In the realm of aquatic flora, the Sagittaria Rigida, otherwise known as the rigid arrowhead, stands a notable species. Your understanding of marine biodiversity can be broadened by studying this intriguing plant species, which thrives in the unique dynamics of freshwater habitats. Not only is the study of these plants integral to comprehending ecological health, but it also has practical implications for you in the management of aquatic ecosystems. Through exploring the growth, characteristics, and implications of the Sagittaria Rigida, a profound insight into the nature of aquatic weeds can be envisaged.
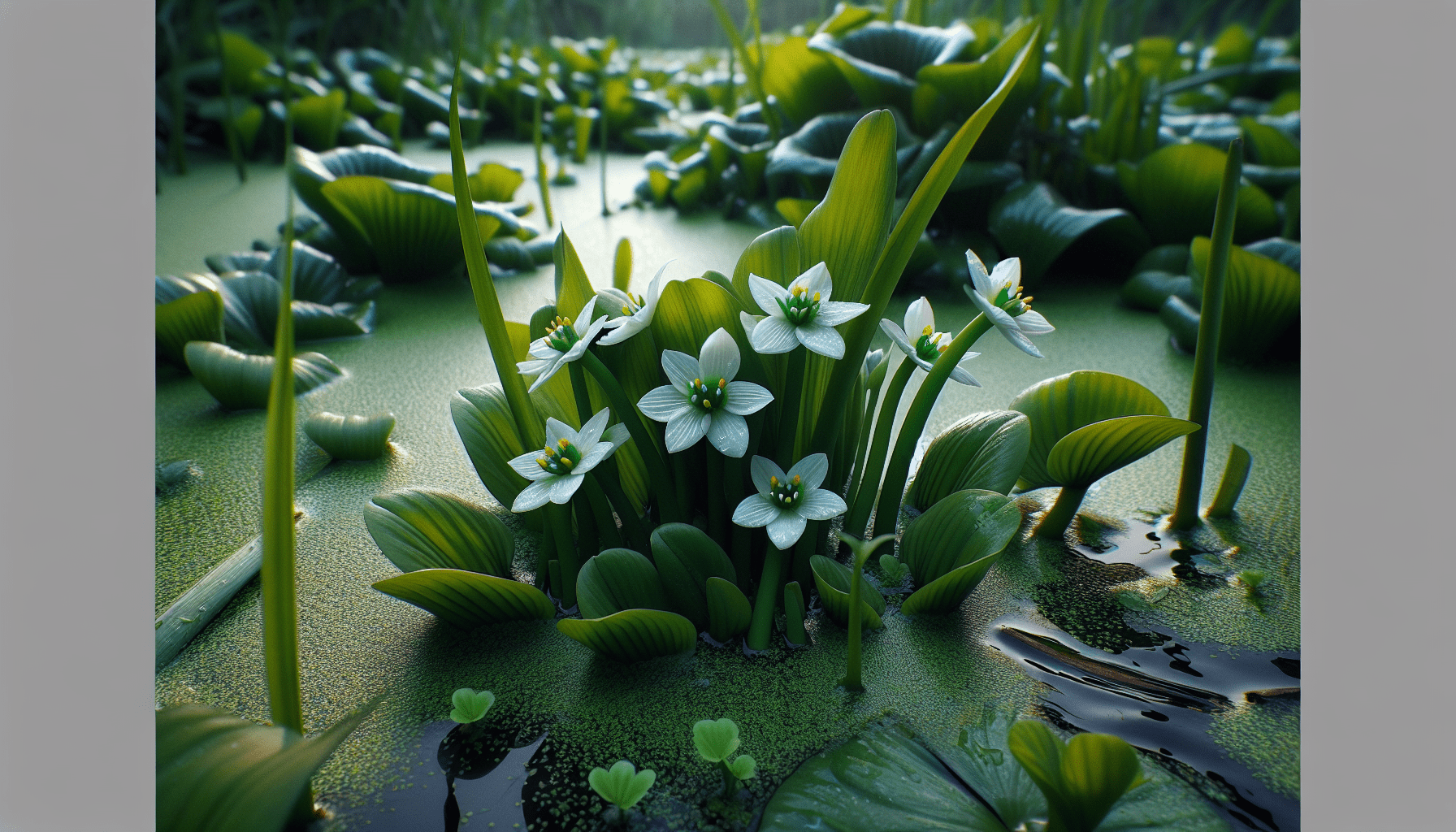
Identification of Sagittaria Rigida
Sagittaria Rigida, an aquatic weed otherwise known as the stiff arrowhead, is a native flowered perennial plant. As an easily identifiable member of the Alismataceae family, its supposed common name ‘Rigid Arrowhead’ aptly speaks to its rigid leaf structure which readily distinguishes it from others in its specie family.
Defining features of Sagittaria Rigida
The majority of Sagittaria Rigida’s distinguishing characteristics are borne out of its notable morphological structure. It possesses long, slender, and stiff leaves which typically range from 1 to 3 feet. In addition, its flowers, mainly characterized by their bright white color, are arranged in a raceme atop a robust rutty stalk.
Visual differentiation from similar species
You may notice Sagittaria Rigida bears a striking resemblance to fellow sagittaria species, such as Sagittaria cuneata or Sagittaria latifolia. While they share similar definitional traits like arrowhead-shaped leaves and white flowers, the subtle stiffness and the placement of the three-arrow-like outline of the leaf in Sagittaria Rigida acts as a full visual differentiator.
Geographical distribution
The geographical distribution of Sagittaria Rigida spans across northern parts of North America, including the central and west regions of the United States and Canada. This prevalence is mainly seen around fresh water bodies, wetlands, and marshy grounds in these locales, indicating its preference for wet and moist habitats.
Characteristics of Sagittaria Rigida
Sagittaria Rigida is a unique plant species that provides an insightful look into the world of aquatic botany.
Detailed description of plant structure
The unique structure of the plant is characterized by its distinctive leaves which are mostly stiff, vertical, and linear, growing up to 3 feet in length. The flowers genetically display a trio of white petals, a yellow center, and a series of purplish-brown lines along the vein. Furthermore, this plant annually grows back from thick, round tubers anchored in the soil.
Growth habits
Sagittaria Rigida is highly adaptable and can grow both submerged and emersed, often found in slowly moving or still waters of ponds or along the edges of marshes. The plant succeeds in full sun but can tolerate partial shade. However, the lush nature of the growth may be compromised.
Life cycle and reproduction
As a perennial plant, Sagittaria Rigida regenerates yearly from underground tubers. It blooms in late summer and produces flowers that open mid-day. Its reproduction is accomplished either by seed distribution from the dried out fruits or through vegetative propagation via the thickened roots.
Ecological Role of Sagittaria Rigida
Despite being characterized often as a weed, Sagittaria Rigida plays a significant role in the ecosystem.
Role in aquatic ecosystems
In aquatic ecosystems, Sagittaria Rigida plays an essential role in providing habitat and food supply for aquatic species. The plant’s tuberous roots help stabilize sediments, aiding in maintaining the water body’s structural integrity. Concurrently, its leaf structure provides an excellent hiding place for small fishes and other aquatic organisms.
Interactions with other plants and animals
Being rich in starch, Sagittaria Rigida’s tubers are a valuable food source for several animal species, notably waterfowl. As a food source, it supports other plants’ growth by attracting wildlife that in turn aid in the seed spread and fertilization of these other plants.
Impact on water quality
Sagittaria Rigida helps improve water quality by stabilizing sediments, reducing erosion, and absorbing excess nutrients from the water. This process prevents harmful algal blooms, ensuring a healthier aquatic environment.
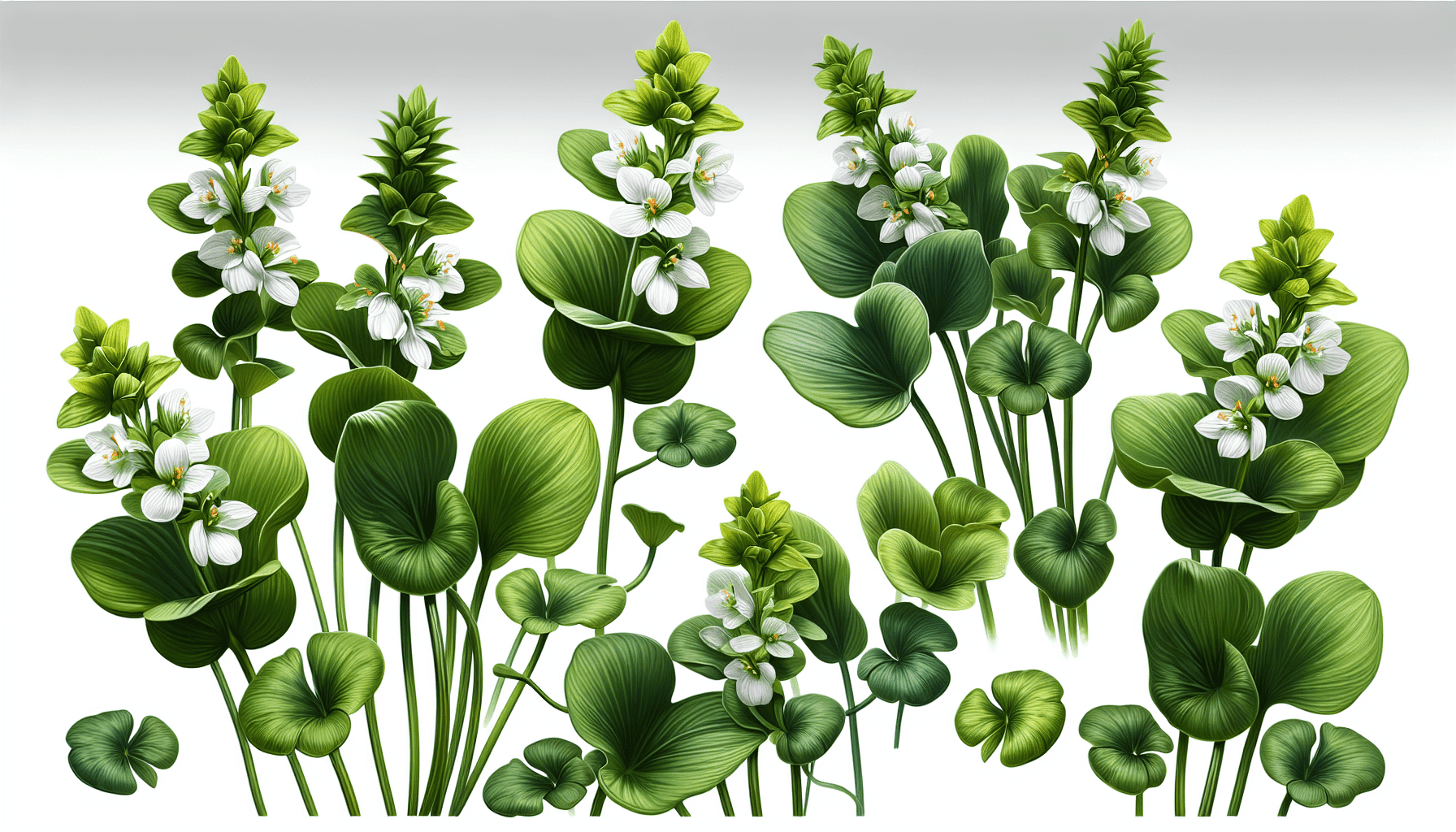
Sagittaria Rigida as an Invasive Species
In instances where Sagittaria Rigida thrives outside its native area, it may often be characterized as an invasive species.
Regions affected by Sagittaria Rigida invasion
While native to North America, Sagittaria Rigida has been introduced to various parts of the world where it has developed into an invasive species. It has spread across Europe and parts of Asia, where it outcompetes native species for resources.
Environmental impact of invasion
The unchecked growth of Sagittaria Rigida in non-native locales leads to a decline in biodiversity as it replaces indigenous flora, disrupts aquatic ecosystems, and alters the natural habitat of some wildlife.
Economic consequences of Sagittaria Rigida proliferation
The economic consequences of Sagittaria Rigida proliferation can be quite severe. As the weed spreads, controlling its growth and prolonging its damage to commercial water bodies can cause significant financial strains.
Control and Management of Sagittaria Rigida
Sagittaria Rigida’s rapid growth and propagation necessitate the implementation of control and management strategies.
Methods of physical control
Physical control methods involve uprooting or cutting the plant during its active growing period. However, it’s critical to ensure that all parts of the root system are removed to prevent regeneration.
Chemical control options
Chemical control methods involve the use of herbicides. These should be applied selectively considering the potential for ancillary non-target species impact while also weighing the susceptibility of Sagittaria Rigida to the specific herbicide.
Biological control strategies
Biological control methods involve the use of natural enemies of the plant to inhibit its growth. However, this method requires extensive testing to prevent the unintended introduction of new invasive species.
Benefits of Sagittaria Rigida
Despite the typical classification as a weed, Sagittaria Rigida has multiple benefits.
Use in erosion control
The profound root system of Sagittaria Rigida helps in securing sediments, thereby controlling erosion along the banks of water bodies.
Value as a food source for some wildlife species
The tuberous roots of Sagittaria Rigida are a rich source of starch, which is essential to various wildlife species.
Aesthetic value in water gardens
Sagittaria Rigida adds a touch of natural beauty to water bodies with its elongated leaves and striking white flowers, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of water gardens.
Considerations in Using Sagittaria Rigida
Optimal use of Sagittaria Rigida includes necessary precautions to prevent adverse impacts.
Safety concerns and precautions
Since Sagittaria Rigida grows best in wet, marshy areas, ensure safety by implementing protective measures to prevent any injuries from slipping or falling.
Potential impacts on non-target species
Extensive use of herbicides to control this weed could have harmful effects on non-target species. It is critical to use pesticides selectively or apply other control methods to protect the biodiversity of the ecosystem.
Regulations prioritizing indigenous species
You should be aware of the regulations prioritizing indigenous species in your area before introducing Sagittaria Rigida outside of its native territory.
Cultivation and Propagation of Sagittaria Rigida
While it’s essential to exercise caution in planting Sagittaria Rigida, this can be cultivated and propagated under controlled conditions.
Optimal growing conditions
Sagittaria Rigida thrives in bogs, marshy areas, and along water banks in full sun or partial shade, in preferably acidic soil.
Techniques for propagation
Propagation of Sagittaria Rigida can be achieved either through seeds or by the division of the tubers.
Maintaining Sagittaria Rigida in controlled environments
While in cultivation, regular pruning is required to prevent excessive growth. It’s also crucial to ensure the pant doesn’t invade surrounding habitats.
Research on Sagittaria Rigida
Scientific inquires into Sagittaria Rigida have yielded insightful understanding into this plant species.
Current scientific inquiries about Sagittaria Rigida
Ongoing research is focused primarily on understanding the invasive potential of Sagittaria Rigida under different ecological conditions and identifying effective and environmentally-friendly control methods.
Previous discoveries about Sagittaria Rigida
Previous research has unearthed the plant’s crucial role in various aquatic ecosystems, in which it improves water quality, and provides a food source for wildlife while helping to control erosion.
Potential future areas of research
Future research could examine the medicinal potential of Sagittaria Rigida, considering it has been used in native cultures to treat various illnesses.
Historical and Cultural Relevance of Sagittaria Rigida
The cultural significance of Sagittaria Rigida dates back centuries and includes various uses across different cultures.
Historical use across different cultures
Historically, Native American tribes reportedly used Sagittaria Rigida as a food source during winter, and to treat various ailments.
Symbolic significance
In certain cultures, this plant symbolizes strength and protection, thanks to its rigid structure that is resilient against the elements.
Modern cultural relevance
Currently, Sagittaria Rigida is popularly utilized in water gardens for its aesthetic appeal and resilience. In the scientific community, it represents an exemplary study in aquatic botany and invasive species management.