As a keen enthusiast of aquatic ecosystems, you may have encountered Sagittaria platyphylla, a prevalent aquatic weed prominently established in ponds and marshes across North America and Northern Europe. Too often, its impact on indigenous species and its potential applications are overlooked, but this comprehensive article provides a thorough examination of Sagittaria platyphylla, its unique characteristics, propagation, ecological significance, and the role it plays within the larger ecosystem.
Overview of Sagittaria Platyphylla
The aquatic domain is filled with a variety of flora that plays fundamental roles in sustaining their ecosystems. One such remarkable species which commands attention is the Sagittaria Platyphylla. This article aims to delve into various facets surrounding this fascinating aquatic plant.
Definition of Sagittaria Platyphylla
As you step into the world of aquatic plants you will find that Sagittaria Platyphylla is a member of the Alismataceae family, comprising over 100 genera. It is one of the numerous species lying under the genus Sagittaria, which is a genus of flowering plants often referred to as “arrowheads” due to their distinctive leaf shape.
Typical habitat of Sagittaria Platyphylla
Sagittaria Platyphylla is a truly aquatic plant. It thrives best in freshwater environments, such as marshes, ponds, and slow-moving rivers. Given its preference for such environments, it can be found mostly in shallow water or often in waterlogged soil.
Origin and distribution of Sagittaria Platyphylla
The plant is believed to have originated in North America and found its way across different continents due to human activity, and now can be found in temperate to tropical zones across the globe including Europe, Australia, and Asia. Within these continents, its distribution varies, being heavily concentrated in some regions while scarce or absent in others.
Characteristics of Sagittaria Platyphylla
Engaging with the nature of Sagittaria Platyphylla involves observing several aspects. These include its distinct physical features, growth pattern, and reproductive mechanisms.
Physical Features of Sagittaria Platyphylla
Your first interaction with this plant will reveal its captivating physical features. Sagittaria Platyphylla has bright green, arrowhead-shaped leaves, which give it its common name. The plant stands upright underwater, its long, stout stalks supporting the clumps of leaves. It produces small, three-petaled white flowers at the tips of the long inflorescences, characteristics of the Sagittaria genus.
Growth pattern of the plant
The growth pattern of Sagittaria Platyphylla parallels that of many of its aquatic counterparts. The plant’s growth rate is profoundly influenced by the availability of sunlight and nutrients. Under ideal conditions, it displays a submersed form with clumps of leaves that can reach up to 60 cm in height.
Reproductive mechanisms of the plant
Reproduction in Sagittaria Platyphylla is quite fascinating. The plant reproduces sexually through its flowers and seeds and asexually through the production of tubers, which can disperse and grow into new plants.
Ecological Importance of Sagittaria Platyphylla
Despite certain challenges, Sagittaria Platyphylla plays an integral part in ecological balance by supporting habitats, improving water quality, and providing food and cover for wildlife.
Role in habitat and ecosystems
Sagittaria Platyphylla functions as a foundational species in many freshwater ecosystems. As an aquatic plant, it supports and stabilizes the substrate, helping to prevent erosion. It also provides crucial habitats for a myriad of animals, including insects, fish, and birds.
Contribution to water quality
Sagittaria Platyphylla contributes significantly towards improving water quality by absorbing excess nutrients, keeping in check algal blooms and other water quality problems.
Significance for wildlife
The terrestrial and underwater coverage of Sagittaria Platyphylla serves as suitable breeding grounds and shelters for diverse aquatic species while also becoming a source of food for herbivorous animals.
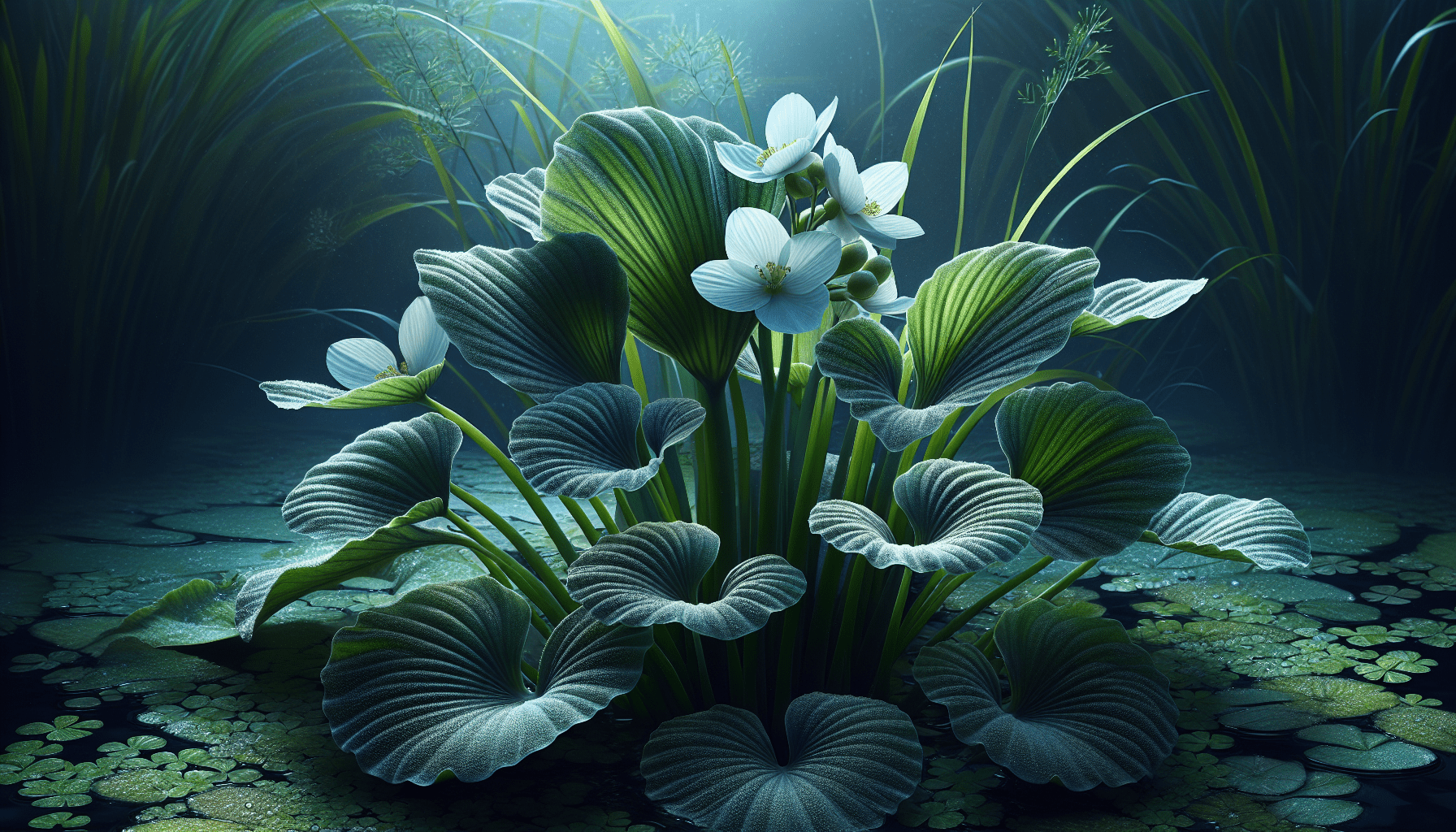

Cultivation and Care of Sagittaria Platyphylla
Successfully maintaining Sagittaria Platyphylla calls for certain specific conditions. Understanding these can enhance your ability to cultivate and care for these aquatic plants.
Ideal conditions for growth
As mentioned before, Sagittaria Platyphylla is an aquatic plant that prefers shallow, freshwater habitats. It flourishes best in muddy substrates under full exposure to sunlight.
Maintenance requirements
Like all plants, Sagittaria Platyphylla requires regular maintenance in order to thrive. This includes ensuring that it has access to enough light and nutrients in the water.
Propagation methods
The primary method of propagating Sagittaria Platyphylla is through its tubers, which can be separated and planted individually to grow into a new plant.
Identification of Sagittaria Platyphylla
Recognizing Sagittaria Platyphylla in the vast aquatic landscape involves noticing certain distinguishing features and significant markers.
Distinguishing features from other similar plants
While there are numerous species within the Sagittaria genus, Sagittaria Platyphylla can be distinguished by its arrowhead-shaped leaves, which are wide at the base and taper towards the tip.
Significant markers of the plant
Signal traits in identifying Sagittaria Platyphylla enclose the white, three-petaled flowers that emerge above the water surface during blooming season.
Common mistakable identities
Given their similar appearances, Sagittaria Platyphylla can often be mistaken for other plant species such as Vallisneria or Eelgrass.
Sagittaria Platyphylla as Invasive Species
The ability of Sagittaria Platyphylla to rapidly reproduce and expand can cause it to become invasive in certain situations.
Defining as an invasive plant
An invasive plant is one that expands beyond its natural range and causes harm to the new ecosystems it inhabits. Sagittaria Platyphylla becomes invasive when it grows unchecked, outcompeting native plant species for resources.
Negative impacts on ecosystems
Uncontrolled growth of Sagittaria Platyphylla can lead to a decrease in biodiversity as native species are displaced. It can also modify habitats and upset the balance of the ecosystem, leading to negative consequences for wildlife.
Comparison with other invasive plant species
Like many other invasive species, Sagittaria Platyphylla has the ability to quickly adapt to new environments. However, compared to some, it poses fewer threats due to its specific habitat requirements.
Management and Control of Sagittaria Platyphylla
It is crucial to manage and control the growth of Sagittaria Platyphylla to avoid its negative ecological impacts.
Common control measures
Measures to control Sagittaria Platyphylla involve mechanical removal, restriction in water bodies, and, as a last resort, the use of specific herbicides.
Challenges in managing the weed
Key challenges in controlling this plant include its quick reproduction, wide distribution spread, and its ability to regenerate from fragments or tubers.
Impact of control measures on habitats
Efficient control measures need to be employed with care, ensuring negligible harm to the surrounding environment and habitats.
Uses of Sagittaria Platyphylla
Sagittaria Platyphylla serves several useful purposes ranging from decorative to medicinal and culinary.
Use in aquariums and ponds
Sagittaria Platyphylla, owing to its attractive appearance, is used widely for decorative purposes in aquariums and ponds.
Potential medicinal properties
There is ongoing research into the potential medicinal properties of Sagittaria Platyphylla. In traditional medicine, certain Sagittaria species have been used for their purported benefits.
Culinary uses of the plant
Some species of Sagittaria, including Sagittaria Platyphylla, are known to be edible, and its tubers are sometimes used as a food source.
Adaptation Strategies of Sagittaria Platyphylla
Understanding the survival tactics and resilience of Sagittaria Platyphylla can help explain the plant’s invasive tendencies.
Survival tactics in various water conditions
Sagittaria Platyphylla can survive various water conditions, such as varying degrees of salinity and water levels, demonstrating its high adaptability.
The plant’s resilience to environmental changes
Its resilience to environmental changes and capacity to regenerate from plant fragments or tubers give it an edge in surviving and thriving in different circumstances.
Traits that make it invasive
Traits that make Sagittaria Platyphylla invasive include its rapid reproductive rate, adaptability, and ability to disperse over large areas, often helped by human activity.
Sagittaria Platyphylla in Research
Delving into the research done on Sagittaria Platyphylla can shed light on its properties, potential benefits, and impacts on nature.
Recorded research studies
While there have been several studies focusing on its ecology and control methods, less attention has been dedicated to its potential uses such as medicinal or culinary.
Gaps in the understanding of the plant
There are yet unexplored dimensions around Sagittaria Platyphylla, particularly concerning its genetics, metabolic pathways, and precise physiological mechanisms.
Possible future research directions
Future research could focus on exploring the plant’s medicinal properties, environmental impact assessment, designing better control strategies, and understanding its genetic make-up.
In summary, Sagittaria Platyphylla is a unique aquatic plant characterized by its striking features, ecological contributions, and invasive tendencies. By dissecting various aspects surrounding this species, we gain imperative insight not just into this fascinating plant, but also into wider concerns related to aquatic ecosystems, invasive species management, and the potential uses of such plants.