An exploration of the aquatic weed Nymphoides spinulosperma awaits you. Found predominantly in water bodies across Australia, this specific flora species has adapted to survive and thrive in watery ecosystems. You shall glean an understanding of its distinctive biological characteristics, its relevance in the ecological balance, and how it has been viewed as both a valuable asset and a potential menace in its natural habitat. This informed tour compels you to appreciate the complex world of aquatic flora and, more specifically, provides valuable insights into the existence and vigor of Nymphoides spinulosperma.
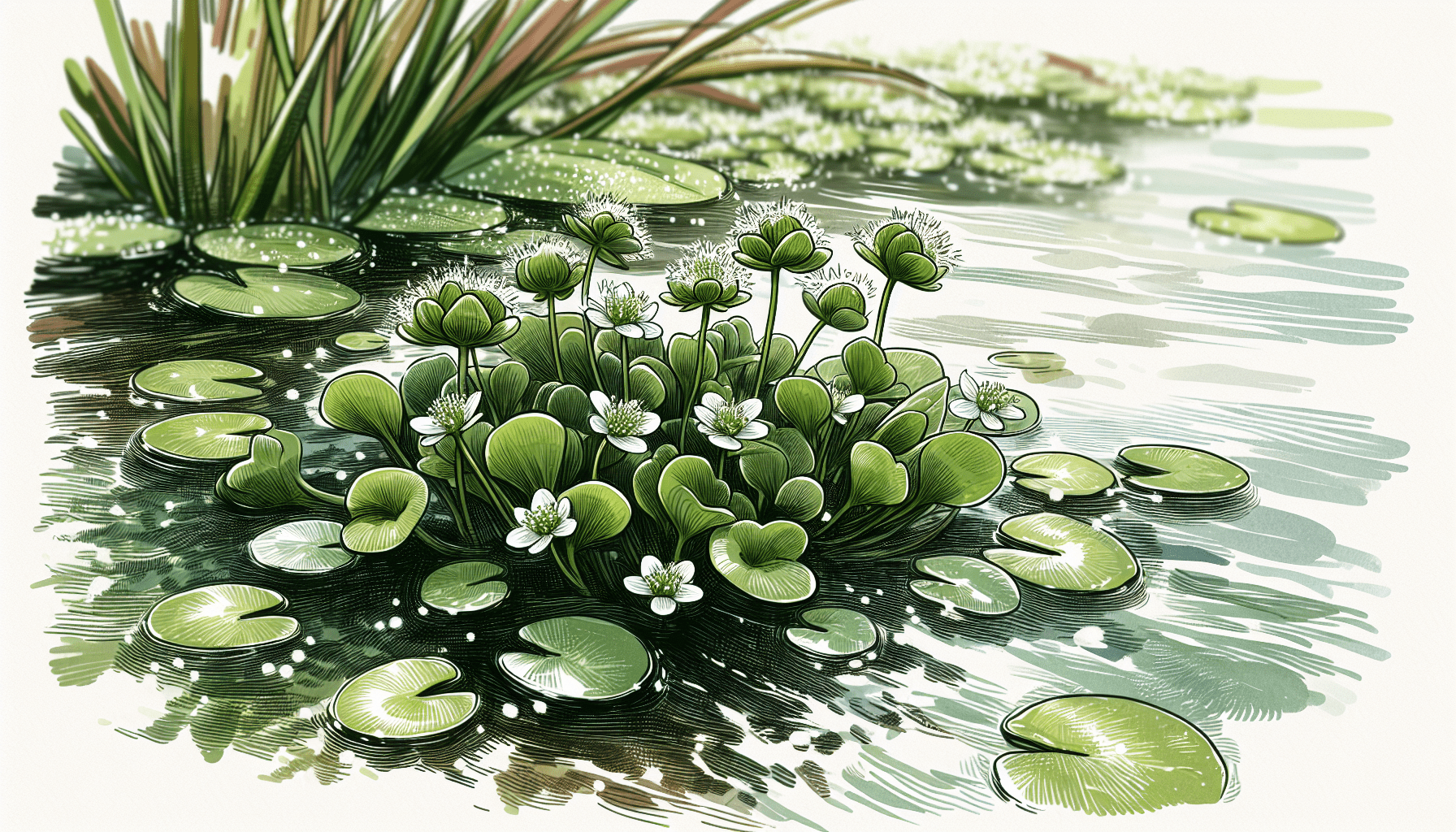
Definition of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Nymphoides Spinulosperma, is a distinctive species of aquatic plant belonging to the family Menyanthaceae. This moist terrestrial or aquatic herb is typically found in still or slow-moving waters such as ponds, ditches, swamps, and river’s edges. It is known for its highly specific morphological, physiological, and ecological characteristics which contribute to both its survival and reproduction in its preferred habitats.
Scientific classification of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
In scientific taxonomy, Nymphoides Spinulosperma is categorized under the kingdom of Plantae, in the order of Asterales, within the family Menyanthaceae. The genus Nymphoides encompasses numerous aquatic species, of which Nymphoides Spinulosperma is one member.
Common names for Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Aside from its scientific name, Nymphoides Spinulosperma is known by a variety of common names. These include “warty fringed water-lily,” “warty marshwort,” or simply “fringed water-lily” in reference to its unique appearance and preferred aquatic environments.
Description of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Nymphoides Spinulosperma is known for its floating leaves and solitary bright yellow flowers, which imbue it with a lily-like appearance. The leaves are heart-shaped and float on the surface, while the small yet distinctly warty seeds sit beneath. The flowers, dominant during summer and early autumn, are characterized by their fringed margins.
Habitat and Distribution
Typical habitats of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Nymphoides Spinulosperma thrives in shallow, still, or slow-moving water sources such as wetlands, marshes, ponds, and swamps. It prefers waters with ample organic deposits, silts, and sands where it can root itself while leaving its leaves and flowers to float on the surface.
Geographical distribution of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Geographically, Nymphoides Spinulosperma is characteristic of Eastern Australia, specifically the states of New South Wales, Victoria, and Tasmania.
Climatic conditions for the growth of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Nymphoides Spinulosperma is a follower of mild and temperate climates, favoring conservatively cool to warm weather conditions. As an aquatic herb, it requires environments with consistent and abundant sources of water.
Growth and Life Cycle
Growth characteristics of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
The growth characteristics of Nymphoides Spinulosperma are linked closely to its seasonal life cycle. It demonstrates rapid vegetative growth, with extensive leaf and flower production during warmer months. Conversely, during cooler months, the plant enters a state of rest and conserves its energy for the next growth period.
Stages in the life cycle of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
The life cycle of Nymphoides Spinulosperma begins with the germination of seeds embedded in the water’s sediments. After germination, the young plant develops a floating leaf rosette and a root system that anchors it to the soil. As the plant matures, it produces distinct yellow flowers, which upon pollination, produce warty seeds. These seeds fall into the water and settle into the sediment, ready to germinate when conditions favor.
Seasonal changes in Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Among notable seasonal changes in Nymphoides Spinulosperma are the visible fluctuations in leaf and flower production. The plant actively grows and reproduces during the warmer months of summer and early autumn, displaying numerous floating leaves and attractive yellow flowers. As the temperature drops in late autumn and through winter, Nymphoides Spinulosperma slows its growth and enters a state of dormancy.
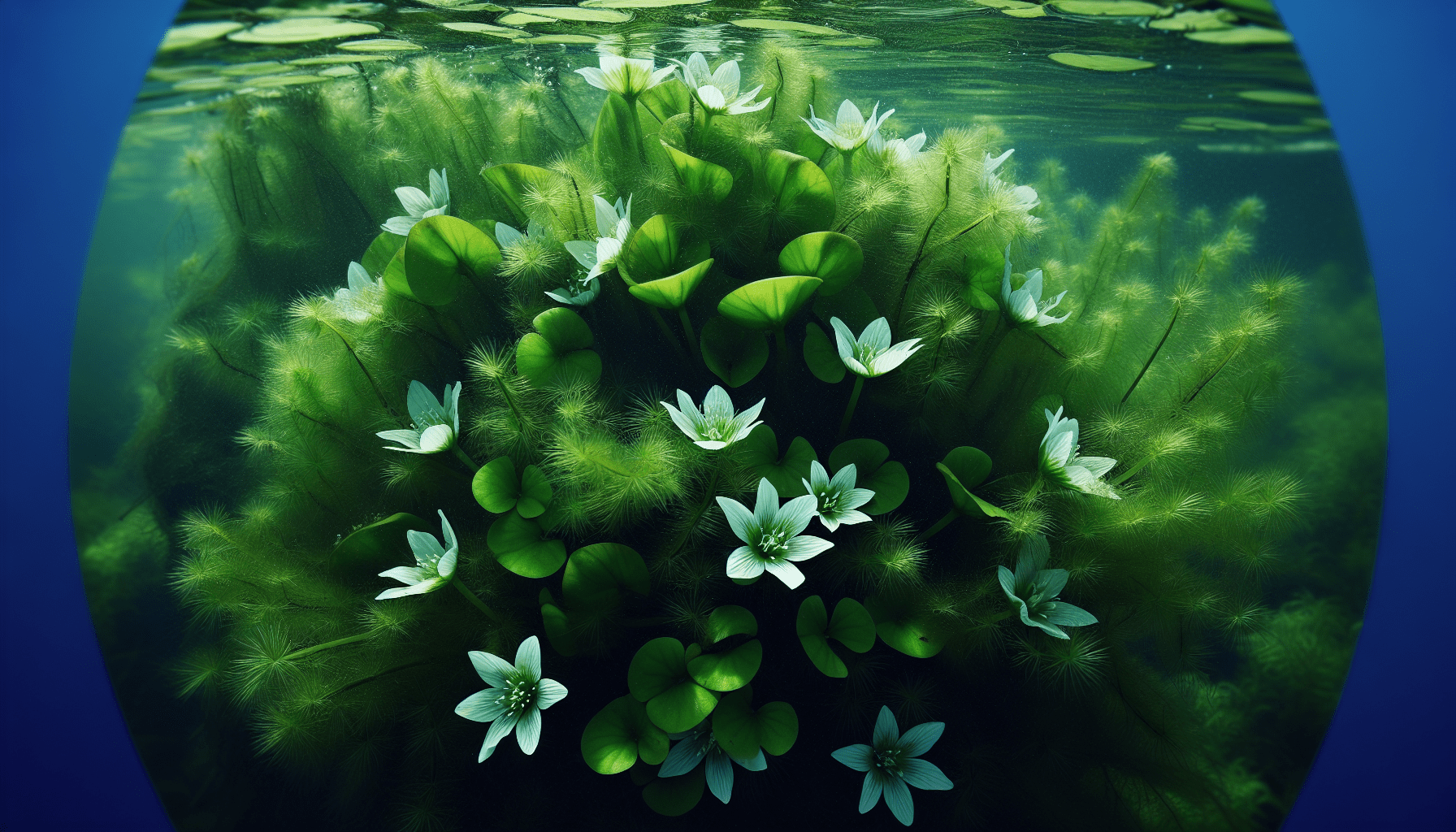

Morphological Characteristics
Leaf structure and arrangement in Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Nymphoides Spinulosperma has heart-shaped leaves that float on the water surface. These leaves are typically arranged in a rosette pattern, emanating from a central point on the surface of the water.
Flowers of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
The flowers of Nymphoides Spinulosperma, which appear during summer and early autumn, are bright yellow and typically have five fringed petals. These fringed flowers—another reason for the plant’s common name—sit above the water surface and act as a key means through which the species reproduces.
Stem and root system of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Nymphoides Spinulosperma possesses a robust root system that anchors the plant to the sediment of its aquatic environment. The stems of this plant are generally rhizomatous, meaning they grow horizontally underwater, sending out roots and leaves from their nodes.
Physiological Characteristics
Photosynthetic activity in Nymphoides Spinulosperma
As an aquatic plant, Nymphoides Spinulosperma is fully capable of photosynthesis. Its floating leaves contain chlorophyll—the green pigment responsible for trapping sunlight—and use this energy to convert water from their aquatic environment and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into glucose and oxygen.
Adaptive features of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
One of the primary adaptive features of Nymphoides Spinulosperma is its ability to maintain its leaves and flowers above the water surface, thereby making photosynthesis possible. Another adaptation includes the possession of small, warty seeds which are ideally designed to settle into aquatic sediments and germinate.
Reproductive mechanisms of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Reproduction in Nymphoides Spinulosperma is primarily through seeds and secondarily through the fragmentation of their stems. During the flowering season, the plant’s yellow, fringed flowers undergo pollination, resulting in seed production. These seeds eventually sink into the water sediments and germinate when conditions are optimal. Furthermore, portions of the plant’s stems can break off and float away, eventually growing into a new plant in a process known as vegetative propagation.
Ecological Role
Interactions with other aquatic organisms
Nymphoides Spinulosperma shares a symbiotic relationship with other aquatic organisms. Its leaves provide shelter and reproductive sites for small invertebrates and fish, which, in turn, help the plant by providing necessary nutrients from their waste.
Role in nutrient cycling in aquatic ecosystems
Because of its substantial biomass, Nymphoides Spinulosperma contributes significantly to nutrient cycling within its aquatic ecosystems. Upon the decay of its tissues, it contributes organic matter to the water body—matter that is subsequently decomposed by microbes to dietary components for other aquatic organisms.
Impacts on water quality and clarity
Nymphoides Spinulosperma serves an essential role in improving water quality and clarity. Through its photosynthetic activity, it oxygenates the water and helps in balancing the ecosystem’s pH. Moreover, its large biomass helps to reduce turbidity by preventing soil erosion and by absorbing nutrients that would otherwise contribute to unwanted algal growth.
Uses and Benefits
Uses in traditional medicine
While Nymphoides Spinulosperma’s use in traditional medicine is not extensively documented, other Nymphoides species have been used in remedies for ailments like fever, hydrophobia, coughs, asthma, and liver diseases. Understanding the medical properties of this species might prove fruitful for similar future uses.
Other uses of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Nymphoides Spinulosperma presents potential use in the reclamation and rehabilitation of wetland ecosystems because it is adaptive and grows vigorously. Its attractive yellow, fringed flowers are also proving popular in ornamental water gardens and for flower arrangements.
Potential benefits of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Being native to Australia, Nymphoides Spinulosperma is a critical part of the ecosystem and contributes to biodiversity. Additionally, it is beneficial for balancing the ecosystem’s nutrient cycling and maintaining water clarity, and oxygen levels. Lastly, its potential uses in medicine, reclamation efforts, and ornamental gardening represent added benefits that further enhance its positive impacts.
Hazards and Management
Hazards associated with Nymphoides Spinulosperma
While Nymphoides Spinulosperma is beneficial within its native range, it can become an invasive species if introduced into non-native waters. Its fast growth and reproductive rate may lead to dense populations that outcompete native flora and hinder water flow.
Strategies for managing Nymphoides Spinulosperma infestations
Managing Nymphoides Spinulosperma infestations requires limiting its spread by removing existing plants and monitoring waters for new populations. Proper disposal of the plant material is also crucial to prevent unintentional introductions into new locations.
Legislation and regulations pertaining to Nymphoides Spinulosperma
There are currently no specific legislations or regulations pertaining to Nymphoides Spinulosperma. However, general environmental laws apply, including those protecting native species and habitats and controlling the introduction and spread of invasive species.
Research and Studies
Recent scientific research on Nymphoides Spinulosperma
While there is ongoing research into the ecological role, physiology, and potential uses of Nymphoides Spinulosperma, much remains to be learned about this unique species.
Knowledge gaps and future research directions
Current knowledge gaps regarding Nymphoides Spinulosperma include its specific physiological processes, in-depth habitat preferences, interactions with other species, and the precise mechanisms and effects of its potential invasiveness. Future research should focus on these areas to further our understanding and enable us to utilize this species more sustainably and beneficially.
Conservation and Threats
Conservation status of Nymphoides Spinulosperma
As of now, the conservation status of Nymphoides Spinulosperma has not been formally assessed. However, as a native species of Australia, its conservation is crucial for the preservation of local biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Threats and challenges to Nymphoides Spinulosperma populations
Threats to Nymphoides Spinulosperma populations include habitat loss and degradation, pollution, and non-native invasive species which could outcompete it for resources. Additionally, the potential for Nymphoides Spinulosperma to become invasive in non-native waters also threatens its standing within its original habitats.
Measures to protect and conserve Nymphoides Spinulosperma
Protecting and conserving Nymphoides Spinulosperma involve maintaining the quality and integrity of its natural habitats, controlling pollution, and regulating the introduction of potential competitor species. Furthermore, responsible human conduct that reduces the inadvertent spread of Nymphoides Spinulosperma to non-native waters is also a critical preventative measure in conserving this species.