In this in-depth exploration, you will obtain a comprehensive understanding of the aquatic weed Nasturtium Africanum. Commonly unnoticed yet significantly detrimental to freshwater habitats, this aquatic weed plays a substantial role in ecosystem health and biodiversity. Your journey through this article will enlighten you about the origin, identification, survival strategies, and impacts of Nasturtium Africanum on aquatic environments. This academic insight aims to enhance your knowledge about this often overlooked element of biodiversity and its intriguing role in aquatic ecosystems.
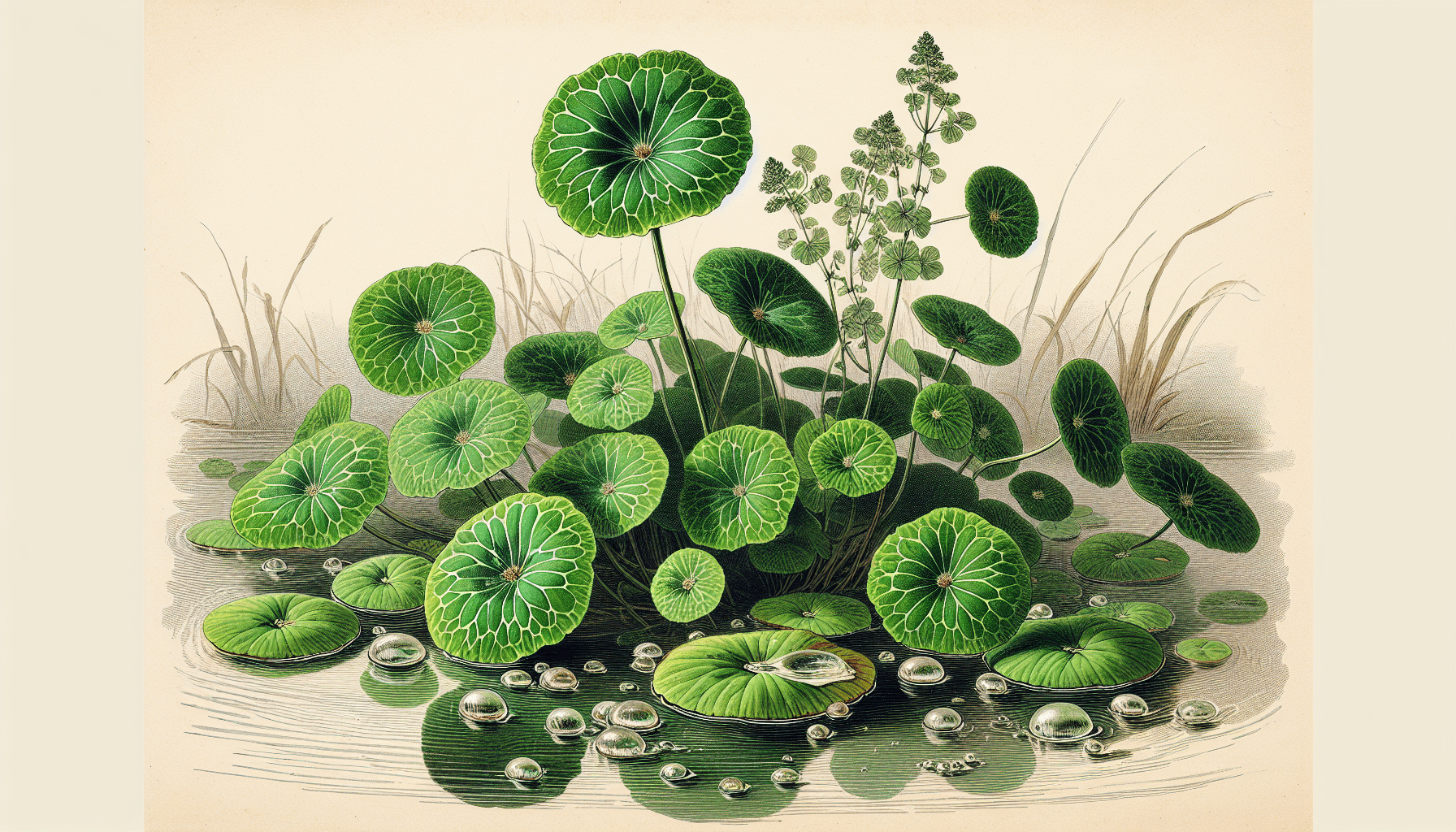
Overview of Nasturtium Africanum
Definition of Nasturtium Africanum
Nasturtium Africanum, is a specific species of aquatic plants hailing from the Brassicaceae family. Renowned for its vibrant beauty, this plant can superficially be appreciated for its aesthetic appeal. However, in the realm of flora, Nasturtium Africanum essentially dons a deceptive cloak, hiding its invasive nature that can cause significant eco-environmental harm upon its unchecked proliferation.
Native regions of Nasturtium Africanum
Your curiosity might be directed towards the origins of this aquatic species, which can be traced back to the southern regions of Africa. Predominantly known to inhabit freshwater bodies, Nasturtium Africanum has exhibited an impressive adaptability to diverse terrains and water conditions, contributing to its rapid propagation across various regions.
Common names and synonyms
The universality of Nasturtium Africanum is reflected not only in its ubiquitous presence but also in the myriad names associated with it. Depending on the locale, this aquatic weed is commonly known as watercress or African watercress, and scientifically recognised as Rorippa nasturtium-aquaticum; thus reflecting a multitude of synonyms and common names due to regional variation.
Botanical description of Nasturtium Africanum
Morphological features
One notable feature of Nasturtium Africanum is its distinct morphology. The leaves and shoots, which often float on the water surface, display a lush green hue, lending a deceptive charm to this invasive weed. The leaves are pinnately-arranged with an elliptical shape, and present a somewhat leathery texture. This plant also shows a profusion of small, white flowers, which are cross-shaped and typical of the Brassicaceae family.
Growth habits
Nasturtium Africanum showcases aggressive growth habits, capable of forming dense clusters over water bodies rapidly. It functions as a perennial in its native environment. However, its characteristic versatility has granted it the ability to thrive as an annual in colder regions.
Flowering and fruiting patterns
Particularly regarding its reproductive biology, Nasturtium Africanum exhibits flowering throughout the year in favorable conditions. The plant produces siliqua fruits, which are dehiscent and contain numerous tiny seeds.
Environmental requirements for Nasturtium Africanum Growth
Water and temperature requirements
Being an aquatic species, Nasturtium Africanum requires a freshwater habitat for its proper growth. It can survive in a wide range of temperatures, which contributes to its adaptability across different bioclimatic zones.
Light and nutrient requirements
For optimal growth, Nasturtium Africanum considerably relies on generous sunlight exposure and nutrient-rich environments, especially those abundant in nitrogen and phosphorus.
Soil or substrate preferences
Though Nasturtium Africanum prefers to root in water, it is versatile and can root in a variety of substrates, including sandy or clayey soils, provided it receives sufficient hydration.

Reproductive Strategies of Nasturtium Africanum
Sexual reproduction
Nasturtium Africanum primarily employs sexual propagation. Its self-fertilizing flowers lead to the formation of seeds, which upon maturity, are released into the surrounding environment.
Asexual reproduction
In addition to a sexual mode of reproduction, this plant can also propagate asexually through fragmentation. Any broken segments of the stem may establish a new plant, enhancing the spread of this aquatic weed.
Seed dispersal mechanisms
The seeds of Nasturtium Africanum are dispersed predominantly by water currents or can adhere to wildlife or machinery, ultimately facilitating their introduction into novel environments and imparting them with expansive coverage.
Nasturtium Africanum as an Aquatic Weed
Explanation of Nasturtium Africanum as a weed
While initially concealing its true identity with a pleasing appearance, Nasturtium Africanum reveals its invasive nature with unchecked growth and causes disruption in the ecological balance of the invaded habitat. This trait categorises it as an aquatic weed.
Problems caused by Nasturtium Africanum infestation
Uncontrolled proliferation of Nasturtium Africanum can lead to blockage of waterways, suffocation of aquatic life by restricting light penetration into the water, and alterations in the nutrient content of the habitat, posing a grave threat to the ecosystem.
Areas most affected by Nasturtium Africanum
Due to its aggressive growth and adaptability, regions across the world, particularly those with freshwater habitats, are susceptible to infestation by this weed. Its influence is notably apparent in portions of Europe, North America, and Australasia.
Identifying Nasturtium Africanum
Key features for identification
The distinct leaves, small white flowers, and floating stems are key features to identify Nasturtium Africanum. Once established, its propensity to form dense mats on water surfaces further points to its identification.
Similar species and differences
Nasturtium Africanum can be confused with other members of the Brassicaceae family, although its floating leaves and white flowers predominantly favour its identification.
Where it is most likely to be found
Given its environmental requirements, Nasturtium Africanum is most likely to be found in freshwater habitats such as ponds, rivers, and damp soil areas alongside water bodies.
Economic and Ecological impact of Nasturtium Africanum
Impact on local flora and fauna
The unchecked growth of Nasturtium Africanum can negatively impact local biota by outcompeting native species for resources, thereby disrupting local biodiversity.
Effects on fishing and other water-based industries
An infestation of Nasturtium Africanum can cause significant disruption to fishing industries and aquatic transportation by blocking waterways, thereby incurring considerable economic losses.
Impact on water quality and supply
By altering nutrient compositions and cluttering water bodies, Nasturtium Africanum poses a significant threat to water quality and can disrupt the supply of clean water.
Current methods of controlling Nasturtium Africanum
Chemical control methods
One popular method to mitigate the spread of Nasturtium Africanum is the use of selective herbicides considered safe for use in water environments. However, the consequences of chemical pollutants should also be considered.
Physical removal methods
The physical extraction of Nasturtium Africanum can mitigate its spread, although it is labor-intensive. Manual removal, however, can prevent the additional release of seeds or fragments during the removal process that can potentially exacerbate the infestation.
Biological control methods
Research is ongoing on the possible use of biological control agents like insects or fungi that can specifically target Nasturtium Africanum without adversely affecting other flora or fauna.
Research on Nasturtium Africanum
Existing academic studies
Numerous studies have investigated the biology, ecology, and management of Nasturtium Africanum, providing a foundation of understanding about this invasive weed.
Current research gaps
Despite extensive research, more work needs to be done to understand the long-term ecological impacts of this weed and to identify effective, sustainable, and environmentally friendly solutions for its control.
Potential future directions
Future research themes could focus on eco-friendly biological control agents, potential uses of Nasturtium Africanum, and further understanding its dynamics and interaction with the environment.
Public awareness and education about Nasturtium Africanum
Current level of public awareness
Currently, the public awareness of Nasturtium Africanum is variable, depending on the region and the extent of its infestation.
Educational programs in place
Several regions affected by Nasturtium Africanum have initiated educational programs to facilitate its identification, understand its impact, and promote effective management practices.
How individuals can help prevent its spread
Public cooperation is integral in preventing the spread of this invasive species. Individuals are encouraged to report sightings, ensure cleanliness of water equipment, and avoid the intentional growth or movement of Nasturtium Africanum.