In the realm of aquatic plant life, Nyssa Aquatica stands unique. Although referred to colloquially as an ‘aquatic weed,’ this plant is far from an unwanted nuisance. It forms an integral part of wetland ecosystems, exhibiting a fascinating life cycle and survival strategies that set it apart from its counterparts. This article seeks to familiarize you with the distinctive nature of Nyssa Aquatica, presenting a comprehensive study into its physiology, habituation patterns, and role in maintaining the delicate balance of aquatic biotopes. Harness your curiosity and prepare to explore the intriguing world of this aquatic ‘weed,’ a term we shall come to question in the following discourse.

Overview of Nyssa Aquatica
Nyssa Aquatica, often referred to as the Tupelo or Water Tupelo, is a type of deciduous tree native to the southeastern United States. It is notably an aquatic plant, and is well-adapted to environments with high levels of water. Despite being revered for its robust nature and multitude of uses, it has earned a reputation as an invasive aquatic weed in some localities.
Primary Characteristics of Nyssa Aquatica
The primary distinguishing features of Nyssa Aquatica involve its tall growth, distinct elongated leaves, and its tendency to thrive in water-saturated environments. It is a hardy tree, requiring minimal maintenance in suitable conditions and is in fact, known for its resilience in water-logged areas where other species may struggle to survive.
Distribution and Habitat
The habitat of Nyssa Aquatica is primarily concentrated within the southeastern regions of the United States, spanning across states such as Florida, Texas, and Missouri. This tree prefers marshy, waterlogged areas, often found growing alongside streams, rivers, or in swamps, making it a crucial component of wetland ecosystems.
Aquatic Nature
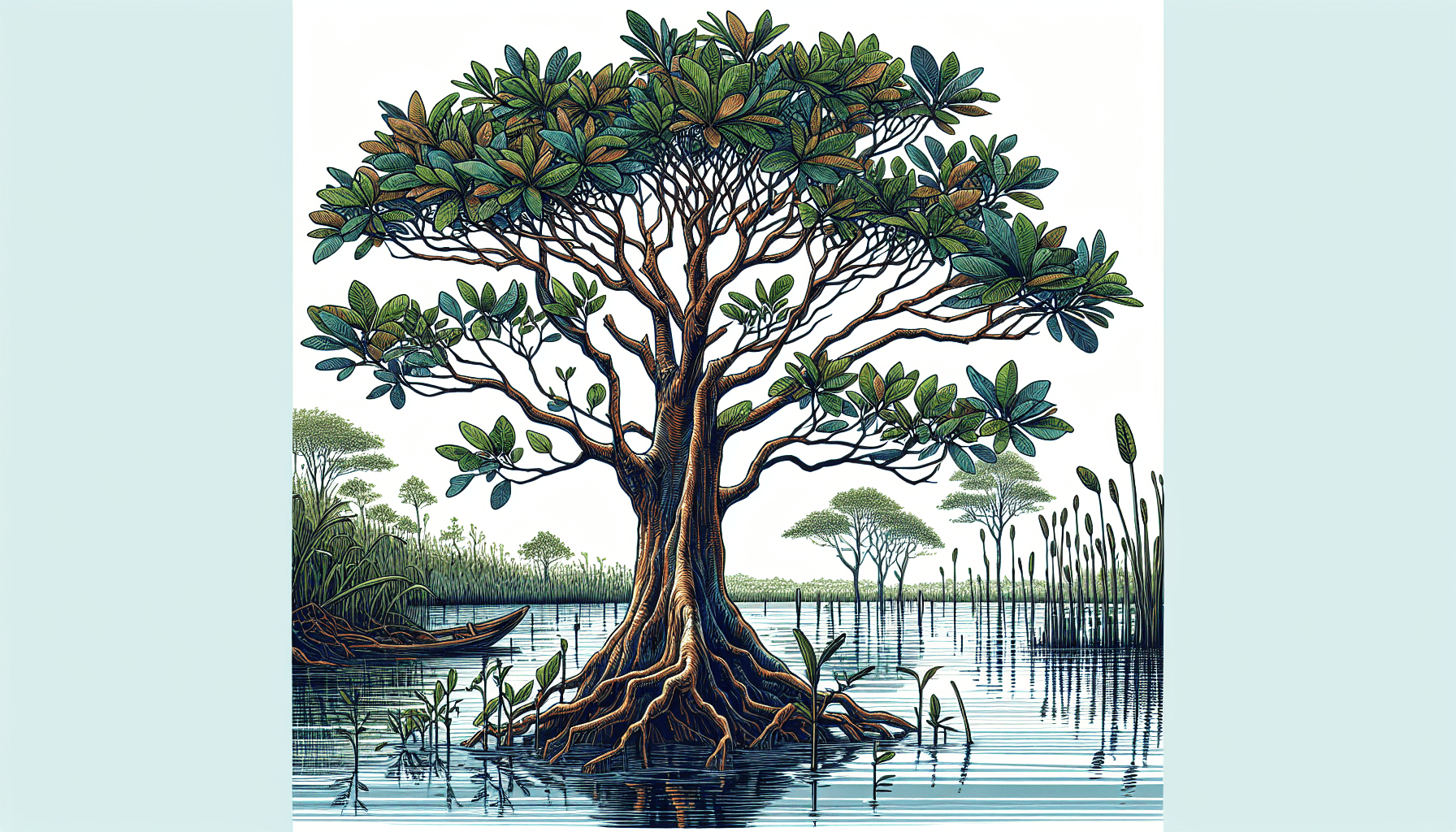
As the name indicates, Nyssa Aquatica exhibits an innate preference for wetlands and marshes, using its specially adapted root system to cope with waterlogged ground and even occasional flooding. Its aquatic nature and the accompanying adaptive mechanisms enable it to flourish in an environment that is challenging for many other tree species.
Common Names
While its scientific name is Nyssa Aquatica, this aquatic weed is popularly referred to as Tupelo or Water Tupelo, Swamp Tupelo, or Cotton Gum, amongst many other names. These derivations are often based on the region or the physical attributes of the tree.
Structural Characteristics of Nyssa Aquatica
Height and Spread
Nyssa Aquatica can mature into impressive heights, reaching up to 30 meters or more, while spreading up to 15 meters. The trunk is typically swollen or fluted at the base, giving it a characteristic shape that helps distinguish it from other species.
Leaf Structure
The leaves of Nyssa Aquatica are simple, alternate, and elliptical to oblong in shape, with smooth margins. The foliage is deciduous, displaying a vibrant green color which becomes a striking yellow or bright scarlet during the autumn season.
Flower Formation
Nyssa Aquatica blooms in modest, greenish-white flowers during spring. The flowers are small, inconspicuous, and tend to occur in clusters. The plant is dioecious, meaning separate trees carry either male or female flowers.
Seed Production
Nyssa Aquatica produces small, oval fruit, which are usually blue-black in color when mature and contain one seed each. The seeds are primarily dispersed by water, aligning with the tree’s aquatic nature.
Root System
The root system of Nyssa Aquatica is highly adapted to waterlogged conditions. It consists of a taproot with wide-spreading lateral root branches and, uniquely, pneumatophores. These oxygen-absorbing structures rise from the waterlogged soil and serve to enable the tree’s survival in its typical water-rich environments.
Cultivation of Nyssa Aquatica
Climate Requirements
This species thrives in USDA hardiness zones 6-9, where the average annual minimum winter temperature falls between -10 to 30 degrees Fahrenheit. Nyssa Aquatica generally prefers a humid climate and adapts well to areas with ample yearly precipitation.
Soil Conditions
Nyssa Aquatica grows optimally in acidic, loamy or clay soil that is constantly moist or waterlogged. Despite this affinity for water, the species can tolerate short periods of dry conditions.
Watering Needs
Given its predilection for water-rich areas, it should come as no surprise that Nyssa Aquatica needs a substantial amount of water. The tree can particularly thrive in areas where the soil is consistently damp or waterlogged.
Lighting Preferences
Regarding light preferences, Nyssa Aquatica plants respond favorably to full sunlight but can also grow in partial shade. Consistent and prolonged exposure to sunlight aids in healthier growth and better foliage color.
Propagation Techniques
This species can be propagated by seed, but it is notorious for having a low germination rate. Propagation practices may involve sowing fresh seeds in a cold frame or pre-germinating them indoors before outdoor planting in early spring.

Ecological Role of Nyssa Aquatica
Effects on Aquatic Ecosystem
As a water-loving plant, Nyssa Aquatica plays a vital role in shaping the aquatic ecosystems it inhabits. The tree’s branched root system aids in preserving water clarity by stabilising the soil, thus reducing erosion and sedimentation.
Interaction with Wildlife
Nyssa Aquatica provides critical habitat and food to a broad array of wildlife. Birds and small mammals are known to feed on its fruit, while the tree itself offers shelter to various wildlife species.
Role in Soil Erosion Control
Given its robust root system and affinity for waterlogged areas, the Nyssa Aquatica serves as an efficient wall against soil erosion. It is instrumental in maintaining the stability of riverbank and marshland ecosystems.
Nyssa Aquatica as an Invasive weed
Invasive Nature
Despite its many benefits, Nyssa Aquatica can establish itself in areas outside its native range and endanger local flora by competing for water, nutrients, and sunlight, earning itself the title of an invasive species in these localities.
Negative Impacts on Aquatic Ecosystems
The invasive nature of Nyssa Aquatica, coupled with its rapid growth and extensive root system, can lead to an imbalance in local aquatic ecosystems. By rivalling native species for resources, the invasive plant can shift biodiversity and disrupt food chains.
Control and Management Strategies
Strategies for controlling the spread of Nyssa Aquatica include mechanical removal, chemical control or, in some severe cases, the introduction of natural plant pathogens. Moreover, updated legislation and public awareness campaigns are key elements of sustainable control strategies.
Commercial Uses of Nyssa Aquatica
Landscaping Uses
Due to its unique structure, vibrant fall color and resistance to pests and diseases, Nyssa Aquatica is a popular choice for wet areas in landscaping. It is ideal for pond edges, river banks, and spaces that often get waterlogged.
Culinary Usage
While not widespread, there is a history of indigenous tribes utilizing the fruits of Nyssa Aquatica in their diets. The fruit, when ripe, has been known to be eaten raw or used in jellies and preserves.
Wood and Timber Utilization
The wood of the Nyssa Aquatica tree is moderately hard, making it suitable for a variety of applications such as furniture, boat building, and pulpwood.
Medical Importance of Nyssa Aquatica
Traditional Uses
In traditional medicine, extracts from various parts of Nyssa Aquatica have been used for their purported healing properties.
Research on Medical Properties
While traditional medicine has laid the groundwork, rigorous scientific research exploring the medical and pharmacological potential of Nyssa Aquatica is still limited.
Potential Medical Applications
Present research recognizes potential applications of Nyssa Aquatica in addressing a range of medical challenges. The antiviral, antimicrobial, or anti-inflammatory properties identified have sparked interest in ongoing exploration.
Nyssa Aquatica in Literature and Culture
Cultural Significance
The significance of Nyssa Aquatica extends beyond the ecological, with local communities, particularly indigenous ones, incorporating it into their folklore, mythology, and cultural practices.
Literary References
The tree has found its way into literary works as a symbol of vitality and endurance, reflective of its capacity to thrive in the harsh wetland environment.
Symbolic Meanings
In various cultures, the Nyssa Aquatica is viewed as a symbol of resilience and adaptability because of its unique ability to thrive in frequently flooded environments that other species find intolerable.
Threats to Nyssa Aquatica
Environmental Changes
Climate change poses a significant threat to Nyssa Aquatica, with increasing temperatures and unstable weather patterns affecting habitat suitability and causing stress to these water-loving trees.
Human Activities
Unregulated land-use activities such as deforestation, development projects, and those causing water pollution are threatening the survival of Nyssa Aquatica in its native habitats.
Disease and Pest Infestations
While naturally resistant to many pests and diseases, Nyssa Aquatica is not immune to them all. Prolonged pest infestations or the introduction of new diseases can pose serious threats as they can hinder growth or mortality rates.
Conservation Efforts for Nyssa Aquatica
Government Regulations
Governments in regions where the Nyssa Aquatica thrives have put measures in place to protect these plants. This includes designating protected areas and enacting legislation that restricts activities detrimental to its survival.
Non-Governmental Organizations and their Efforts
Several non-governmental organizations have undertaken conservation efforts for the Nyssa Aquatica. Their activities often involve the protection and restoration of the habitats where these plants flourish.
Community Initiatives
Community-driven initiatives often play a significant role in conserving Nyssa Aquatica. These initiatives involve a range of activities from tree planting to raising awareness about this crucial species and its threatened habitats.
In conclusion, Nyssa Aquatica, despite its reputation as an aquatic weed, is a species possessing ecological, economic, and cultural values that warrant understanding and preservation. Notwithstanding its capacity for invasiveness, its role in native environments is of critical importance, providing a host of benefits and services. Continued efforts in research, conservation and management will ensure the survival and utilization of this intriguing tree.