As you embark on a journey through the realm of aquatic vegetation, one species that may pique your curiosity is Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis, often referred to as an aquatic weed. Found predominantly in warm, tropical climates, this particular type of water lily has numerous complexities and traits that set it apart in the aquatic world. In this article, the aim is to shed light on the physiology, growth habits, uses, and challenges surrounding the propagation and management of this intriguing plant species. Embrace this opportunity to expand your botanical knowledge and discover the fascinating world of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis.

Botanical Description of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis
General Description
Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis, more commonly known as aquatic weeds, is considered a perennial, herbaceous aquatic plant. Belonging to the Nymphaeaceae family, this plant is predominantly recognized for its spectacular purple, red or blue flowers that float above the water’s surface, adding to the natural and aesthetic mystique found within the aquatic biosphere.
Leaf Characteristics
Its leaves, termed as lily pads, are typically round, veined, flat and feature pronounced notches which are deeply divided, protruding towards the leaf stalk or petiole. The upper side of the leaves is intensely green while the underside is reddish or purplish. Like most water lilies, the leaves of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis float on the surface of the water, forming a dense layer that serves an ecological function as well as an aesthetic one.
Floral Characteristics
The truly star features of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis are its strikingly beautiful flowers that bloom above the water surface. Full and vibrant, the flowers open during the day, displaying four to five sepals and numerous petals often with a violet or bluish hue. The stamens are vibrant yellow, adding to its visual appeal.
Geographical Distribution of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis
Native Regions
Originally, Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis originated in the freshwater habitats of East Africa and Southeast Asia. However, due to its hardiness and adaptability, it has spread to other parts of the world.
Current Global Spread
Today, it can be found in water bodies across numerous global regions. Notwithstanding, it is particularly prevalent in subtropical and temperate regions where the aquatic ecosystems provide optimal growing conditions.
The Ecosystem of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis
Natural Habitat
Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis thrives in a wide range of freshwater environments including ponds, lakes, marshes, and slow-moving rivers. These water bodies often provide the still or slow-moving water preferred by the plant, along with a wealth of nutrients available in the sediment.
Role in the Ecosystem
Due to its dense foliage, Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis provides shade, shelter, and food for numerous fishes, insects, and amphibians. Its lily pads are often utilized as a spawning ground for certain species of fish, while the plant’s root systems serve to stabilize the water body’s sediment, reducing erosion.
Interactions with Other Species
The leaves, flowers, and seeds of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis attract a variety of water-dependent and terrestrial wildlife, including bees and butterflies which aid in the plants’ pollination process. However, its rapid growth and spread can displace native plant species and disrupt the balance of the ecosystem.
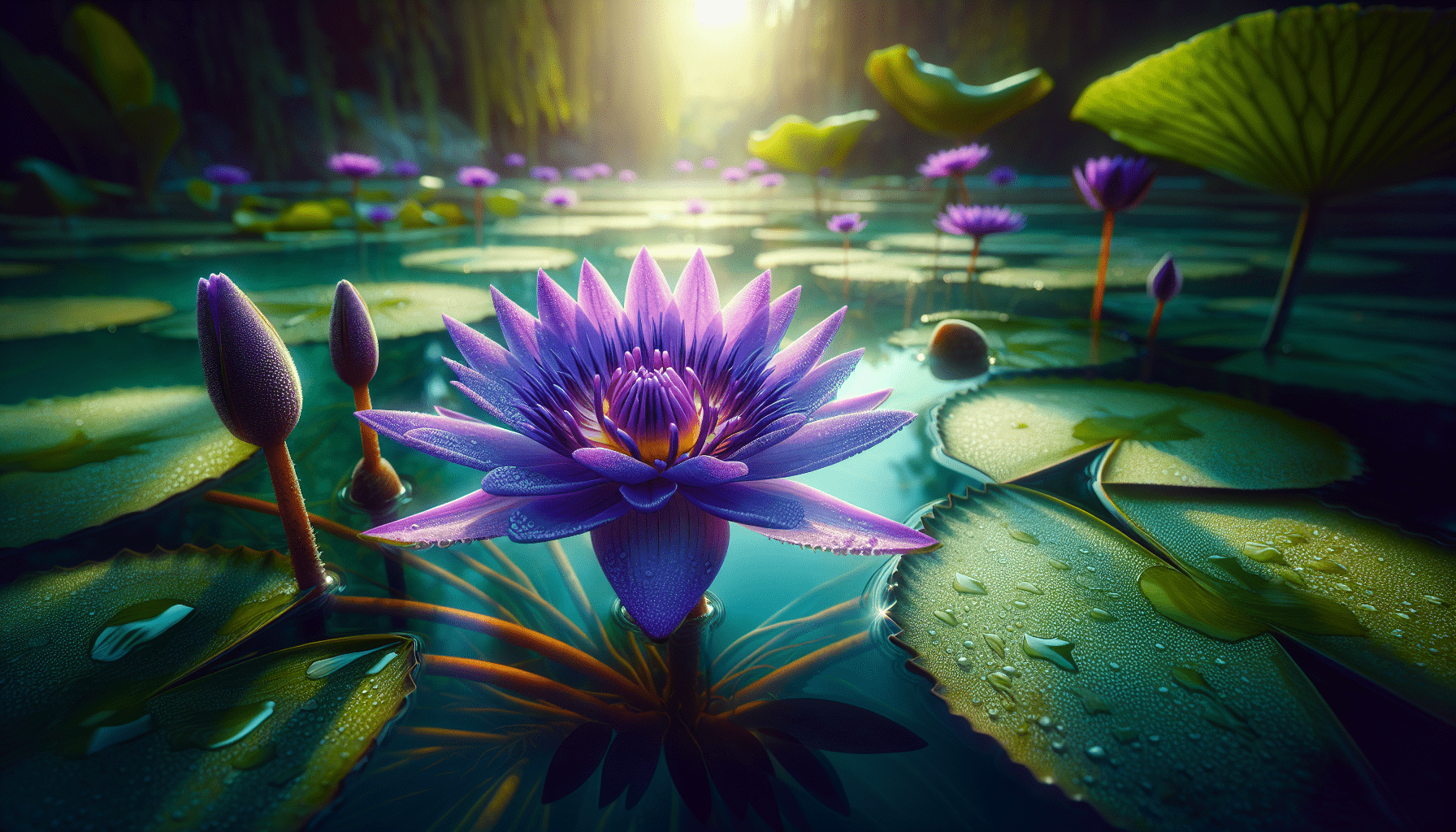
Reproduction and Growth of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis
Reproductive Cycle
Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis reproduces both vegetatively and sexually. The flowers are insect-pollinated, leading to the production of seeds. Vegetative reproduction occurs through the growth and split of rhizomes present in the sediment.
Growth Patterns
Depending on the appropriate favorable conditions, this aquatic plant can grow rapidly and cover extensive areas of water bodies. Its growth is typically seasonal, and the plant can proliferate at a fast rate during warmer months.
Adaptations for Survival
Its favorable characteristic of tolerance to a wide range of climatic conditions and water depths allows Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis to thrive in various habitats. Further, its production of protective tubers also enables it to survive unfavorable periods and regrow when conditions become suitable.
Cultivation of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis
Cultivation Conditions
Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis grows well in locations with full sunlight to partial shade. It prefers nutrient-rich, loamy sediment, and its ideal water depth is 30-60 centimeters, although it can tolerate deeper waters.
Propagation Techniques
Propagation is primarily achieved through the division of rhizomes or the planting of seeds. Seeds should be sown in wet soil and subsequently covered with water once germination has occurred. Rhizomes are divided in the spring.
Potential Challenges in Cultivation
While Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis is relatively easy to cultivate, issues can arise. These include a susceptibility to water lilies leaf beetle which can damage the foliage, potentially inhibiting growth.
Characteristics That Make Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis a Weed
Rapid Growth and Spread
While its ability to quickly cover a large water surface is lovely from an aesthetic viewpoint, it’s this very ability that can quickly transform Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis into an invasive liability, especially when it’s growing in environments where it has no natural predators.
Adaptation to Diverse Conditions
Its ability to adapt to a diverse range of conditions- be it climate, water depth or nutrient availability, aids in its proliferative potential.
Impacts on Aquatic Ecosystem
Aside from the chokehold it can have on other plant life, Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis’s dense surface growth can restrict sunlight penetration into the water, impacting aquatic organisms. It can also affect water quality and flow.
Benefits and Uses of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis
Ornamental Uses
Due to its stunning flowers and attractive foliage, Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis is a desirable plant for water gardening and landscape beautification in ponds and lakes.
Medicinal Uses
In various traditional medicinal systems, multiple parts of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis have been used to treat ailments such as dyspepsia, diarrhea, and other conditions. However, more scientific research is required to verify these uses.
Potential Uses in Research
In addition to its aesthetic and potential medical value, the species may serve a role in scientific research, particularly in studies regarding aquatic plant physiology, aquatic ecosystem dynamics, and the effects of invasive species on native biodiversity.
Management and Control of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis
Preventive Measures
Such measures may include careful monitoring of public and private water bodies, particularly those used for recreational activities, as well as the regulation of plant trade and transport to prevent its accidental introduction to new areas.
Manual and Mechanical Control
These methods involve physically removing the plants from the water bodies. However, due to the capacity of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis to reproduce from small fragments, manual removal can often further spread the plant if not carried out correctly.
Chemical Control
Herbicides can be an effective deterrent but they can have potential toxic effects on the rest of the flora and fauna in the ecosystem. Therefore, the use of herbicides should only be adopted where other methods have failed.
Biological Control
This involves introducing a natural enemy of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis into its habitat. However, this method should be used with caution to avoid imbalances in the ecosystem.
Climate Change Impacts on Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis
Potential Impacts of Rising Temperatures
Rising temperatures might favor Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis as it could promote faster growth rates and longer growing seasons. However, high temperature extremes could potentially disrupt this plant’s life cycle.
Impacts of Altered Precipitation Patterns
Altered precipitation patterns, particularly heavy periods of rainfall or prolonged drought, may significantly impact the habitats of Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis.
Future Research Directions on Nymphaea Nouchali Var. Zanzibariensis
Unexplored Aspects of its Biology
For future study, more knowledge needs to be garnered about its biological attributes that enable it to become invasive. Understanding these adaptations can help in the control and management of this plant.
Potential for Development as an Ornamental Plant
Extensive research into its use as ornamental plants can be beneficial, given its impressive aesthetics. This line of research may contribute to the horticulture industry.
Need for New Control Measures
There is a necessity for more research into developing safe control measures. While existing methods are somewhat effective, there is a need for ecologically sound and cost-effective strategies to manage this invasive species.