Embarking on a journey to understand the realm of aquatic botany, your attention is brought to a specific plant that has intrigued both scientists and horticultural enthusiasts alike. The focus of this enriching article is to shed light on a different breed of an aquatic weed, termed Nymphoides Peltata or commonly known as Floating Heart. An exploration of its origin, biological structure, growth patterns, impact on aquatic ecosystems and its role in home aquariums are meticulously explained to offer you a comprehensive understanding of this unique aquatic weed. Balancing scientific accuracy with readability, this article aims to refine your knowledge base in this specialized botanical field, while stirring your curiosity about the fascinating world of aquatic vegetation.
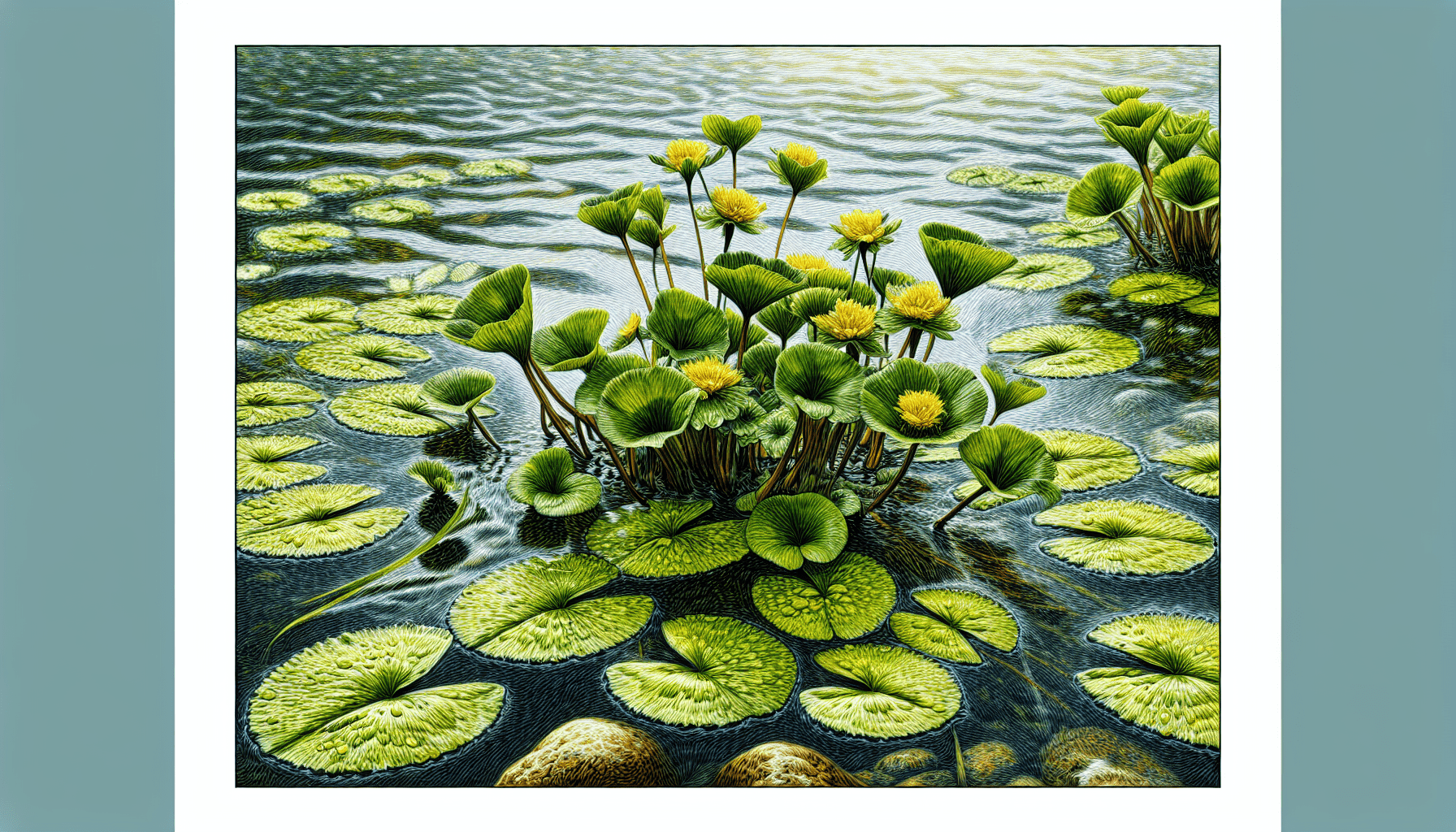

Basic Description of Nymphoides Peltata
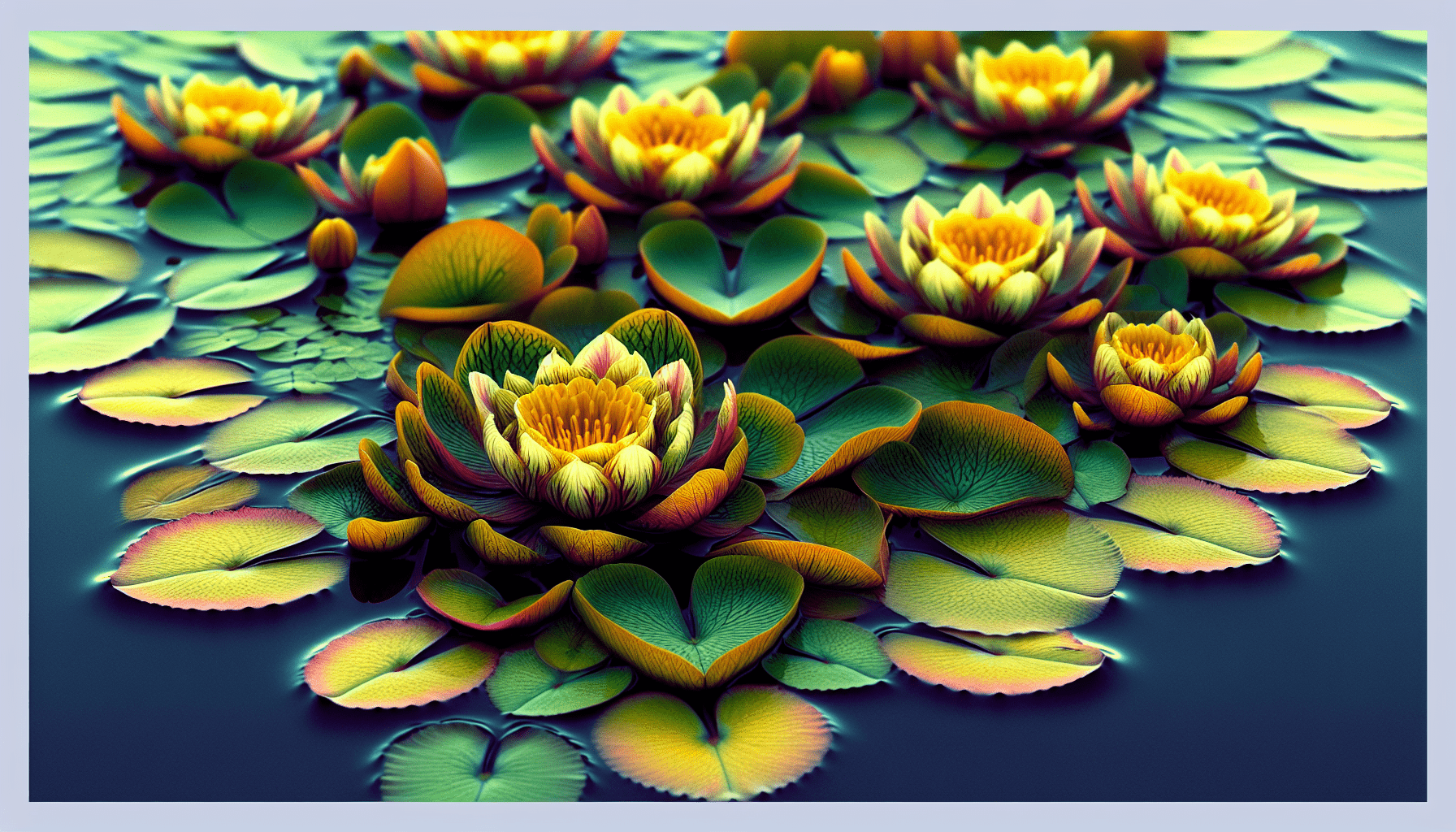
Nymphoides peltata, colloquially known as the floating heart, is quite a unique aquatic plant. It belongs to the family Menyanthaceae and is exemplary for its fascinating biological and ecological traits. This semi-evergreen perennial weed may appear harmless, but its pervasive nature allows it to become invasive over time.
Physical Characteristics of the Weed
The physical features of Nymphoides peltata are distinctive and relatively easy to recognize. You’ll find the leaves of this weed to be heart-shaped and initially borne on long stalks under the water. As the weed matures, the leaves float on the water surface. Fragrant, five-petalled yellow flowers adorn the weed in summer, appearing to float atop the water, lending this aquatic plant one of its common names, ‘Floating Heart’. The weed also has a rhizomatous root system which enables it to grow rapidly in favourable conditions.
Common Names of Nymphoides Peltata
Nymphoides peltata is known by various names across different regions. Besides Floating Heart, it is also commonly known as Fringed Water Lily, Yellow Floating Heart, Water Fringe, and Entire Marshwort. Each of these names often describes an observable characteristic or behavior of the plant.
Regions Where Nymphoides Peltata is Found
Historically, Nymphoides peltata is native to parts of Europe and Asia, including the UK, Ireland, Central Asia, Siberia, and the Indian Subcontinent. Nevertheless, the weed has spread and been introduced to various other regions. It is now found in North America, New Zealand, and Australia, often becoming invasive in these regions.
Ecological Role of Nymphoides Peltata
The ecological role of Nymphoides peltata is manifold, interacting and influencing its surrounding aquatic environment in various ways.
Contribution to Aquatic Ecosystems
As an aquatic perennial, Nymphoides peltata contributes significantly to the biological productivity of its habitat. Its extensive root and rhizome system provides a sheltering and breeding ground for several smaller aquatic animals. It also reduces water speed, which can reduce erosion and sediment disturbance.
Interaction with Aquatic Organisms
Several aquatic creatures interact with Nymphoides peltata. Aquatic insects are attracted to its blossoms and nectar, while small fish and amphibians often find shelter beneath the foliage. Ducks and other water birds feed on the seeds, thus aiding in the plant’s dispersion.
Role in Nutrient Cycling
Nymphoides peltata plays a vital role in nutrient cycling within aquatic ecosystems. The plant absorbs nutrients from the water for its growth, acting as a biofilter. Upon decomposition, these nutrients are released back into the aquatic system, supporting nutrient-rich water bodies’ overall productivity.
Reproductive Strategies of Nymphoides Peltata
Reproduction in Nymphoides peltata happens through various strategies, ensuring its widespread dispersion and survival.
Flowering and Seed Production
The flowering period extends from June to September, during which the plant produces small yellow flowers. Following pollination, these flowers eventually lead to seed production. The seeds are buoyant and can float on water aiding their dispersion over a broader area.
Clonal Reproduction Methods
Apart from sexual reproduction, Nymphoides peltata also employs vegetative or clonal reproduction. This typically involves the formation of new plants from existing plant parts like roots, stems, or leaves. This method can result in dense infestations and rapid spread of the weed, particularly in favorable conditions.
Dispersion of Seeds
The seeds of Nymphoides peltata, as mentioned before, are buoyant and can be carried by water currents over large distances. Further, water birds that feed on the seeds contribute significantly to the seed dispersion, carrying these seeds to different water bodies.
Human Uses of Nymphoides Peltata
Despite its potential invasiveness, Nymphoides peltata has been utilized by humans in various ways.
Use in Traditional Medicine
Historically, different parts of Nymphoides peltata have been used for medicinal purposes, particularly in Asia. The plant is known for its anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, and cicatrizing (wound healing) properties. The leaves are often used to treat eye disorders, while the root is known to possess diuretic properties.
Roles in Aquascaping and Aquariums
The aesthetic appeal of Nymphoides peltata, particularly its floating heart-shaped leaves and bright yellow flowers, has made it a popular choice for ornamental uses in water gardens, ponds, and aquariums. However, its invasive characteristics demand that its growth is cautiously managed in such settings.
Culinary Uses in Certain Regions
In some parts of East Asia and particularly in China, Nymphoides peltata has culinary uses. The young leaves, shoots, and flower buds are edible and are often used in salads and stir-fries. Despite these uses, it is advisable to consider the weed’s potential toxicity before consuming.
The Impact of Nymphoides Peltata on Biodiversity
The Biodiversity implications of Nymphoides peltata are mixed, providing both benefits and detrimental effects.
Effects on Native Species
If not managed well, the rapid spread of Nymphoides peltata can lead to local native species being outcompeted for resources. This can result in a decrease in biodiversity and the potential loss of native species.
Production of Aquatic Habitats
On the other hand, the aquatic habitats created by Nymphoides peltata can enhance local biodiversity by providing habitats for various aquatic organisms. The dense growth of plants provides nesting sites for birds and shelter for fish and invertebrates.
Changes in Water Chemistry
Nymphoides peltata can modify the surrounding water chemistry. The dense growth of these plants can lead to a decrease in dissolved oxygen levels in the water, which might adversely affect other water-dwelling species.
Threats and Challenges Posed by Nymphoides Peltata
The primary threats posed by Nymphoides peltata involve its invasive behavior, which may adversely affect both ecosystems and human activities.
Invasion into Non-Native Habitats
Nymphoides peltata has been known to invade non-native habitats, where it can grow and spread quickly due to the lack of natural predators or control mechanisms. This can lead to a significant alteration of the local ecosystems.
Impact on Human Activities like Fishing and Boating
The aggressive growth of Nymphoides peltata often leads to the formation of dense mats on the surface of water bodies. This can impair recreational and commercial activities such as boating and fishing. It also raises the cost of water treatment processes.
Potential Harm to Local Biodiversity
As Nymphoides peltata can potentially outcompete native species, it poses a direct threat to local biodiversity. This plant’s unchecked expansion can lead to a dominance shift from a diverse ecosystem to a monoculture, with negative effects on ecosystem services.
Management and Control of Nymphoides Peltata
Given the challenges posed by Nymphoides peltata, various management and control strategies can be employed.
Mechanical Removal Methods
Mechanical removal of the weed involves physically extracting the plant from the water body. This can be done manually or using machines and is generally the most efficient method to manage small infestations.
Chemical Control Methods
Chemical control mainly involves the use of herbicides to kill the weed. While effective, these methods must be used sparingly, as excessive use could harm non-target species and the water’s overall chemistry.
Biological Control Through the Use of Insects
Biological control is an innovative method where natural enemies of the weed, mostly insects, are introduced to control the weed’s population. This is considered a more sustainable and eco-friendly method but must be carefully administered to prevent unplanned disruptions of the ecosystem.
Studies and Research on Nymphoides Peltata
Ongoing research and studies on Nymphoides peltata have provided crucial insights into its biology and ecology, contributing to the development of control and management strategies.
Current Studies on Growth and Reproduction
There is ongoing research into understanding the conditions that promote the growth and reproduction of Nymphoides peltata. These studies are crucial for predictively managing and controlling its spread in various regions.
Research on Control Methods
Simultaneously, research is being undertaken to develop efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly methods to control Nymphoides peltata. These range from improved mechanical and chemical methods to more eco-friendly biological control methods.
Future Potential Medicinal Uses
There is potential for future research into the medicinal uses of Nymphoides peltata. Despite its known use in Traditional Medicine, there is plenty to learn about the plant’s possible pharmaceutical applications, particularly in the context of modern medicine.
Cultural Significance of Nymphoides Peltata
Despite being a weed, Nymphoides peltata holds certain cultural significance in some regions.
Roles in Folklore and Mythology
In some cultures, folklore and mythology often incorporate elements of the natural world, including a variety of plants, and Nymphoides peltata is no exception. In particular, east Asian cultures have often associated the plant with certain mythical entities or symbolisms lending it cultural importance.
Significance in Art and Literature
The picturesque charm of Nymphoides peltata has been the muse of several artists who incorporated its image into their artworks. Plus, the plant has found its way into literature, primarily through poetry and prose, often used to symbolize beauty and purity.
Symbolism Associated with the Weed
In various cultures, Nymphoides peltata is seen as a symbol of light, purity, and transcendence. The floating, luminescent qualities of the flowers are often associated with these symbolisms.
Potential Future Impact of Nymphoides Peltata
Looking forward, Nymphoides peltata might continue to have significant impacts, some of which can already be foreseen.
Expected Changes in Distribution Due to Climate Change
Climate change and global warming can potentially alter the distribution and spread of Nymphoides peltata. Rising temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns could create new habitats for the weed, posing additional challenges for its management.
Future Threats to Biodiversity
With expanding distribution, there is a growing concern about the future threats posed by Nymphoides peltata to biodiversity. The risk of local extinction of native species might increase further due to the competitive advantage provided to this weed by climate changes.
Potential Economic Impacts
There are potential economic impacts too. Rising costs of control and management, potential reduction in recreational and commercial river-based activities, and impacts on water treatment processes are some likely economic consequences. Thus, effective management is crucial to mitigate the future environmental and economic impacts of this plant.