The exploration of the aquatic world hurl you headfirst into the lush but often overlooked realm of aquatic vegetation; among these, the aquatic weed Typha Lugdunensis particularly stands out. This seemingly unassuming plant bears significant ecological importance and yet is frequently underestimated or dismissed. This article seeks to cast the spotlight onto Typha Lugdunensis, unraveling its unique characteristics, ecological roles, and its potential impact on the habitats it resides in. As you venture through these lines of text, you will develop an enriched understanding of this aquatic marvel and the intricate web of life that thrives beneath the water surface.
Overview of Aquatic Weeds
Definition of aquatic weeds
Aquatic weeds, in their most basic sense, are any unwanted or disruptive plants that grow in or around bodies of water. These plants can cover large expanses of water and grow at an astonishingly rapid pace, causing serious imbalances within the environments they inhabit. Such imbalances may directly and indirectly affect not only the diversity and health of aquatic ecosystems but also impact human activities, particularly those associated with water use and management.
Different types of aquatic weeds
Aquatic weeds are immensely diverse, ranging from microscopic phytoplankton to larger species like water hyacinths, duckweed, and Cattails (Typha). The nature of the problems they pose and their management demands are heavily dependent on the specifics of their biology and ecology.
Effects of aquatic weeds on the ecosystem
Aquatic weeds drastically reshape ecosystem dynamics by outcompeting native plant species for resources, altering habitats, reducing water quality, and disrupting human uses of water bodies. However, some aquatic weeds, when controlled, can serve important ecological and economic roles.
Detailed Explanation of Typha Lugdunensis
Scientific classification of Typha Lugdunensis
Typha Lugdunensis is a species of Cattail that falls within the Kingdom Plantae. It belongs to the class Magnoliopsida, order Poales, and family Typhaceae. In essence, it is a monocot belonging to a small family of herbaceous plants that primarily grow in wet habitats.
Other names for Typha Lugdunensis
Typha Lugdunensis is also popularly known by its English common name, the Greater Bulrush. The vast range of this plant across different regions has led to the adoption of various names.
Habitat and Distribution of Typha Lugdunensis
Original and current habitat of Typha Lugdunensis
Typha Lugdunensis is native to many parts of the world, notably Europe, Asia, and North America. By nature, these plants thrive in freshwater settings – wetlands, ponds, marshes, lakes, and riverbanks being their preferred habitats.
Distribution and spread of Typha Lugdunensis worldwide
This species has spread beyond its original habitats to new regions across the globe thanks to its incredible adaptability and human activities. Effects of climate change, water manipulations, and disturbances have also contributed to its spread.
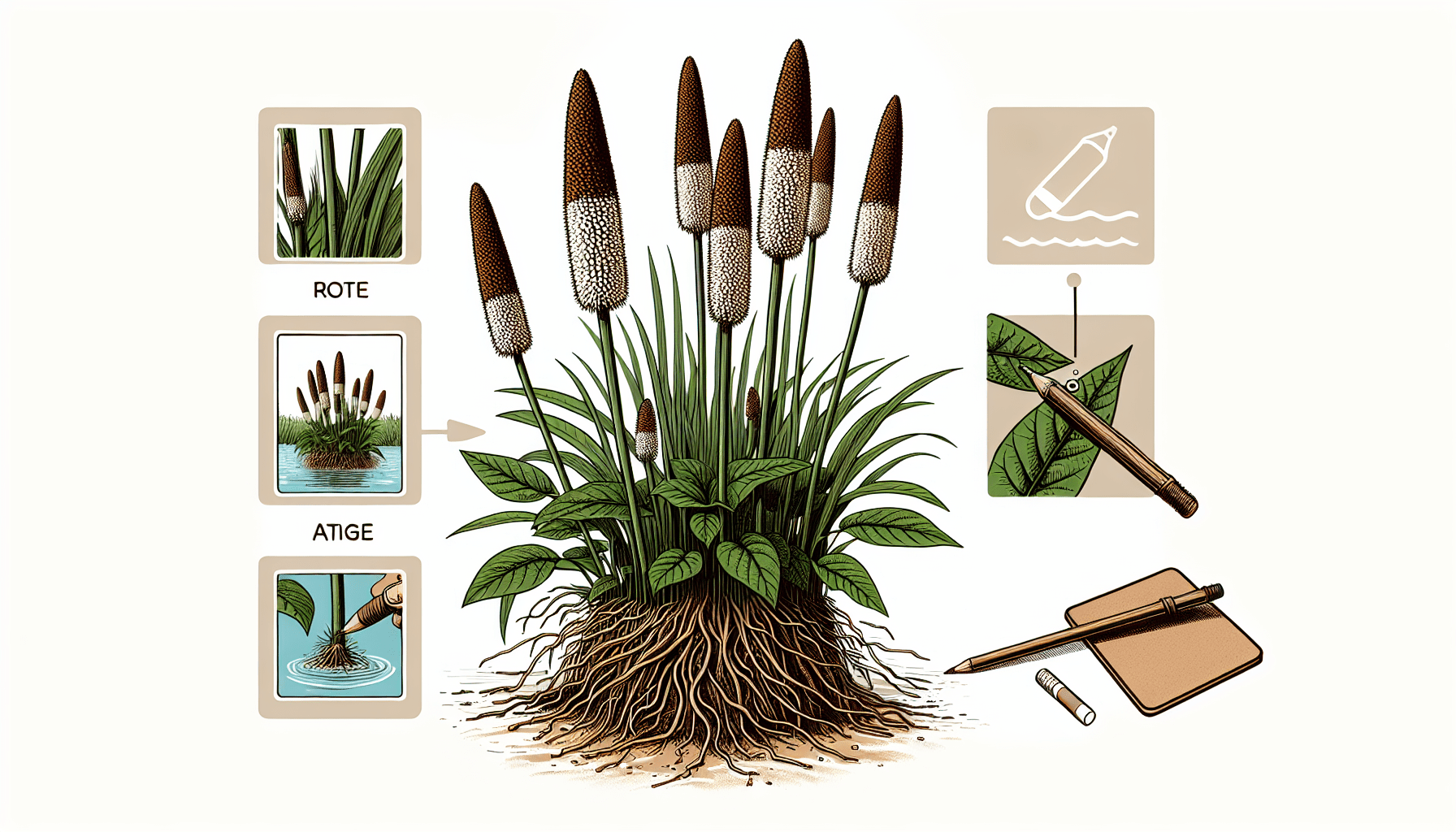
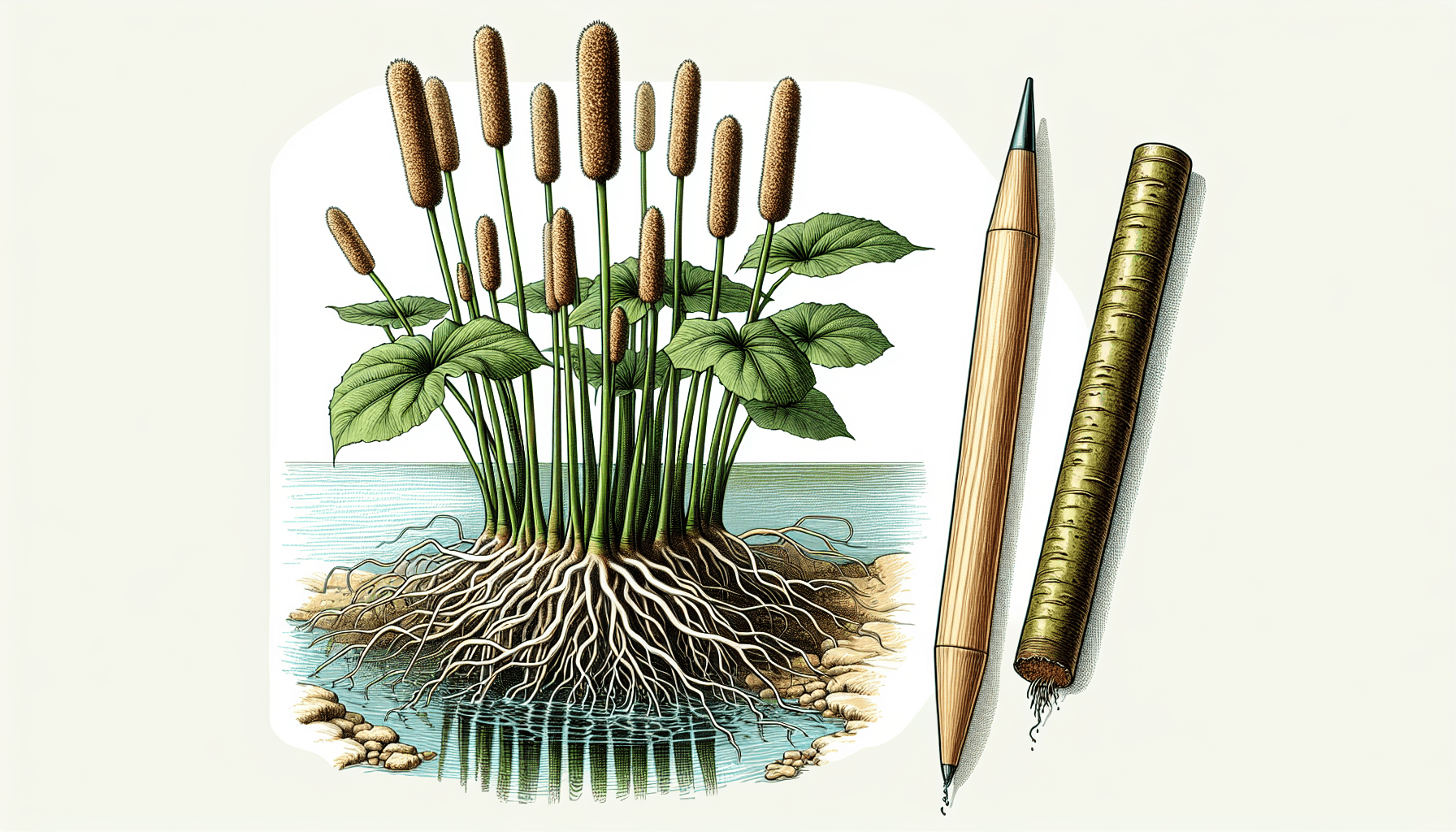
Characteristics of Typha Lugdunensis
Physical attributes of Typha Lugdunensis
Typha Lugdunensis is a tall perennial aquatic plant, characterised by its long, slender leaves and distinctive brown, sausage-like flower spikes at the tip of the stout, round stems. The seeds are tiny and have long, hair-like extensions which assist in wind dispersal.
Growth habits and life cycle of Typha Lugdunensis
Typha Lugdunensis exhibits rapid growth, primarily through vegetative reproduction. While it does produce seeds, it primarily spreads through rhizomes, forming expansive colonies in a relatively short time frame.
Adaptations of Typha Lugdunensis for its aquatic environment
Typha Lugdunensis is adapted for survival in aquatic environments, with aerenchyma that facilitates gas exchange under flooded conditions, and adaptations for both seed and vegetative reproduction.
Ecological Impact of Typha Lugdunensis
Interaction with other aquatic plants and animals
In its dense stand, Typha Lugdunensis provides a habitat for many aquatic animals. However, if too abundant, it can outcompete other aquatic plants, significantly reducing biodiversity and altering the habitat structure.
Impact on water bodies and wetland ecosystems
Typha Lugdunensis has notable impacts on water bodies and wetland ecosystems. It modifies water flow, sedimentation patterns, and can contribute to infilling of wetlands over the longer term.
Economic Importance of Typha Lugdunensis
Uses in industry for light manufacturing goods
Typha Lugdunensis has been extensively used for manufacturing objects such as mats, baskets and even in construction as roofing material, thanks to its sturdy and lightweight physical characteristics.
Potential use as a biofuel source
Research has pointed out the potential of Typha Lugdunensis as a source of biofuel. Its high productivity, considerably low demand for nutrients, and ability to grow in adverse conditions make it an attractive prospect.
Role in water purification
Typha Lugdunensis plays a significant role in water purification. It absorbs heavy metals, pesticides, and other pollutants, mitigating adverse environmental effects.
Control and Management of Typha Lugdunensis
Methods for controlling the spread of Typha Lugdunensis
Controlling Typha Lugdunensis typically involves mechanical, chemical, and biological methods. The appropriate method(s) usually depend on the specific conditions and requirements of the area in question.
Impact of these methods on the environment
While these control methods can mitigate the negative impacts of Typha Lugdunensis, they also have their drawbacks, such as the potential for harm to non-target species and the disruption of existing ecological relationships.
Conservation Status of Typha Lugdunensis
Current conservation status
As Typha Lugdunensis is widespread, it is typically not considered under threat and does not have a specific conservation status.
Threats to the survival of Typha Lugdunensis
Despite its general resilience, Typha Lugdunensis might face challenges due to changes in land-usage patterns, pollution, and changes in hydrological regimes.
Research on Typha Lugdunensis
Current and ongoing research efforts
Many current research efforts are focused on the use of Typha Lugdunensis in biofiltration systems and as a source of renewable energy.
Significant findings and breakthroughs
Significant discoveries include its role in ecosystem services, particularly in wetland habitats, its potential as biofuel, and its utility in phytoremediation.
Role of Typha Lugdunensis in Climate Change
How Typha Lugdunensis may influence or be influenced by climate change
Typha Lugdunensis, like other wetland plants, can potentially aid in carbon sequestration, thus playing a role in climate change mitigation. However, changes in climate may alter the distribution and growth dynamics of this species.
Potential uses of Typha Lugdunensis in climate change mitigation efforts
The potential utilization of Typha Lugdunensis in biofuel production is one promising avenue for climate change mitigation efforts. Its capacity to act as a carbon sink in wetlands can help offset certain greenhouse gas emissions.