As you embark on the exploration of the world of aquatic botany, a particular species, Potamogeton crispus, may spark your curiosity. This entity, colloquially known as the curled pondweed, is a recurring subject of scientific studies due to its peculiar attributes and growth patterns. The article ahead provides a profound understanding of this aquatic weed, its biology, distribution, environmental impact, and its influence over various aquatic ecosystems around the globe.
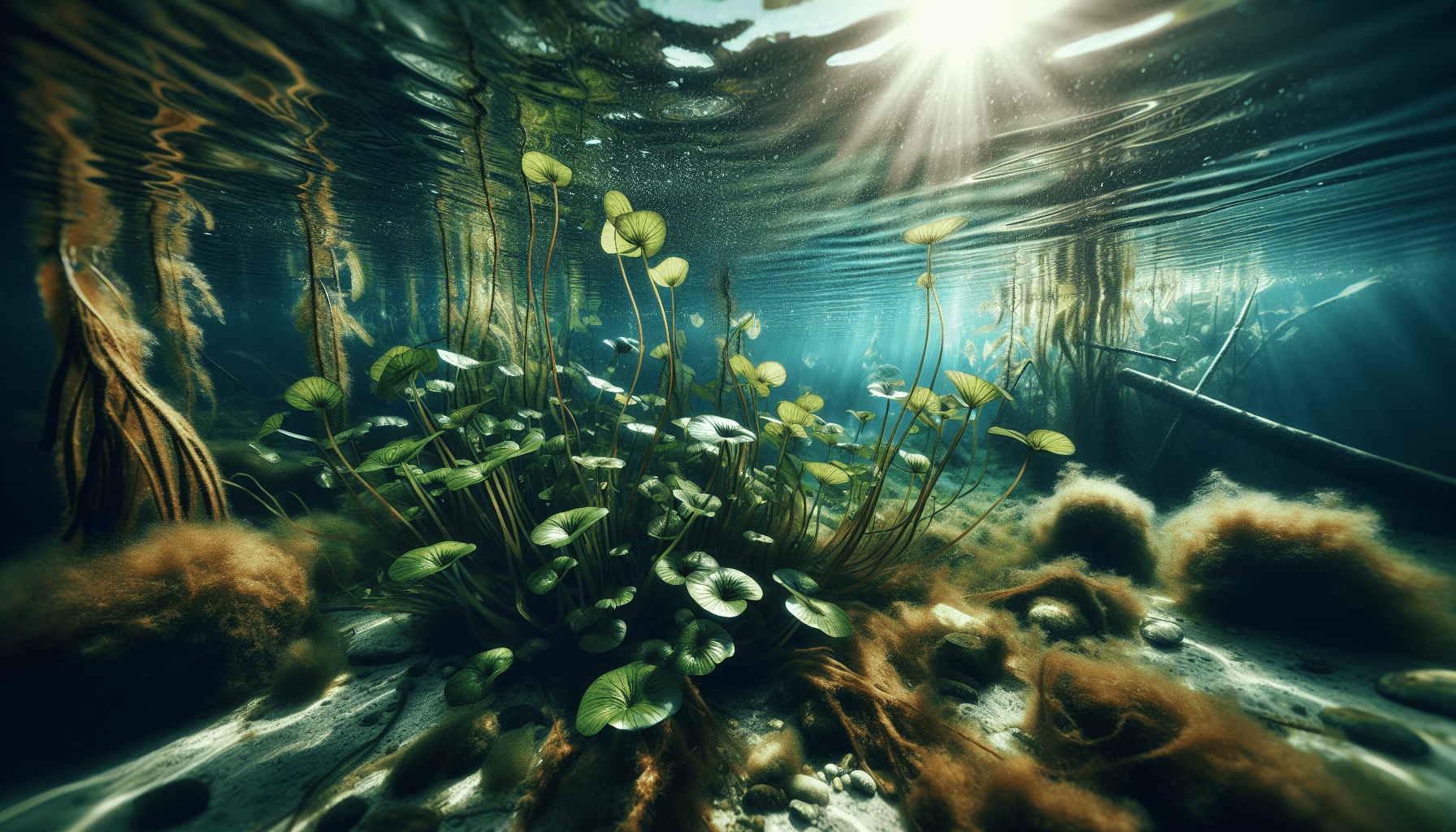

Basic Overview of Potamogeton Crispus
Potamogeton crispus, commonly known as curled pondweed, is a perennial aquatic plant that thrives in submersed freshwater environments. It is a key species in aquatic ecosystems due to its role in providing habitat and food for aquatic creatures.
Scientific classification of Potamogeton Crispus
Belonging to the family Potamogetonaceae, Potamogeton crispus is one of around 100 species recognized within the genus Potamogeton. This genus, as its Greek roots suggest—’potamos’ for river and ‘geiton’ for neighbor—consists primarily of plants found in aquatic environments.
Brief description and physical properties
Potamogeton crispus possesses long and flexible stems that can grow up to three meters in length. The leaves are conspicuously crinkled or curled—giving rise to its common name—and can vary in color from green to reddish-brown. The plant produces small, inconspicuous flowers on a spike that rises above the water surface during the flowering season.
Origin and distribution
Native to Europe and Asia, Potamogeton crispus is now widespread across the globe. Its presence is reported in North America, Australia, and several countries in Africa. Its distribution is seemingly aided by water currents, transporting it to new locations where it readily establishes populations.
Habitat of Potamogeton Crispus
Potamogeton crispus favors freshwater settings, from ponds and lakes to rivers and streams.
Preferred water conditions
Potamogeton crispus thrives ideally in alkaline to neutral pH levels. It tolerates a wide range of water conditions, from nutrient-poor to eutrophic waters. It is also quite tolerant of turbid waters, where many other aquatic plants fail to prosper.
Geographical areas where it thrives
This plant is highly adaptable, thriving in a wide range of climates, including temperate, tropical, and subtropical regions. It is not, however, salt-tolerant, limiting its existence to freshwater environments.
How it adapts to different environments
Possessing a formidable ability to aggregate and form dense stands, Potamogeton crispus is well-suited to surviving in highly competitive and disturbed environments. Its ability to spread both sexually, through seeds, and vegetatively, through sections of its stems or rhizomes, aids in its survival.
Growth and Reproduction of Potamogeton Crispus
Potamogeton crispus exhibits a fascinating growth pattern, getting a head start on growth before many other aquatic plants in a range of water bodies.
Growth pattern & rate
Often the first aquatic plant to emerge in the spring, Potamogeton crispus tends to grow at an accelerated rate in response to increased sunlight. It forms dense mats at the water’s surface until it exhausts its stored nutrient reserves.
Reproduction methods
The plant propagates both sexually, producing seeds from its flowers, and asexually through vegetative reproduction, utilizing fragments from stems, roots, or rhizomes.
Lifecycle stages and duration
Potamogeton crispus exhibits an annual lifecycle, often dying back in the summer, with seeds and overwintering buds facilitating its survival during harsh winter conditions.
Ecological Role of Potamogeton Crispus
Potamogeton crispus plays a significant role in its aquatic habitats, both as part of the extended food web and as contributors to the structuring and functioning of these environments.
Role in aquatic ecosystems
This plant functions as shelter and breeding grounds for many species of fish and invertebrates, while also serving as food for various waterfowl species.
Significance for aquatic fauna and flora
The existence of Potamogeton crispus helps to increase species richness among both flora and fauna, promoting a biodiverse ecosystem.
Impact on reservoir siltation and water quality
Potamogeton crispus aids in stabilizing sediments and improving water clarity. However, its dense growth can lead to reduced water flows, contributing to siltation in reservoirs.
Use of Potamogeton Crispus in Human Practices
Humans have found various ways to utilize Potamogeton crispus, from traditional medicine to energy resources.
Application in traditional medicine
In traditional medicine, Potamogeton crispus is said to possess antimicrobial and antipyretic properties. It is used in the treatment of various ailments, including fevers and inflammatory conditions.
Use in aquariums and ornamental ponds
This plant provides aesthetic appeal in home aquariums and ornamental ponds, providing shelter for fish and contributing to the overall health of the aquatic environment.
Potential for biomass and bioenergy production
Potamogeton crispus has shown promise as a source of biomass for bioenergy production, potentially contributing to renewable energy solutions.
Challenges Posed by Potamogeton Crispus
Despite its many benefits, Potamogeton crispus can present certain challenges to aquatic ecosystems and their human uses.
Problems for recreational water use
The rapid and dense growth of Potamogeton crispus can interfere with recreational activities such as boating, swimming, and fishing, physically obstructing access to water bodies.
Negative impact on aquatic biodiversity
In certain conditions, the dominance of Potamogeton crispus can negatively impact aquatic biodiversity, outcompeting native plants for space, sunlight, and nutrients.
Contribution to eutrophication
Potamogeton crispus contributes to the process of eutrophication, a condition where excessive nutrients in a lake or pond often lead to a surge in plant growth and subsequent oxygen depletion.
Management Techniques for Potamogeton Crispus
Due to the challenges posed by Potamogeton crispus, a range of management techniques have been devised to control its growth.
Physical control and manual removal
One of the simplest ways to manage Potamogeton crispus is through physical removal—either manually or utilizing specialized machinery. However, it can quickly regrow from remaining fragments, making this a short-term solution.
Biological control methods
Biological controls, such as introducing plant-eating insects or fish, has shown promise in some cases. However, finding appropriate species that specifically target Potamogeton crispus while not negatively impacting the ecosystem can be challenging.
Chemical control substances and their impact
Chemical control, using herbicides, is often effective. However, this method must be used judiciously due to potential impacts on non-target organisms and the wider environment.
Research and Studies on Potamogeton Crispus
Scientific research into Potamogeton crispus is continually evolving, providing new insights into its biology, ecology, and potential applications.
Recent research findings and insights
Recent research has explored the use of Potamogeton crispus in phytoremediation—using plants to clean up soil or water contaminated with pollutants. The plant’s ability to accumulate heavy metals from water bodies presents an interesting avenue for further investigation.
Ongoing studies and future research directions
Ongoing studies are increasingly focusing on beneficial applications of Potamogeton crispus. These include its value within biomonitoring assessments and its potential within bioenergy production and carbon sequestration strategies.
Impact of climate change on Potamogeton Crispus
Climate change is likely to impact Potamogeton crispus, with changing water temperatures, precipitation patterns, and nutrient levels affecting its distribution and growth. Further research is needed to understand these potential impacts.
Conservation and Sustainable Use of Potamogeton Crispus
Given its ecological significance, conservation, and sustainable use of Potamogeton crispus are important considerations.
Biodiversity conservation measures
Measures such as the establishment of protected areas, restrictions on destructive activities, and ecosystem restoration can all help ensure the conservation of Potamogeton crispus.
Sustainable harvesting and utilization techniques
Adopting sustainable harvesting methods like selective harvesting and applying utilization techniques such as composting or bioenergy production can help ensure the species’ longevity.
Community involvement in conservation
Involving local communities in conservation efforts can be beneficial, with traditional knowledge often helping to inform management strategies.
Legal and Institutional Frameworks for Potamogeton Crispus
A range of legal and institutional frameworks govern the use and management of Potamogeton crispus.
National and international laws regulating its growth and use
Different countries have varying laws regarding the cultivation, use, and management of Potamogeton crispus. Internationally, various treaties and agreements may also apply.
Institutional roles and responsibilities
Institutions ranging from local to national government departments, research institutions, and environmental organizations all have a part to play in the regulation and management of Potamogeton crispus.
Compliance and enforcement mechanisms
Enforcing these laws and compliance is enabled through a range of mechanisms, including permits, fines, and education initiatives. These help maintain the balance between the species’ benefits and the challenges it can pose.