In the exploration of aquatic flora, the prominence of Ranunculus aquatilis, commonly referred to as the aquatic buttercup, often goes unnoticed. This article seeks to elucidate you about this aquatic weed that resides ubiquitously in still and streaming water bodies. Your understanding of this plant species, its unique features, and ecological significance will be amplified, effectively molding your perspective on the integral role it plays within various ecosystems. Let the journey of discovering the intriguing existence of Ranunculus aquatilis begin.

Understanding Ranunculus Aquatilis
Definition of Ranunculus Aquatilis
Ranunculus Aquatilis is a renowned aquatic perennial herbaceous plant, part of the Ranunculaceae family, a large genus that encompasses around 600 species of plants, which are identifiable by their bright yellow flowers and forked submerged leaves. Known for its dominance in still or slow-moving water bodies, it is also referred to as an ‘aquatic weed’ due to its rapid growth and the potential to cover large water bodies.
Where the name comes from
The term ‘Ranunculus Aquatilis’ is derived from Latin where ‘Ranunculus’ refers to ‘little frog’. This is an appropriate metaphor since just like frogs, many species of the Ranunculus family tend to thrive in wet areas. ‘Aquatilis’, on the other hand, means ‘growing in water’ indicating its primary habitat.
Alternate names and synonyms
Often, Ranunculus Aquatilis is colloquially referred to as ‘Water crowfoot’ owing to the unique shape of its leaves that resemble the foot of a crow. Other alternate names for this aquatic plant include ‘Common water crowfoot’ and ‘Water buttercup’, reflecting its characteristic of developing yellow buttercup-like flowers.
Physical Characteristics of Ranunculus Aquatilis
Description of its appearance
Ranunculus Aquatilis exhibits the characteristics of submerged plant growth, with finely divided thread-like underwater leaves that bestow it with a feathery appearance. In contrast, its floating leaves, if present, are small and undivided. One of the distinguishing features of this species is its buttercup-like five-petaled pale yellow flowers.
How it changes throughout seasons
The notable adaptability of Ranunculus Aquatilis enables it to change throughout the seasons. While in the months of summer, it extensively colonizes freshwater habitats, during late winter or early spring it retreats to being a tight bud at the bottom.
Comparison with similar aquatic plants
Ranunculus Aquatilis, similar to its other siblings in the Ranunculus genus, often gets misidentified due to their shared characteristic of floating leaves. However, the specific laciniated submerged and unbearded floating leaves distinctively set Ranunculus Aquatilis apart from its lookalikes.
Habitat of the Aquatic Weed
Preferred water conditions
Ranunculus Aquatilis exhibits a preference for mesotrophic waters- waters that are nutrient-rich yet well-oxygenated. It also shows a preference for slightly alkaline to neutral pH conditions.
Geographic locations where it thrives
Ranunculus Aquatilis is widely distributed across various geographic locations including North America, Europe, North Africa, and parts of Asia. It has a particularly high presence in Northern Ireland and Scotland.
Types of water bodies it is found in
You’ll find Ranunculus Aquatilis inhabiting a wide range of static or slow-flowing water bodies. These include ponds, lakes, ditches, slow streams, and canals, where it forms extensive underwater beds.
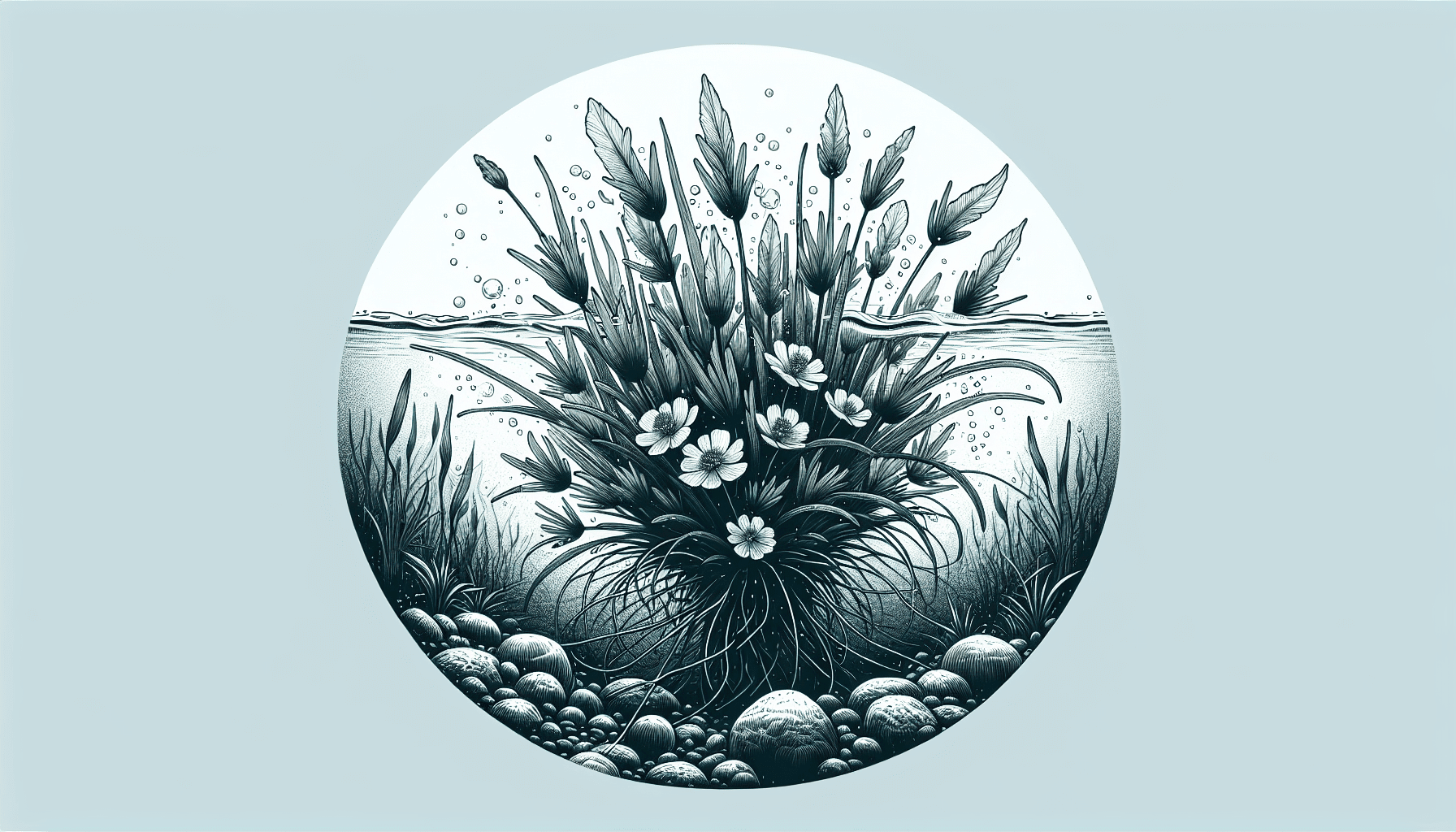
Life Cycle and Reproduction
How and when Ranunculus Aquatilis reproduces
Ranunculus Aquatilis reproduces both vegetatively and through seeds. The vegetative reproduction is carried out by the constant growth of its rosettes which self-root and form new plants. Seed reproduction occurs when the flowers wither, forming achenes that disperse and give rise to new plants.
Details about its life cycle
The life cycle of Ranunculus Aquatilis is characterized by a late winter vegetation phase, a spring flowering phase, a late summer seeding phase, and finally a winter dormant phase.
Strategies it uses for survival and propagation
The survival and propagation strategy of Ranunculus Aquatilis involve the production of large quantities of lightweight seeds that are easily carried by wind or water. Its ability to switch between different forms of leaves depending on water availability also aids in its survival.
Ecological Role of Ranunculus Aquatilis
Its contribution to its ecosystem
Despite being a perceived nuisance, Ranunculus Aquatilis contributes significantly to its ecosystem. It purifies water by absorbing excess nutrients, offers shelter to invertebrates, and serves as food source to aquatic animals. Its floating leaves also provide shade, which regulates the water temperature and prevents algal bloom.
Species that interact with it
Various species interact and coexist with Ranunculus Aquatilis. This includes certain species of snails, crustaceans and insects that feed on this aquatic plant. Furthermore, various species of birds are also known to utilize these plants for nest building or as a food source.
How it impacts biodiversity
Ranunculus Aquatilis positively influences biodiversity by providing a habitat for a wide range of organisms and serving as a food source for others. Nevertheless, its ability to form dense canopies can also impact biodiversity negatively by outcompeting other native plants and altering the habitat.
Possible Threats for Ranunculus Aquatilis
Environmental risks
Environmental risks, such as water pollution and eutrophication, pose threats to Ranunculus Aquatilis by disrupting its preferred living conditions and affecting its survival.
Human activities that pose a threat
Human activities such as over-fishing, dredging and the resultant physical disturbance of the habitat, and introduction of invasive species can negatively impact Ranunculus Aquatilis.
Effects of climate change
With increasing global temperatures and rising sea levels due to climate change, freshwater bodies and their habitats are undergoing transformations. Changes in the season lengths, precipitation patterns, and water temperatures can alter growth patterns and disrupt the life cycle of Ranunculus Aquatilis.
The Reaction of Animals and Birds to Ranunculus Aquatilis
Which fauna consume it
Aquatic snails, certain insect larvae, and waterfowl are known to feed on Ranunculus Aquatilis.
Influence on bird species
Bird species frequent areas populated by Ranunculus Aquatilis not only for feeding but also for nest-building materials. The plant proves to be a good source of cover for bird nests.
How it affects fish and other aquatic animals
Fish and other aquatic animals often use beds of Ranunculus Aquatilis for shelter and spawning ground. However, extensive growth of these plants may affect the water quality, indirectly affecting these animals.
Ranunculus Aquatilis as an Invasive Species
Where and why it becomes invasive
When introduced outside its native range, Ranunculus Aquatilis has the potential to become invasive. Its nature to form dense mats and rapid multiplication aids in its invasiveness.
The impact of its invasiveness
When invasive, Ranunculus Aquatilis can alter the water spread in its inhabited area, depleting nutrients for other species, causing oxygen depletion, affecting the recreational use of water bodies and potentially leading to the decline of native plant species.
Control measures taken
Some of the control measures taken to manage the invasiveness of Ranunculus Aquatilis include mechanical removal, usage of herbicides and introduction of biological control agents.
Use of Ranunculus Aquatilis in Human Activity
Its role in traditional medicine
In the traditional medical practice of homeopathy, Ranunculus Aquatilis is utilized to treat ailments associated with severe chill or cold, and for individuals with a skin condition that gets worse with the contact of water.
Usage in gardening or decoration
With its delicate underwater foliage and bright yellow flowers, Ranunculus Aquatilis is often used in garden ponds and as a decorative species in aquariums.
Possible industrial applications
Due to its efficiency in taking up heavy metals, Ranunculus Aquatilis has potential for use in the remediation of polluted water bodies.
Research and Studies on Ranunculus Aquatilis
Scientific studies conducted on the plant
Numerous studies have been conducted on Ranunculus Aquatilis, predominantly focusing on its ecology, distribution, medicinal properties, and its potential for bioremediation.
Areas yet to be studied
While much research has been conducted on this plant, there is a void in the understanding of the specific genome structure, mechanisms behind its high adaptability, and comprehensive evaluation of its invasive nature.
Recent discoveries about the plant
Recent studies have shed light on the ability of Ranunculus Aquatilis to hyperaccumulate zinc, highlighting its potential use in phytoremediation. Moreover, research is being conducted on the phytochemistry of Ranunculus Aquatilis, seeking to understand its chemical composition and potential medicinal properties at a deeper level.