As an avid scholar of botany or simply a curious mind, you might have come across the term Typha × Glauca and wondered what it represents. This fascinating aquatic weed, surprisingly familiar yet perhaps unknown by its scientific name, is the subject of this rigorous exploration. As you journey through the concise prose of this article, you shall gain an intriguing glimpse into the world of this aquatic vegetation, unearthing its origins, growth characteristics, potential benefits, and challenges it poses. Instruction on its identification and management offers practical knowledge with real-world applications, while discussion on its ecological and economic impacts broadens your perspective on the importance of understanding this unique plant species.

Definition of Typha x Glauca
Typha x Glauca is a hybrid species that belongs to the Typha genus, commonly known as the cattail family. This particular hybrid is a cross between two member species of the Typha genus – Typha latifolia and Typha angustifolia, giving it the distinct characteristics of both parents. It is an aquatic plant, characterized by a tall, slender, reed-like structure and typically grows in dense clusters along the water’s edges in both freshwater and brackish environments.
Scientific classification of Typha x Glauca
This hybrid species falls under the Plantae kingdom and the Tracheophytes division. It belongs to the Angiosperms class, signifying that it is a flowering plant. Moreover, it is part of the monocots clade and the Typhaceae family.
Common names and synonyms
Typha x Glauca is commonly referred to as the white cattail, or hybrid cattail in English. Another common name is the blue cattail. Typha x Glauca’s synonyms include Typha domingensis and Typha elatior.
Identifying characteristics of Typha x Glauca
This plant species is distinctively characterized by tall, narrow, linear leaves that are flat and have a grayish-green hue. The flowering spikes are also a distinguishing feature, appearing as dense, cigar-shaped, and brown in colour. Often, the male and female flowers are separated by a space on the same stalk, a characteristic feature of the Typha genus.
Habitat of Typha x Glauca
Types of water bodies where Typha x Glauca is found
As an aquatic plant, Typha x Glauca thrives in a variety of water bodies. These include but are not limited to freshwater marshes, lake margins, ditches, ponds, and riparian zones.
Geographical distribution of Typha x Glauca
This aquatic weed has a wide geographical distribution, spreading across large parts of North America and Europe. It is prominently seen in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom.
Preferred environmental conditions
Typha x Glauca thrives best in waterlogged conditions ranging from shallow standing water to water depths of up to 1 meter. It prefers areas with full sunlight and is tolerant of a variety of soil types.
Life Cycle of Typha x Glauca
Overview of Typha x Glauca life cycle
Typha x Glauca undergoes a typical life cycle which includes seeding, germination, growth, and reproduction. Usually, the life cycle begins in the spring season when temperatures and moisture levels are auspicious for germination.
Seasonal changes and their impact on Typha x Glauca
Changes in the seasons directly impact the life cycle of Typha x Glauca. In the spring season, seed germination occurs. The summer season promotes growth and maturation while fall sees the plant enter the flowering and seeding stage. In winter, the plant becomes dormant.
Longevity and survival strategies of Typha x Glauca
This aquatic weed is a perennial plant, hence, it can live for several years. It survives through winter dormancy and spreads aggressively using both seeds and rhizomes, allowing it to often dominate the areas where it grows.
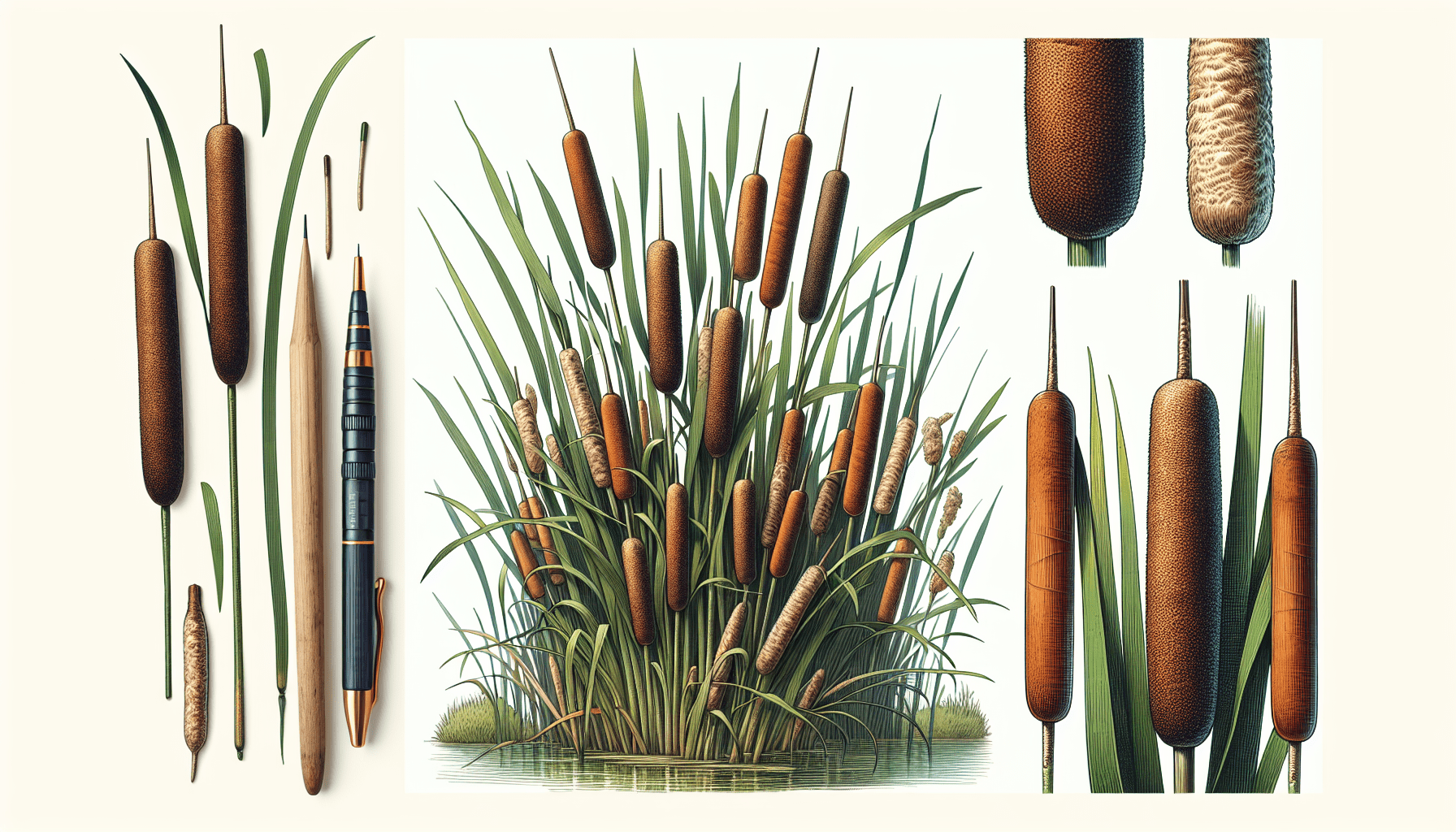
Growth and Morphology of Typha x Glauca
Structural features of Typha x Glauca
Typha x Glauca has long, linear leaves that grow up to 10 ft tall and spread outwards to form a dense clump. The plant features a thick, reed-like stem, and a strong root system that aids in water absorption and anchoring in the soil.
Size and growth rate
This hybrid cattail grows rapidly to a height of up to 3 meters. It can spread across large areas, dominated by its typically aggressive growth rate.
Adaptations for life in water
Typha x Glauca is well-adapted for life in water bodies. Its root system can grow in waterlogged soils, while its tall stem and leaves protrude above the water surface to facilitate photosynthesis. The plant also has specialized tissues, known as aerenchyma, that enable it to transport oxygen from the leaves down to the roots, ensuring respiratory processes even under water.
Reproduction and Propagation of Typha x Glauca
Methods of reproduction in Typha x Glauca
Typha x Glauca can reproduce sexually via seeds and asexually via rhizomes. The flowering spikes produce numerous seeds. Additionally, the plant’s extensive rhizome system allows for vegetative propagation.
Seed production and dispersal
The female flower spikes of Typha x Glauca produce thousands of tiny seeds that are equipped with small, hair-like structures, aiding in their wind dispersal. Furthermore, these seeds can also float on water, allowing for water-based dispersal.
Germination requirements
For successful germination, the seeds of Typha x Glauca require moist to waterlogged conditions, combined with full sunlight. They generally sprout in the spring season, when these conditions are optimal.
Interactions with other Organisms
Role of Typha x Glauca in ecosystem
Typha x Glauca plays a significant role in the ecosystem. It provides food and habitat for a variety of wildlife including birds and insects. It also contributes to being a key component of the wetland ecosystem, helping in water purification by filtering runoff and trapping sediments.
Common organisms interacting with Typha x Glauca
A variety of organisms interact with Typha x Glauca. It serves as a habitat for insects, and water birds often use it for nesting. Aquatic organisms such as fish and frogs also interact with this plant, using it as a shelter or spawning ground.
Impact on local biodiversity
While Typha x Glauca contributes to the biodiversity of an ecosystem, its aggressive growth can also lead to monocultures, often reducing local biodiversity by outcompeting native vegetation.
Impact on Human Activities
Common uses of Typha x Glauca by humans
Humans have found several uses for Typha x Glauca. These include its use for weaving mats and basketry, and for bio-energy production. It is also used for wastewater treatment in constructed wetlands due to its ability to purify water.
Potential risks and hazards
Despite its benefits, Typha x Glauca can also pose certain risks. Its rapid and uncontrolled growth can result in a dense formation of vegetation which may obstruct waterways, disrupt recreational water activities, and increase the risk of flooding by reducing water flow.
Impact on water quality and access
This plant can improve water quality by absorbing and trapping pollutants from agricultural runoff. However, a dense growth of Typha x Glauca can restrict water access and impact local water usage.
Management and Control of Typha x Glauca
Strategies for controlling Typha x Glauca growth
The management of Typha x Glauca includes various strategies such as mechanical control, chemical control, and biological control. It is important to implement these controls early on before the plant forms a dense growth.
Chemical control methods
Chemical control methods typically involve the use of herbicides. Glyphosate and imazapyr are often used for controlling Typha x Glauca. These chemicals should be applied during the active growth stage for the best results.
Biological control methods
Biological control methods typically involve introducing natural enemies of Typha x Glauca. Some insect species, such as cattail fly and cattail moth, have been studied for potential use in biological control.
Mechanical control methods
Mechanical control methods involve physically removing the plant, either by hand-pulling, cutting, or mowing. Dredging is also often used to effectively eliminate the dense vegetation and root system.
Research and Studies on Typha x Glauca
Overview of major research studies on Typha x Glauca
Numerous studies have been conducted on Typha x Glauca, focusing on its biological characteristics and potential utilizations in wastewater treatment, bio-energy production, and physical uses such as mat weaving and basketry.
Current areas of active research
The complex biology and aggressive growth of Typha x Glauca warrant continuous research. Current areas of active research include its potential role in carbon sequestration, and strategies to control its spread in areas where it negatively impacts biodiversity.
Future directions for research
As concerns over climate change intensify, prospective research is likely to focus on Typha x Glauca’s potential role in carbon sequestration and use in greenhouse gas reduction.
Conservation and Sustainability of Typha x Glauca
Role of Typha x Glauca in habitat conservation
Typha x Glauca plays a critical role in wetland conservation by creating a habitat for a variety of wildlife and promoting the overall health of the ecosystem by filtering pollutants from water systems.
Impact of Typha x Glauca on water sustainability
Typha x Glauca contributes to water sustainability by filtering pollutants from agricultural runoff, purifying water bodies, and aiding in overall aquatic health.
Efforts to protect Typha x Glauca populations
While control efforts are often required to manage its aggressive spread, there are also efforts to protect Typha x Glauca in places where it positively contributes to the ecosystem. These efforts include maintaining ideal habitats and moderate populations to ensure that its benefits are harvested without compromising local biodiversity.
