In the vast realm of aquatic ecology, one entity that merits particular attention is the aquatic weed known as Schoenoplectus subterminalis. This scholarly article endeavors to provide a comprehensive understanding concerning the nature and significance of this aquatic plant species. You will explore various aspects of Schoenoplectus subterminalis, from its biological classification to its ecological role, revealing the complexities of this seemingly simple freshwater weed. By acknowledging these details, your comprehension of aquatic ecosystems, and the role of diverse species within them, is set to expand.
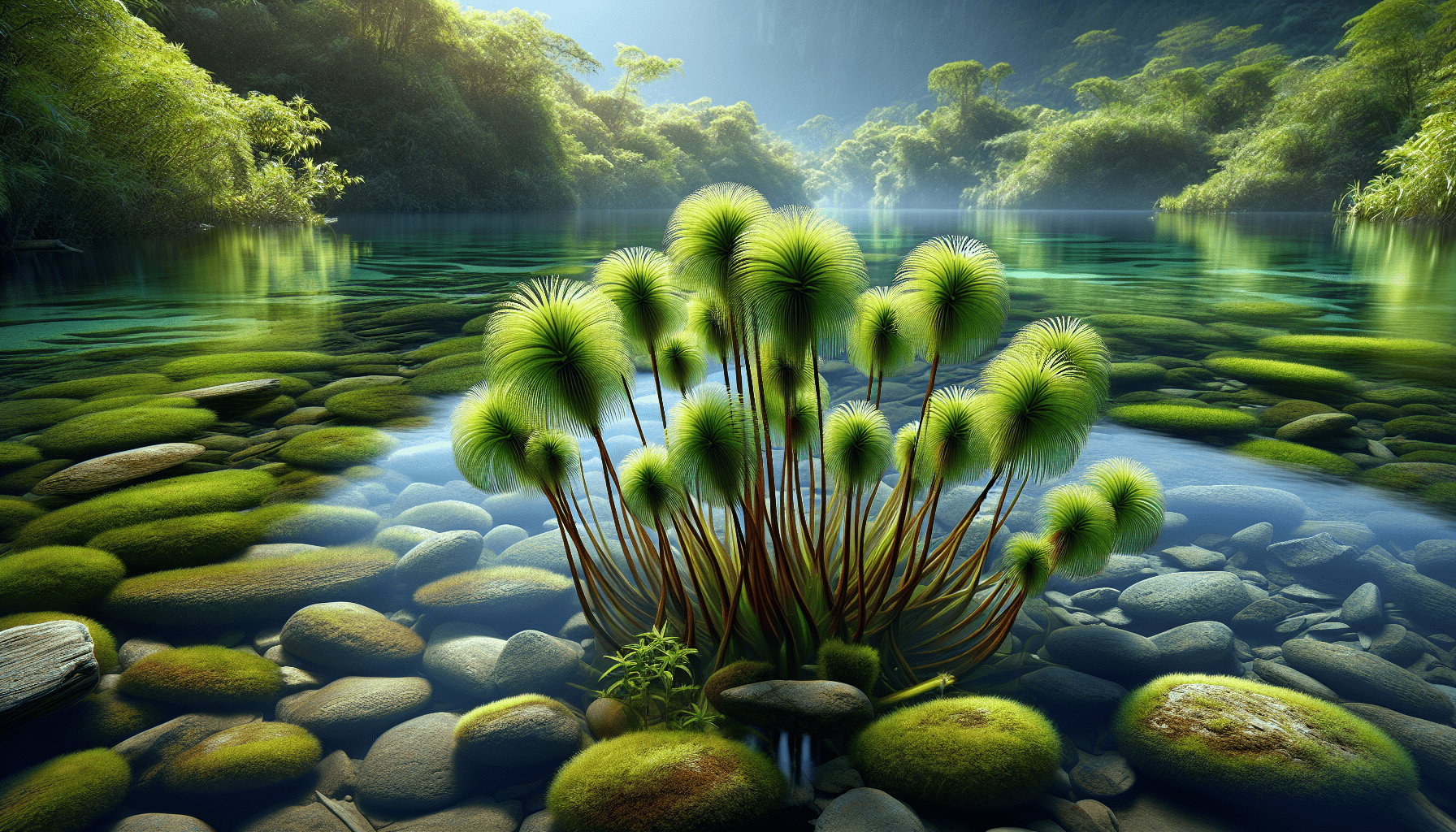

Overview of Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
Schoenoplectus subterminalis represents a distinctive species of aquatic plants often found in wetland environments. Known for its hardy nature and unique physical characteristics, this plant lives in some of the world’s most diverse ecosystems.
Different names for Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
Often referred to by different names depending on the region or specific scientific community, Schoenoplectus subterminalis is also commonly known as water club-rush, swaying bulrush, and northern bulrush, among others. Despite this variety in nomenclature, each moniker reflects the plant’s aquatic lifestyle or some distinctiveness of its physical appearance.
Scientific Classification of Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
Schoenoplectus subterminalis falls under the Kingdom Plantae and is classified in the angiosperms, monocots, and Commelinids clade at the broadest taxonomic levels. It’s a part of the Cyperaceae family (also known as bulrush or sedge family), under the Genus Schoenoplectus.
Physical Description of Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
The structural features of Schoenoplectus subterminalis are multifaceted and remarkably adapted to its wetland environments.
Appearance of the Plant
Schoenoplectus subterminalis is typically a perennial herb that exhibits a reedy, slender appearance, reaching heights between 30 cm to 2 m. It possesses a hollow stem that is upright or slightly inclined, which adds to its distinctive visual aesthetic in the wetland landscapes.
Description of Leaves
The plant’s leaves are often inconspicuous, reduced to sheaths around the plant’s base, while older leaves commonly form a fringe of brown fibers.
Description of Flowers and Fruits
Schoenoplectus subterminalis produces flowers and fruits which are borne in spikelets. These are cylindric, contiguous or slightly apart and form an inflorescence often all on one side. Fruits are achenes, small, brown and noticeably three-sided.
Habitat of Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
This unique plant is decidedly at home in wetlands, displaying a broad preference for a range of aquatic environments.
Geographical Locations where Schoenoplectus Subterminalis Grows
Though originally found in North America, Schoenoplectus subterminalis now has a cosmopolitan distribution. It is widespread throughout Americas, Eurasia, Australasia, and some parts of Africa.
Types of Water Bodies Preferred by Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
This plant thrives best along the banks of freshwater bodies such as marshes, ditches, pond margins, and slow-moving streams where it forms dense proliferations.
Preferred Soil Conditions
Schoenoplectus subterminalis prefers wet, muddy or damp soil, and is often found in areas of standing water. It has a high tolerance for various soil types and water conditions, demonstrating impressive resilience.
Life Cycle of Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
The life cycle of Schoenoplectus subterminalis follows a fairly predictable pattern commensurate with most perennial plants.
Stages of Growth
This plant begins life as a small seed. Once germinated, it undergoes rapid vegetative growth to establish its presence, before maturing and ultimately reproducing via seeds ensuring the continuity of its lineage.
Duration of Each Stage
The timing for each life stage can be contingent on surrounding environmental conditions. The plant generally has a fast growth rate, with flowering and seed production occurring annually, typically from late spring to early autumn.
Propagation Methods
While Schoenoplectus subterminalis mostly multiplies through seeds, it can also propagate vegetatively from fragments of stems or rhizomes, thus enhancing its spread and persistence.
Ecological Impact of Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
The overall impact of Schoenoplectus subterminalis on its environments remains twofold.
Impact on Aquatic Environment
Schoenoplectus subterminalis plays a significant role in stabilizing the water edges, preventing soil erosion and improving water quality by filtering pollutants.
Impact on Other Aquatic Life Forms
The dense stands of this plant create a thriving habitat for a diverse range of organisms including birds, insects, and certain fish species, aiding biodiversity.
Impact on Human Activities
Conversely, the overgrowth of Schoenoplectus subterminalis can restrict water flows, hinder accessibility to water bodies, and impede recreational activities such as swimming and boating.
Economic Impact of Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
The economic implications of Schoenoplectus subterminalis demonstrate both benefits and detriments.
Impact on Commercial Fishing
While providing habitat to some fish species, excess proliferation may hinder fishing activities, affecting commercial fishing profitability.
Impact on Marine Tourism
The overgrowth could reduce the attractiveness of water bodies for activities like boating and swimming, negatively impacting tourism.
Potential Use in Industries
Conversely, there is growing interest in its potential industrial applications, including biomass production and as raw material for paper, thus contributing to local and regional economies.
Control and Management of Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
Managing the infestations of Schoenoplectus Subterminalis is a topic of interest for prevent damages.
Manual Control Methods
Manual removal, including dredging and use of mechanical cutters can be carried out to manage its growth, especially where it’s causing obstructions.
Chemical Control Techniques
The use of specific herbicides can be effective, although they are used sparingly because of the potential detrimental impact on non-target species and surrounding aquatic ecosystems.
Biological Control Techniques
Biological controls, for instance, the introduction of species that feed on the plant, are being researched as sustainable options.
Uses of Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
This versatile plant offers a diversity of uses spanning various fields.
Use in Traditional Medicine
Across different cultures, Schoenoplectus subterminalis has been used for medicinal purposes, including as a diuretic, astringent, and in treating skin ailments.
Use in Craft and Construction
The strong stems have been employed in craftwork and construction, particularly in weaving mats and making thatch.
Potential Role in Bioremediation
Considering the plant’s capacity to absorb heavy metals, it holds potential for bioremediation to clean up polluted water bodies.
Threats and Conservation of Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
Schoenoplectus subterminalis faces various threats, warranting conservation measures.
Threats to Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
The primary threats to this plant include habitat loss and pollution from human activities, and invasive species competition.
Conservation Measures
Efforts like habitat restoration and preservation, along with sustainable water management practices, are currently being employed to conserve this useful wetland species.
Impact of Climate Change on Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
Climate change, particularly changes in temperature and precipitation patterns, could potentially affect the distribution and growth of Schoenoplectus subterminalis, a topic warranting further study.
Scientific Research on Schoenoplectus Subterminalis
The scientific exploration of Schoenoplectus subterminalis remains vibrant and ongoing.
Past Research and Findings
Past studies have shed light on its taxonomy, physical characteristics, life cycle, ecological role, uses, and potential threats.
Current Research and Developments
Present research endeavors focus on its ecological influence, its potential role in mitigating pollution, and exploring bio-energy potential.
Future Research Opportunities
There remain exciting prospects for future investigations about this plant. Potential studies may include understanding its response to climate change, further unraveling its bioremediation potential, and exploring biological control options. Through such research, we can continue to enhance our understanding and ability to manage this unique species for its greatest benefit.