In accessing the article titled “What is the Aquatic Weed Myriophyllum Hippuroides”, you are about to engage with an in-depth analysis of a plant known for both its beauty and detriments in aquatic ecosystems. This robust investigation uncovers the complexity of Myriophyllum Hippuroides, colloquially referred to as the water milfoil, in its biological characteristics, ecological impacts, and potential management strategies.

Definition of Myriophyllum Hippuroides
A brief description of what Myriophyllum Hippuroides is
Myriophyllum Hippuroides is a species of freshwater aquatic plant commonly known as water milfoil or hippurislike watermilfoil. This plant is notable for its highly branched aquatic stems that host feathery leaves and create a dense submerged presence. The species is native to North America and has since spread globally, particularly in temperate or tropical regions.
Scientific classification of the species
In the scientific classification, Myriophyllum Hippuroides falls under the Myriophyllum genus and the family Haloragaceae. It is a part of the order Sapindales, the class Magnoliopsida (also known as dicotyledons), and the division Magnoliophyta, which groups the flowering plants. All these taxonomical ranks contribute to place this species into the kingdom of Plantae, which comprises all the green plants.
Habitat and Distribution
Typical environments where Myriophyllum Hippuroides is found
The Myriophyllum Hippuroides species generally thrives in freshwater habitats. It prefers stagnant or slow-moving waters and can often be found in lakes, ponds, reservoirs, canals, or slow streams. The depth in which it grows typically ranges from shallow to deep water, anchored into the substrate with its root system.
Global distribution of this aquatic plant species
Originally native to North America, Myriophyllum Hippuroides has spread to every continent except Antarctica. It has a wide distribution across North, Central, and South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australia.
Factors influencing its distribution
Various factors such as water temperature, light conditions, nutrient availability, and human-induced spread have contributed to the broad distribution of Myriophyllum Hippuroides. The species is highly adaptive and can survive in diverse aquatic environments.
Characteristics and Identification
Physical characteristics and description of the plant
This aquatic plant has elongated, branched stems with whorls of leaves at the nodes. The leaves are finely divided and somewhat resemble the tail feathers of a bird. The dark green, feather-like leaves are usually 2-4 cm long and have up to 12 pairs of thread-like segments.
How to identify Myriophyllum Hippuroides in the wild
Myriophyllum Hippuroides can be identified by its unique leaf arrangement and node formation. Other distinctive features include emergent flower spikes and its ability to dominate the underwater environment aggressively. Sometimes, it can also be confused with other species of watermilfoil, hence a botanical expert consultation may be required for accurate identification.
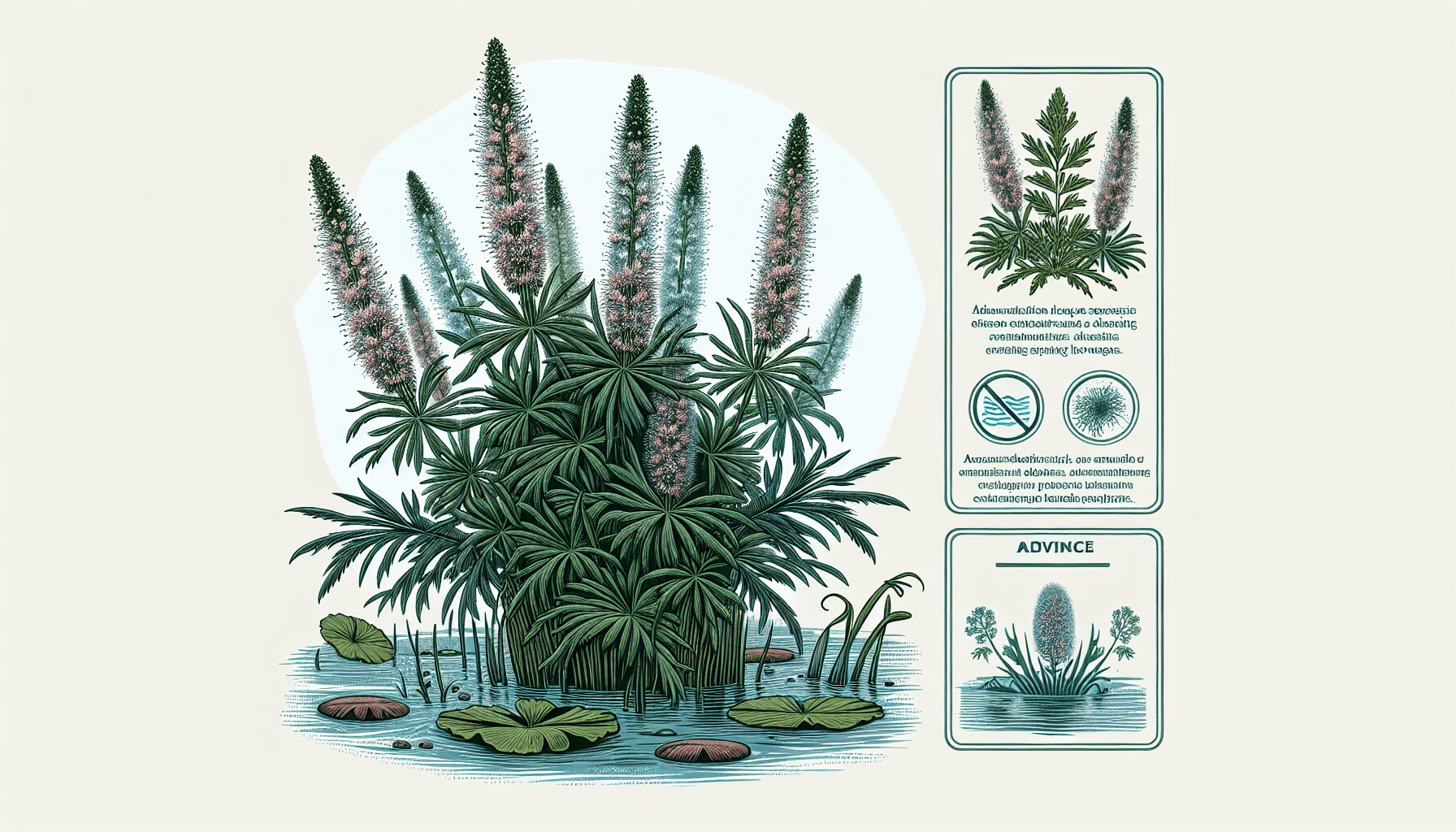
Growth Habit and Reproduction
Growth manner and lifespan of this species
Myriophyllum Hippuroides grows as a perennial plant, meaning it has a lifespan of more than two years. The stems grow out towards the water’s surface, providing ideal conditions for photosynthesis.
Reproductive methods and strategies
The species primarily reproduces vegetatively, with new plants growing from the fragments of parent plants. It can also reproduce sexually by producing flowers that emerge above the water surface and seeds, although this is less common.
Impact of environmental conditions on growth and reproduction
Environmental conditions, such as water temperature and nutrient availability, significantly affect the growth and reproduction of Myriophyllum Hippuroides. High nutrient levels and warmer temperatures typically encourage more rapid growth and proliferation.
Ecological Impact
Role of Myriophyllum Hippuroides in its ecosystem
In its native habitat, this plant plays a significant role in providing protection and food supply for various invertebrates and fish species. However, when introduced to non-native ecosystems, it can out-compete native plants and alter the stability of these habitats.
Interactions with other species
The dense growth of Myriophyllum Hippuroides can affect other plant species by reducing their light and nutrient availability. It also leads to a decrease in oxygen levels which can have detrimental effects on fish and other aquatic lifeforms.
Possible adverse effects on local ecosystems
When this species becomes prolific, it forms surface mats that prevent light penetration and impede the growth of native plant species. This phenomenon can change the physical and chemical aspects of the water body, consequently altering the entire ecosystem.
Culprit of Waterway Obstruction
How and why it obstructs waterways
Due to its rapid and dense growth, Myriophyllum Hippuroides often obstructs waterways, blocking light penetration and creating physical barriers. This growth habit hinders recreational activities such as boating, swimming, and fishing.
Impacts of waterway obstruction on human activities
Aside from limiting recreational activities, obstruction of waterways by this species can interfere with water management systems and impede water flow, which can be problematic for both residential and agricultural uses.
Control and Management
Methods available for controlling the spread of Myriophyllum Hippuroides
Several methods can be used to control the spread of Myriophyllum Hippuroides, including physical removal, chemical treatment, and biological control methods. Achieving effective control generally requires an integrated approach that combines these different methods.
Preventive measures to stop invasion by this plant species
Preventing the spread and establishing early detection measures are crucial elements in managing this species. This includes preventing the plant fragments from entering unaffected water bodies and regularly monitoring for new infestations.
Uses and Potential Benefits
Any commercial or medicinal uses of the plant
Currently, there are limited commercial or medicinal uses for Myriophyllum Hippuroides. However, its capability for phytoremediation, removing pollutants from the water, has potential for future applications.
Potential ecological benefits of Myriophyllum Hippuroides
In its native habitat, Myriophyllum Hippuroides can help to stabilize sediment and provide valuable cover for aquatic animals. Its dense growth also acts as a nutrient sink, helping to maintain water quality.
Threat to Biodiversity
Effect of Myriophyllum Hippuroides on biodiversity
Non-native populations of Myriophyllum Hippuroides can pose a significant threat to biodiversity by outcompeting native plant species and altering food chains, leading to a domino effect on the entire ecosystem.
Actions required to mitigate threats to biodiversity
To protect biodiversity, it is essential to manage the spread of this species actively. This includes implementing control measures, continuous monitoring of water bodies, and increasing public awareness about the risks associated with this plant.
Future Research Directions
Gap areas in current understanding about this species
There are some gaps in the current understanding of this species’ reproductive biology, genetic variability, and its interaction with the environment. Research is also lacking on the long-term impacts of the plant on biodiversity and ecosystem function.
Potential areas for future research
Future research can focus on developing more efficient control methods, improving understanding of the plant’s reproductive strategies and lifecycles, and investigating its potential for phytoremediation in polluted water bodies.
Implications of future findings for management of the species
Findings from these research areas can provide valuable insights to inform management strategies, possibly leading to more effective control and prevention techniques, and leveraging the plant’s potential benefits to the ecosystem.