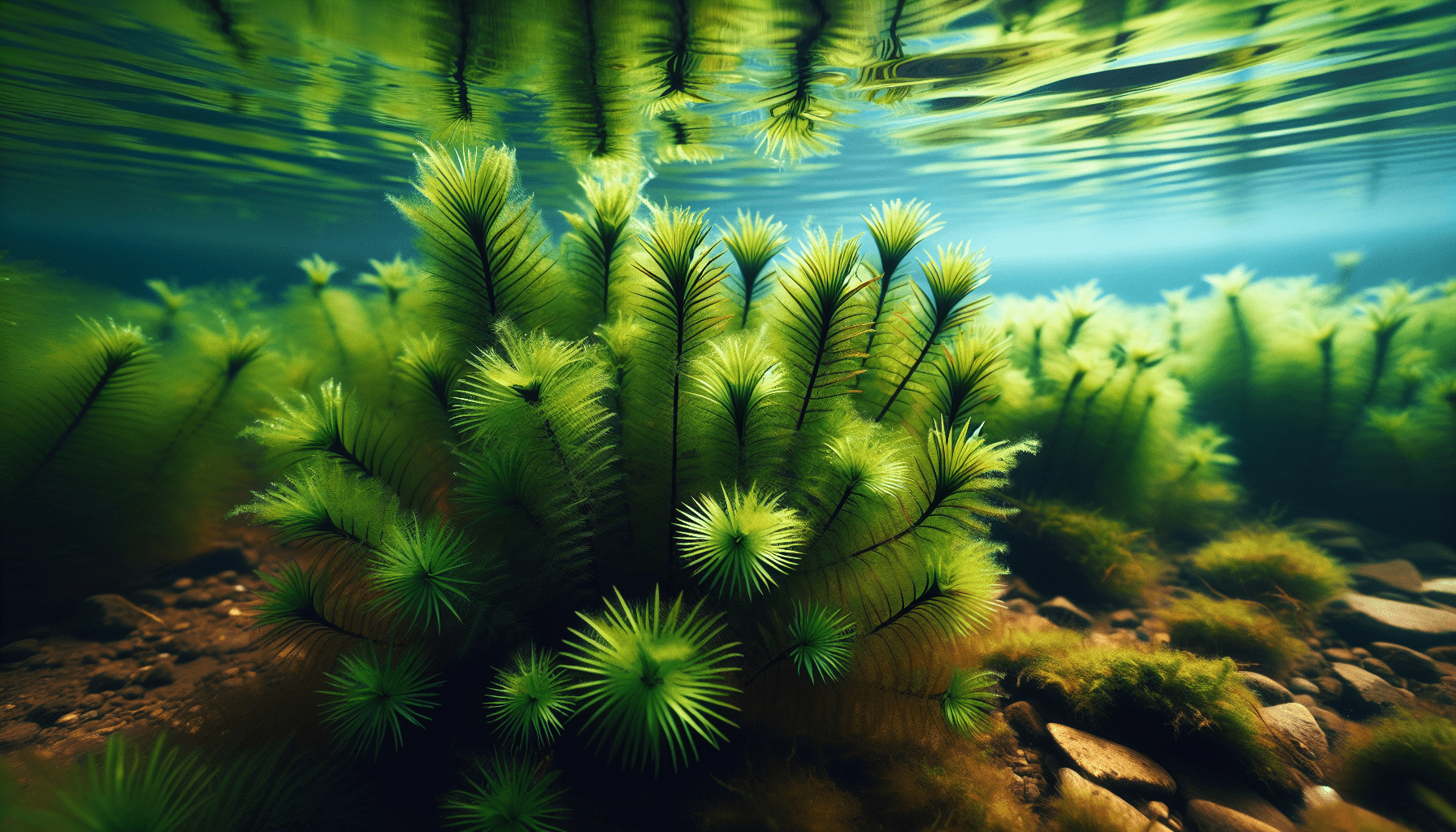

Overview of Elodea Canadensis
Definition and physical description
Elodea Canadensis, often referred to as the Canadian waterweed or Canadian pondweed, is an aquatic, perennial plant characterized by its vivid green coloring and robust growth. As an underwater plant, it possesses a branching stem often covered in a whorl of leaves with a clear veiny structure, each leaf typically consisting of three transparent, narrow, and slightly curved layers. Each mature plant can grow up to 3 meters in length and produce slender white flowers floating above the water surface on fine, slender stalks.
Geographic distribution and habitat
Elodea Canadensis inhabits freshwater environments, more specifically, it thrives in slow-moving or stagnant bodies of water such as ponds, lakes, ditches, and canals. This aquatic plant prefers water bodies rich in nutrients with temperatures between 10-25°C for optimal growth. Although native to North America, this plant has successfully managed to colonize many regions worldwide, reflected in its classification as an invasive species in Europe, Asia, and New Zealand.
Historical Background of Elodea Canadensis
Original native region
Elodea Canadensis originally hails from North America, where it occupies the temperate regions of Canada and the northern United States. Here Elodea was able to adapt to a wide range of climatic conditions, demonstrating the plant’s high physiological plasticity and resilience.
Expansion to non-native regions and causes
The expansion of Elodea Canadensis to non-native regions is attributed primarily to human activity. Many instances of unintentional introduction occurred in the early 19th century, through the transportation of root fragments on ships. Separately, Elodea also became a popular decorative plant for water gardens and freshwater aquariums, before its ability to reproduce rapidly and outcompete native aquatic flora was fully understood.
The Biological and Botanical Characteristics of Elodea Canadensis
Structural features and physiology of Elodea Canadensis
Elodea Canadensis comprises both floating and submerged parts, a feature central to its survival strategy. Its shoots, which can generate roots at any node, are anchored in the substrate but also float freely. This combined attribute allows the plant to colonize both deep and shallow parts of water bodies. This submerged plant possesses a highly branched structure, which allows for high light interception, fundamental for its photosynthesis and survival.
Life cycle and reproductive modes
Elodea Canadensis generally reproduces asexually through fragmentation; it breaks off into small segments that then grow into new plants. Under optimal conditions, it can also reproduce sexually through the production of male and female flowers that float to the surface and are pollinated by wind or water currents; however, this is less common.
Ecological Role of Elodea Canadensis
Role in water bodies’ ecosystem
Elodea Canadensis plays a significant ecological role within water bodies, primarily by providing a habitat for numerous organisms, including insects, crustaceans, and a variety of fish species. The plant’s dense structure provides a well-sheltered breeding ground, hiding spaces from predators, and a hunting ground for various species.
Impact on biodiversity
Although it can reduce native biodiversity in newly colonized regions, within its native ranges, Elodea Canadensis can enhance local biodiversity by creating niche habitats. These created environments can house a multitude of organisms, leading to a more diverse and vibrant ecosystem.
Function as a food and habitat source for animals
Elodea Canadensis serves as a food source for many animals, including ducks, turtles, fish, and insects. As such, it performs a crucial role in the food chain of freshwaters systems.
Elodea Canadensis and Oxygenation in Water Bodies
Contribution to oxygenation in water bodies
As a photosynthetic plant, Elodea Canadensis contributes significantly to oxygenating water bodies. Through the process of photosynthesis, it absorbs carbon dioxide and releases oxygen, ultimately improving water quality and contributing to the maintenance of the aquatic ecosystem.
Role in aquatic photosynthesis process
Elodea Canadensis has an essential role in the aquatic photosynthesis process. This plant’s leaves, submerged under the water surface, contain chlorophyll, the green pigment responsible for photosynthesis. Here, they capture sunlight and convert it, along with carbon dioxide and water, into oxygen, and glucose for growth and development.
Problems caused by Elodea Canadensis Overgrowth
Reasons for rapid growth and overpopulation
Elodea Canadensis can quickly overpopulate, especially in nutrient-rich water bodies. High nutrient loads, especially nitrogen and phosphorus, coupled with ample sunlight, facilitate its rapid growth and fragmentation.
Effects on water bodies and other plants
Elodea Canadensis’s overgrowth can have severe effects on water bodies and other aquatic plant species. Dense overgrowth can hinder water flow, cause fluctuations in oxygen and pH levels, and generate unfavorable conditions for other plant species, leading to a decline in native plant diversity.
Impacts on recreational and commercial activities
Overgrown Elodea Canadensis can interfere with recreational activities such as boating, fishing, and swimming. Moreover, because of its dense growth, it can obstruct water channels and interfere with commercial navigation.
Potential Uses of Elodea Canadensis
Use in freshwater aquariums
Despite the potential for overgrowth, Elodea Canadensis is a popular plant in freshwater aquariums and ornamental water gardens, where its growth can be easily controlled. Its dense structure and bright green color make it an appealing choice in decorative aquarium setups.
Role in scientific research and education
In scientific research, Elodea Canadensis is regularly used to understand aquatic plant physiology and ecology due to its robustness and fast growth. It’s also frequently used in biology classrooms as a readily available and easily manipulated subject for demonstrating photosynthesis and cellular structures.
Controlling the Growth of Elodea Canadensis
Common practices to manage Elodea Canadensis overgrowth
Common practices to control Elodea Canadensis overgrowth typically involve manual removal or the use of specific herbicides. Regular monitoring of the condition of the water bodies and the early detection of Elodea helps control its spread.
Use of herbicides and biological agents
Chemical control using herbicides can be effective, but it also runs the risk of affecting non-target species and upsetting the balance of the ecosystem. More recently, biological control agents like the Elodea-eating moth have been introduced to keep the plant’s growth at bay.
Mechanical removal methods
Mechanical removal, using rakes or specialized machines, is another strategy for managing overgrowth. However, this method may not be effective in the long-term as broken fragments can quickly regenerate into new plants.
Conservation Efforts Involving Elodea Canadensis
Role of conservation organizations and government bodies
Conservation organizations play a critical role in the management and protection of Elodea Canadensis. They work in collaboration with government bodies to monitor water bodies for early detection and rapid response initiatives, to prevent the expansion of this species to non-native regions.
Efforts to preserve native populations
Efforts to preserve native populations of Elodea Canadensis include maintaining its natural habitats against pollution and human intervention. Additionally, it is crucial to control its growth in non-native regions to prevent the displacement of indigenous plant species.
Future of Elodea Canadensis
Projected population trends
Given its ability to adapt and proliferate easily, the worldwide population of Elodea Canadensis is projected to increase, particularly in water bodies with high nutrient content. Current environmental changes such as global warming and increased nutrient run-offs into freshwater bodies can further promote the growth of this plant.
Implications on global biodiversity and ecosystems
The expanding population of Elodea Canadensis has profound implications on global biodiversity and ecosystems. While it enhances biodiversity in its native ranges, it can out-compete native species in new habitats, contributing to reduced biodiversity. Therefore, striking a balance between its beneficial roles and its potential to become invasive is paramount in maintaining healthy ecosystem dynamics.