In navigating through the mesmerizing world of flora that thrives beneath the water’s surface, a notable point of fascination is the aquatic weed known as Rotala Rotundifolia. This elegantly understated entity is an organism of immense importance, notwithstanding its common reference as a weed. As you delve deeper into this text, you will glean a robust understanding of this plant – its ecological significance, cultivation, and its place in the broader ecosystem. Be prepared to expose yourself to an esoteric realm, one that is as intriguing as it is complex.
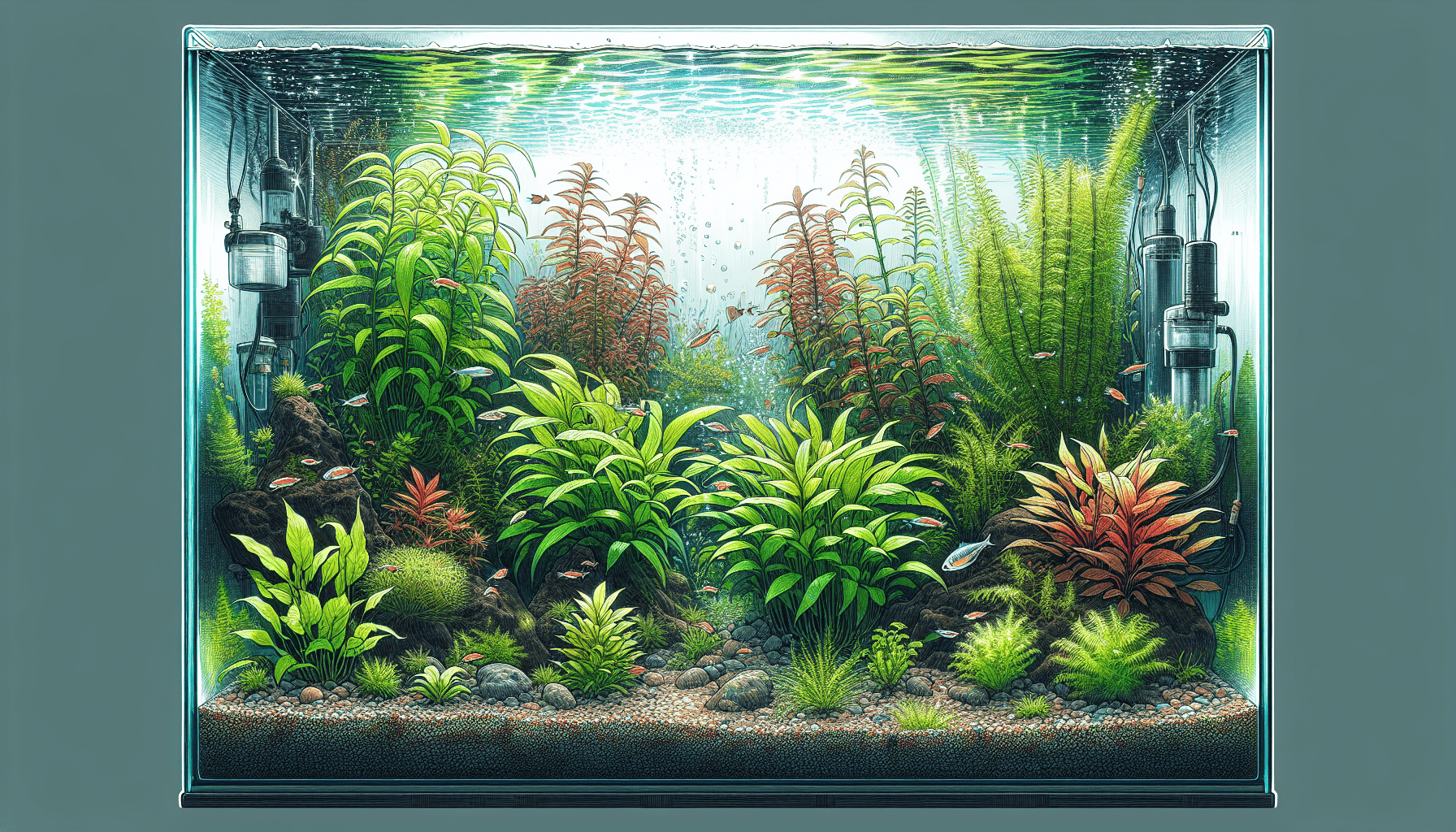
Overview of Rotala Rotundifolia
Definition of the plant
Rotala Rotundifolia, often referred to as the “dwarf rotala” or “roundleaf toothcup,” is a perennial aquatic plant hailed for its enchanting, colorful foliage. This species falls under the category of ‘Rotala,’ a diverse genus within the Lythraceae family. It has scaled delicate leaves and thin pink stems which can fully submerge in water and survive in both terrestrial and submerged states.
Origin and habitat
The Rotala Rotundifolia species are indigenous to Southeast Asia, often featuring prominently in freshwater bodies of countries like Cambodia, Vietnam, and Malaysia. Its habitat extends to paddy fields and wetlands, supplying ample moisture that supports its continuous growth and reproduction cycle. Given its ability to survive across various conditions, it is a dominant presence in aquariums worldwide.
Differences and similarities with other aquatic plants
The elemental features of Rotala Rotundifolia position it distinctly within the genera of aquatic plants. Its unusual behavior of change in leaf color from green to pink depending on the lighting makes it unique. However, like many other aquatic species, its structure alters when moving from an immersed to a submerged state. The comparison with other aquatic plants will be discussed in later sections.
Physical Characteristics of Rotala Rotundifolia
Color and appearance
The most distinct trait of Rotala Rotundifolia is its charming color. Its leaves display a vibrant green color under moderate light, changing to a beautiful pinkish-red hue under intense light conditions, making it a captivating centerpiece in aquariums.
Size and growth rate
In terms of size, Rotala Rotundifolia can reach a height of up to 50 cm with careful nurturing, and its rapid growth rate is a significant attribute of this species. However, its height can be controlled and maintained to suit the requirements of an aquatic setup.
Flowering pattern
Rotala Rotundifolia is unique in its flowering pattern. Normally, flowers bloom singly from leaf axils when the plant is out of water, exhibiting small, yellowish-white flowers. However, underwater flowering is considered rare.
Leaf structure and coloration
Rotala Rotundifolia’s leaf structure is equally distinctive. It possesses small, round leaves that are generally 2-3mm wide and up to 1.5cm long, spirally arranged. The leaf’s coloration, as mentioned earlier, is largely contingent on the tank’s lighting conditions.
Environmental Requirements for Growth
Water temperature
Rotala Rotundifolia displays great flexibility regarding water temperature, with the capacity to tolerate a range between 18-30 degrees Celsius. Although, an ideal temperature hovers around 22-28 degrees Celsius for optimal growth.
Lighting requirements
Lighting exerts a profound impact on the color of Rotala Rotundifolia’s leaves. It is advisable to provide moderate to high light conditions for this plant species to achieve a robust growth and vibrant pink hue.
Substrate preference
This plant’s preference for substrate leans towards a fine-grained nutrient-rich soil, favoring effective root anchoring and nutrient absorption.
Water quality and pH levels
The water quality should always maintain clarity, and the pH level should lie within a range of 6.0-7.5, allowing the plant to exhibit optimal physiological functioning and thriving.

Propagation Methods
Stem cutting and replanting
Propagation is easily achieved through stem cutting, where a healthy stem is simply cut and replanted in the substrate. This method encourages rapid growth and efficient propagation.
Sowing seeds
Sowing seeds directly into the substrate is another propagation technique. This procedure might be slower than the stem cutting method, but it can be cost-effective for commercial purposes.
Natural reproduction through offshoots
Additionally, Rotala Rotundifolia can reproduce by forming offshoots from the plant’s main body, which can be removed and planted independently. This organic propagation method ensures genetic uniformity and promotes vegetation.
Common Uses for Rotala Rotundifolia
Use in aquariums
Rotala Rotundifolia is a favored choice among aquarium enthusiasts due to its vibrant colors, rapid growth rate, and ability to create a stunning backdrop, providing an enchanting scenic view.
Role in aquatic environment
This plant plays a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems by providing shelter and breeding grounds to many small aquatic creatures, contributing to the overall bio-diversity.
Medicinal and cooking uses
Few studies suggest possible medicinal benefits of Rotala Rotundifolia, particularly in wound healing and anti-inflammatory roles. In parts of Asia, it is also consumed as a vegetable, catering to its cooking uses.
Commercial cultivation
The plant’s sturdy nature, eye-catching appearance, and rapid propagation rate augur well for commercial cultivation, especially within the fishkeeping industry.
Nutritive Requirements
Type of nutrients needed
Rotala Rotundifolia requires a nutrient-rich substrate that abounds in essential macro and micronutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorous, and trace minerals for healthy and sustained growth.
Ideal nutrient levels
To observe a classical pinkish-red coloration in Rotala Rotundifolia, optimum nutrient levels are crucial. However, an excessive concentration of nutrients, recognized as nutrient toxicity, can harm the plant.
Effects of nutrient deficiency
Nutrient deficiency displays harmful effects on plant health. A dearth in essential minerals could lead to stunted growth, loss of color, drop in leaves, and may ultimately result in plant death.
Potential Problems with Rotala Rotundifolia
Damage from herbivores
Being an aquatic plant, Rotala Rotundifolia is vulnerable to damage by herbivorous animals, especially snails and certain breeds of herbivorous fish.
Invasive growth
Unchecked, this plant can grow invasively, which may outcompete other aquatic species for resources and potentially disrupt the aquatic ecosystem balance.
Susceptibility to diseases and parasites
Like all aquatic plants, Rotala Rotundifolia is not impervious to diseases and parasites. Poor water quality and inappropriate tank conditions may lead to the manifestation of ailments.
Maintenance of Rotala Rotundifolia
Pruning and shaping methods
Regular pruning helps keep the plant’s height under control, enhancing its appearance and ensures healthier growth. The cut stems can be replanted, contributing to the plant’s propagation.
Water changing frequency
Water changes should be done regularly, preferably weekly, to maintain optimal water quality. This step is critical for sustaining the plant’s health and growth rate.
Adjusting nutrients and lighting
Both nutrient and lighting conditions should be adjusted regularly to cater to the plant’s needs. It must be noted that the Rotala Rotundifolia’s coloration is directly related to these two factors.
Benefits of Rotala Rotundifolia
Environmental impact
Rotala Rotundifolia, given its rapid growth rate and photosynthetic ability, acts as an effective carbon sink and oxygen source, playing a significant part in maintaining the biochemical equilibrium of the aquatic environment.
Effects on water quality
By absorbing excess nutrients from the water, Rotala Rotundifolia helps maintain water quality, mitigating the likelihood of algal bloom outbreaks.
Role in the ecosystem
As a vital part of underwater ecosystems, this plant offers shelter and spawning grounds for various aquatic creatures, promoting biodiversity and fostering a substantial contribution to the ecosystem.
Rotala Rotundifolia VS Other Aquatic Plants
Comparison with Anacharis
While both Rotala Rotundifolia and Anacharis are popular aquatic plants, their requirements differ significantly. Anacharis thrives in cooler waters whereas Rotala Rotundifolia prefers a warmer environment. Additionally, Anacharis tends to remain green irrespective of light conditions, while variations in lighting result in a color change in Rotala Rotundifolia.
Comparison with Hornwort
Hornwort and Rotala Rotundifolia share similar conditions for growth and are excellent oxygenators. However, Hornwort possesses a slightly higher tolerance for colder temperatures and doesn’t exhibit the color transformation seen in Rotala Rotundifolia.
Comparison with Java moss
Java moss, unlike Rotala Rotundifolia, has low light and nutrient requirements, showcasing its potential as an ideal plant for beginners. Java moss, however, is less impactful in terms of aesthetics compared to the brightly colored Rotala Rotundifolia.