In “What is the Aquatic Weed Limnocharis Flava?”, the author presents an in-depth analysis of the plant, commonly known as sawah lettuce. The document provides essential information about its characteristics, growth, and the impact it has on its environment. The author also provides understanding about the various strategies used to control its infestation, and the potential uses of this aquatic plant. Through the course of this document you will come to appreciate the complexity and ecological significance of Limnocharis Flava.
Identification and Description of Limnocharis Flava
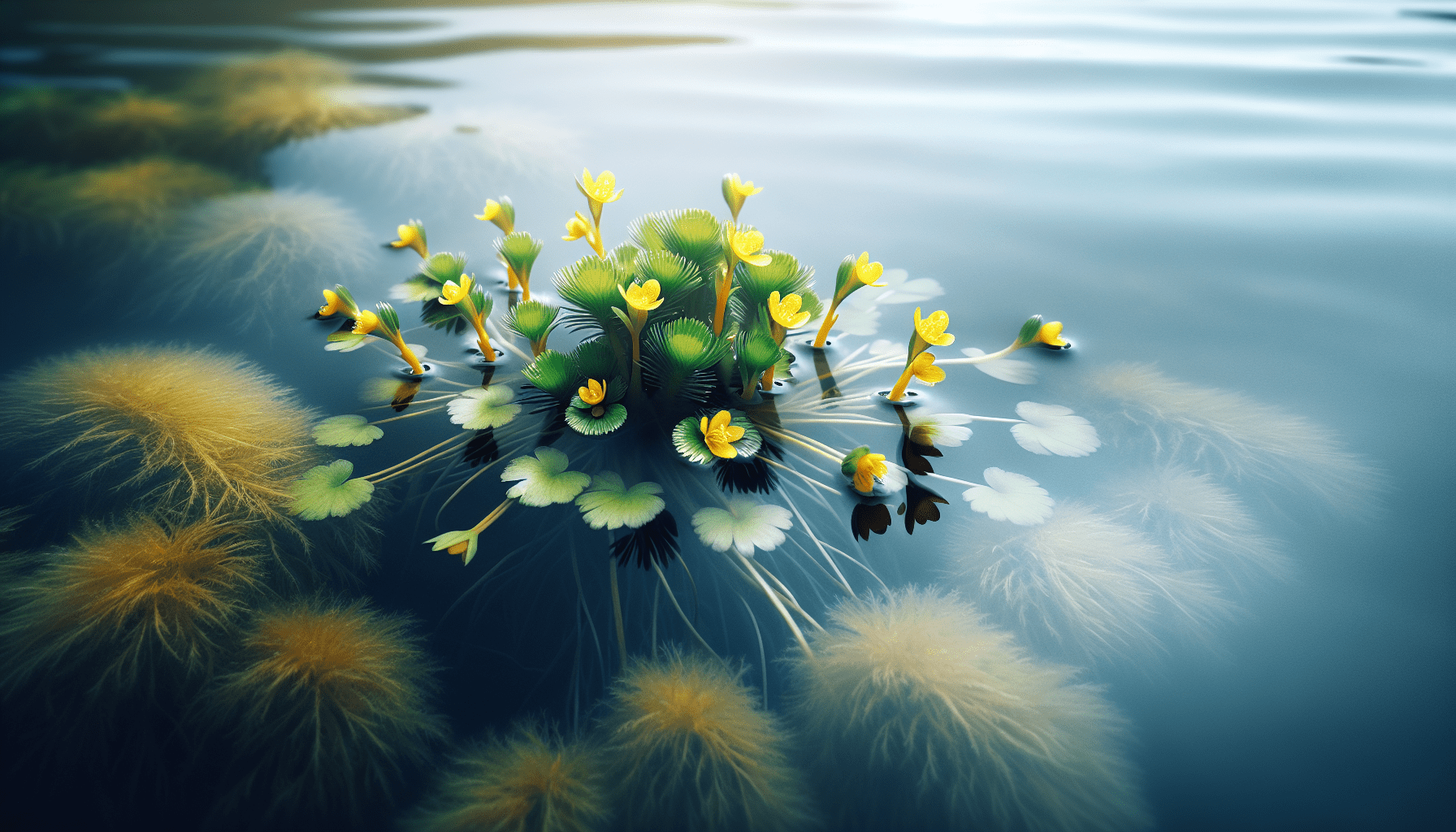
The Limnocharis flava, also known as yellow sawah lettuce, is an aquatic weed that closely resembles a regular lettuce. Its distinct attributes have allowed it to stand out among other water plants, making it relatively easy to identify.
Physical Characteristics
The physical characteristics of Limnocharis flava include a round stem that grows up to 20 to 60 centimeters tall from its roots. It has three yellow petals and a cone-like structure in the middle of the flowers. Its leaves are floaters and are shaped like rosettes. The leaves are generally 6-12 cm long and have distinctive parallel veins on them.
Growth Habits
Limnocharis flava has aggressive growth habits. It colonizes water bodies rapidly and forms dense mats of vegetation on the water surface. It survives and reproduces through both sexual and asexual means. Seeds can survive for a year in the water and more than a decade in sediments.
Flowers and Fruits
The flowers of the yellow sawah lettuce are a vibrant yellow hue. They are small and have three rounded petals. The fruit is a capsule and consists of numerous tiny seeds that enable the plant to propagate. The fruits are reproductive structures that mature to release these seeds into the environment.
Origins and Distribution
The origins and distribution of Limnocharis flava have been expansive and the plant is now considered a significant invasive species in several parts of the world.
Native Regions
Limnocharis flava is a native plant of Central and South America. It flourishes in tropical regions, especially in areas where water bodies exist, and this has allowed it to spread widely.
Current Global Distribution
Currently, Limnocharis flava’s global distribution includes Southeast Asia, parts of Australia and the Pacific Islands. It has more recently started causing significant problems in Africa.
Habitats
As an aquatic plant, Limnocharis flava is found in water bodies such as rivers, ponds, dams, and wetlands. It also thrives in irrigation systems and rice fields.
Biological Classification
Part of understanding Limnocharis flava involves familiarising yourself with its biological groupings.
Family and Genus
Limnocharis flava is part of the Limnocharitaceae family and the Limnocharis genus. The plant’s unique characteristics distinctly place it within this family and genus.
Similar Species
Several similar species exist within the Limnocharis genus that can easily be mistaken for Limnocharis flava. These include Limnocharis buchanani and Limnocharis laforestii. However, their distinguishable characteristics such as petal shape and color significantly differentiate them from the yellow sawah lettuce.
Varieties and Cultivars
There is limited information available pertaining to specific varieties or cultivars of Limnocharis flava.
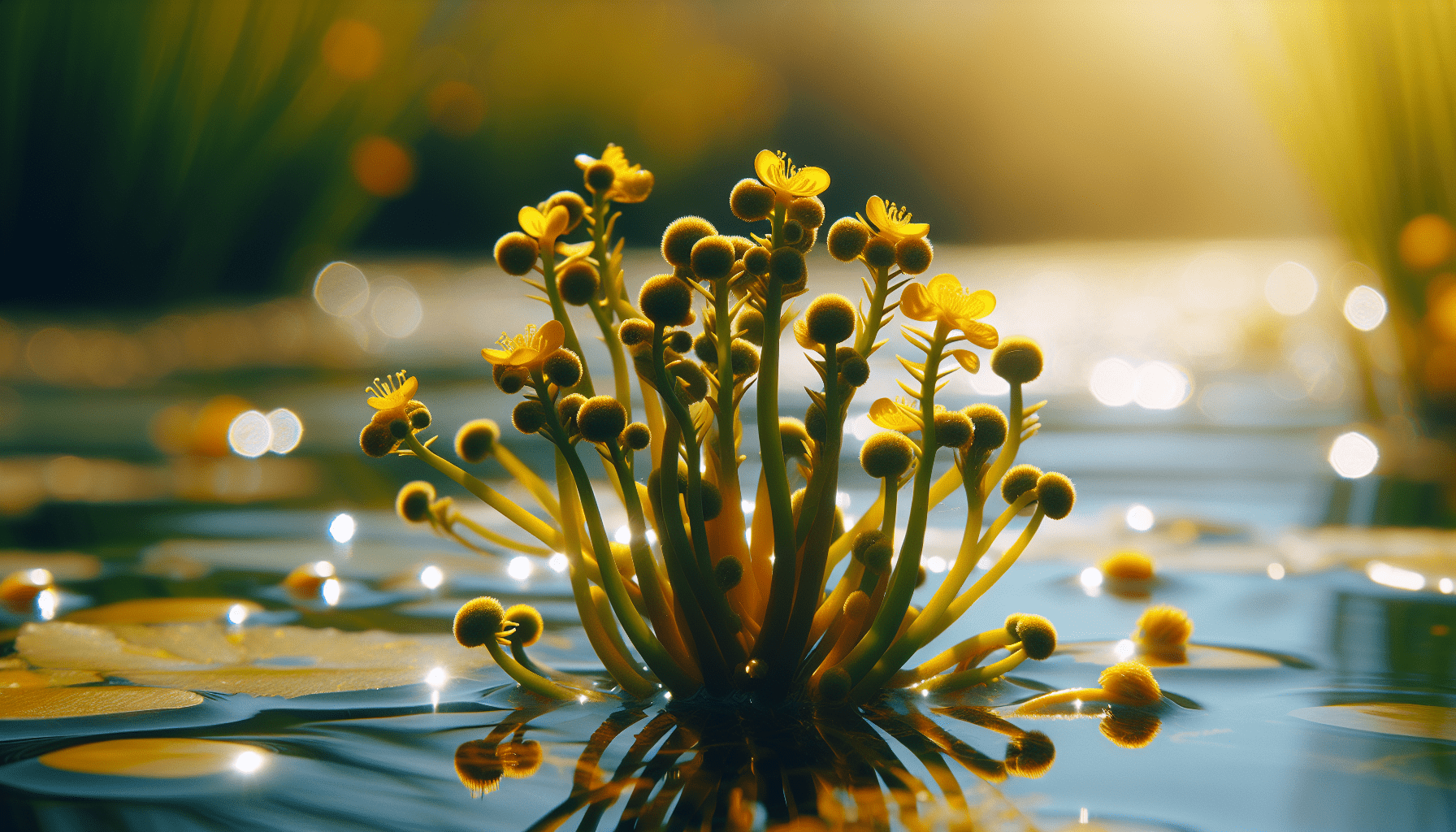

Growth Conditions and Requirements
Limnocharis flava thrives in certain conditions that enable its survival and rapid growth.
Light Requirements
As with many plants, Limnocharis flava requires sunlight for photosynthesis. It does well in full to partial sun exposure.
Water and Soil pH Levels
Limnocharis flava can grow in a variety of pH levels; however, it does best in slightly acidic to neutral conditions.
Temperature Ranges
Limnocharis flava prefers warm tropical climates and is highly tolerant of heat. However, it can also withstand cooler temperatures, making it highly adaptable.
Ecological Impact of Limnocharis Flava
Limnocharis flava presents a significant ecological issue, with impacts on native aquatic plants, water quality, and aquatic life.
Effect on Native Aquatic Plants
This invasive aquatic weed forms dense mats on the surface of water bodies, which can block sunlight and outcompete native aquatic plants for resources, leading to a decrease in biodiversity.
Impact on Water Quality
By blocking sunlight penetration into the water, Limnocharis flava can significantly reduce oxygen levels in the water body, resulting in the deterioration of water quality.
Influence on Aquatic Life
Reduced oxygen levels can have adverse effects on aquatic life, disrupting the balance of the ecosystem. Fish and other aquatic animals may struggle to survive in oxygen-depleted conditions.
Economic Impact
The invasion of Limnocharis flava can significantly impact various sectors of the economy.
Effect on Fishing Industry
The dense vegetation formed by Limnocharis flava can impede the activities of the fishing industry. Fishing nets may get entangled in these weeds, slowing down fishing activities, and decreasing productivity.
Implications on Water-Based Tourism
Aquatic recreational activities such as boating and fishing can be negatively impacted by the presence of Limnocharis flava, affecting the profits of the tourism industry.
Cost of Control and Eradication
Significant financial resources are poured into controlling and eradicating Limnocharis flava, causing a weighty economic burden on those affected, including the government.
Control and Management Strategies
Managing the spread of Limnocharis flava involves various control methods that can be used in combination.
Mechanical Control Methods
Mechanical control methods involve physically removing the weed from the water bodies. This can be done by hand or with the use of machines. The plant and its roots must be removed entirely to prevent regrowth.
Chemical Control Methods
Chemical control involves the use of herbicides appropriate for aquatic environments. It is crucial to apply them precisely to minimize impact on non-target species and the environment.
Biological Control Methods
Biological control methods utilize natural enemies of the weed, such as specific insects, to control its spread.
Benefits and Uses
Despite its invasive nature, Limnocharis flava also has various beneficial uses.
Use in Traditional Medicine
In some native regions, the plant is used in traditional medicine for various ailments, including goiter and lower back pain.
Edible Uses
This species is also edible, with the stems and leaves cooked and consumed in areas like Thailand and the Philippines.
Potential for Phytoremediation
Research has shown potential for the yellow sawah lettuce in phytoremediation, a process that involves the removal of pollutants from water bodies.
Research and Studies on Limnocharis Flava
Various research and studies are conducted to gain a better understanding of Limnocharis flava, its impact, and control strategies.
Latest Scientific Findings
Recent studies suggest that the plant has a potential role in phytoremediation and the removal of heavy metal contaminants from the water.
Ongoing Research Projects
Numerous research projects are ongoing globally to find more effective control measures and to better understand Limnocharis flava and its impact on various ecosystems.
Potential Future Applications
The potential future applications of Limnocharis flava are wide-ranging, although more research is needed to determine its full potential.
Legal Status and Regulations
The spread and introduction of Limnocharis flava are regulated by stringent laws and guidelines in many countries.
Prohibited States or Countries
In some countries and states, the growth, possession or distribution of this plant are strictly prohibited due to its invasive nature.
Laws and Penalties for Possession or Distribution
Breach of these laws can result in penalties such as hefty fines and even imprisonment in some cases.
Conservation Measures
Numerous conservation measures are enacted to preserve habitats and protect native species from the invasion of plants like Limnocharis flava.