In the sphere of aquatic plants, a certain species bears exploration and explication: the Utricularia breviscapa. As part of your botanical journey, you’ll traverse through understanding its morphology, physiology, and ecological role. Let us begin by understanding its basic identity. Known typically as the Utricularia breviscapa, it is a little-explored aquatic weed that provides intriguing insights into the intricate world of water-dwelling flora. This article promises to engage your curiosity and expand your knowledge about the fascinating world of aquatic plants.
The Utricularia Breviscapa: A Basic Overview
Species identification and nomenclature
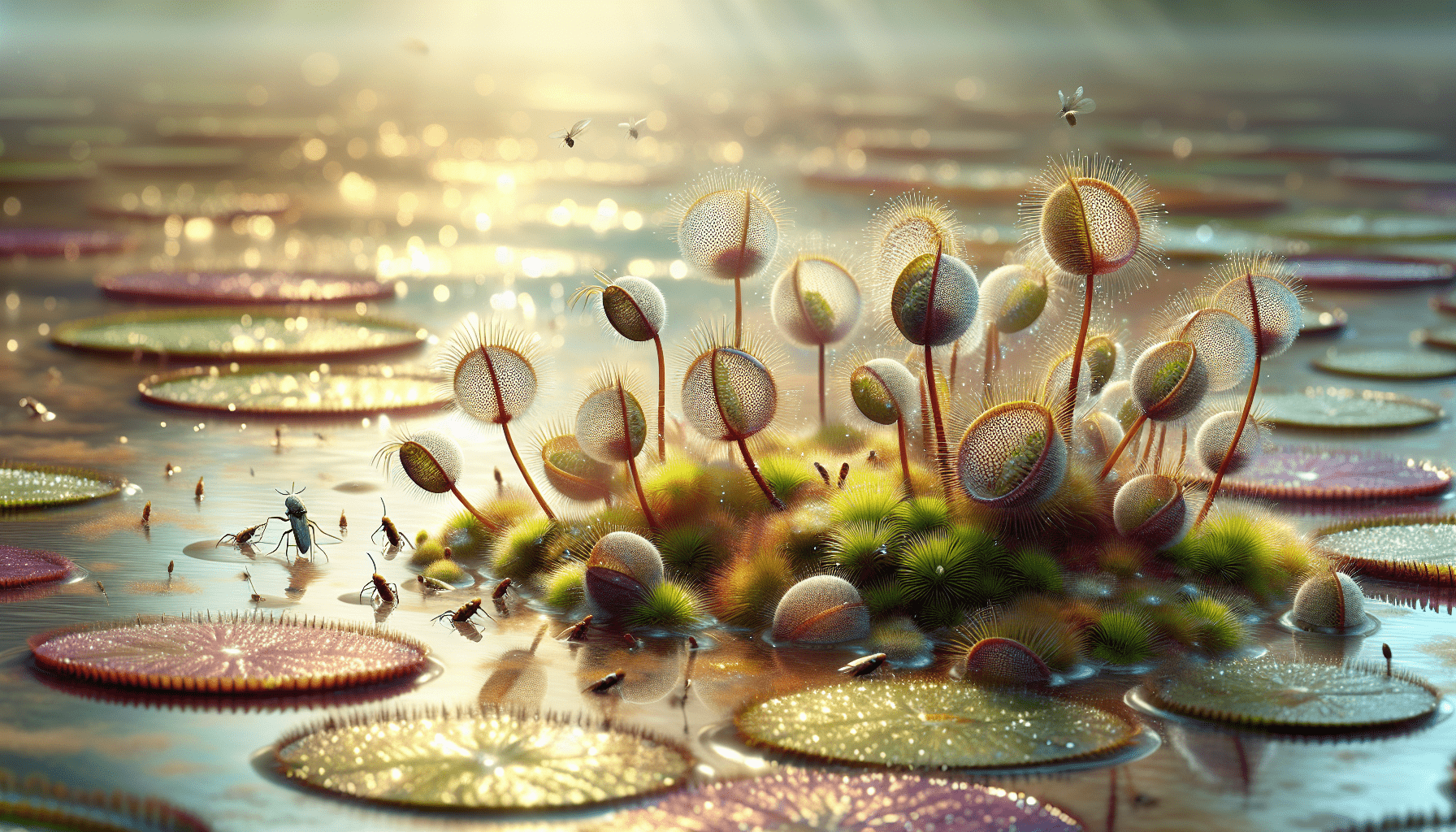
Utricularia breviscapa, widely known as the Lantern Marsh Bladderwort, is one of several species in the Utricularia genus that belongs to the Lentibulariaceae family. This aquatic perennial species is classified as a carnivorous plant due to its unique adaptation to trap and digest tiny invertebrates.
Aquatic nature of Utricularia Breviscapa
Inherently, Utricularia breviscapa thrives in the water bodies. It is an aquatic plant species that is typically submerged in standing or slow-flowing water bodies. Due to its ability to produce specialized structures known as bladder traps, this species becomes uniquely able to thrive in nutrient-deficient aquatic environments.
Geographical distribution
Geographically, Utricularia breviscapa is largely distributed across tropical and subtropical regions. It is natively found in South America, particularly in Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Additionally, this species has shown a tendency to proliferate in different parts of Australia and Southeast Asia.
Characteristic Features of Utricularia Breviscapa
Physical attributes
Physically, Utricularia breviscapa does not have stem-like structures, but it possesses threadlike stolons that allow it to attach itself to substrates in the aquatic environment. Its leaflike structures are usually undifferentiated or filiform, to achieve an efficient water movement around it. The yellowish-green flowers of the plant are typically small and not very noticeable.
Specific growth patterns
Being an aquatic perennial, Utricularia breviscapa typically shows rhizomatous growth in the water. The plant is often observed forming dense mats in the water body as its filiform structures continue to multiply and grow. Owing to its prolific growth, it can spread rapidly under favorable conditions.
Adaptive mechanisms
Utricularia breviscapa has developed unique adaptive mechanisms to survive in nutrient-deficient environments. Its bladder traps are filled with water and maintain a negative pressure inside them. These traps act like a suction device, ensnaring and digesting small invertebrates that brush against the trigger hairs.
The Habitat of Utricularia Breviscapa
Typical setting for Utricularia Breviscapa
The typical habitat for this species is aquatic environments such as ponds, lakes, and slow-moving streams or canals. Utricularia breviscapa can be found in water bodies with a variety of substrates, including clay, sand, and organic matter.
Impact on ecosystem
Due to its carnivorous nature, Utricularia breviscapa plays an important role in influencing nutrient dynamics within its ecosystem. By trapping and digesting small invertebrates, it helps decrease the nutrient limitations that often exist in aquatic environments. On the contrary, the unchecked growth of Utricularia breviscapa can lead to an imbalance in the local ecosystem, causing detrimental effects on other aquatic species.
Survival strategies in common habitats
Utricularia breviscapa thrives largely through its unique survival strategies. It relies on bladder traps as a substitute for root systems, absorbing nutrients directly from the water and trapped prey. This carnivorous adaptation is key for plants like Utricularia breviscapa that inhabit low-nutrient environments.
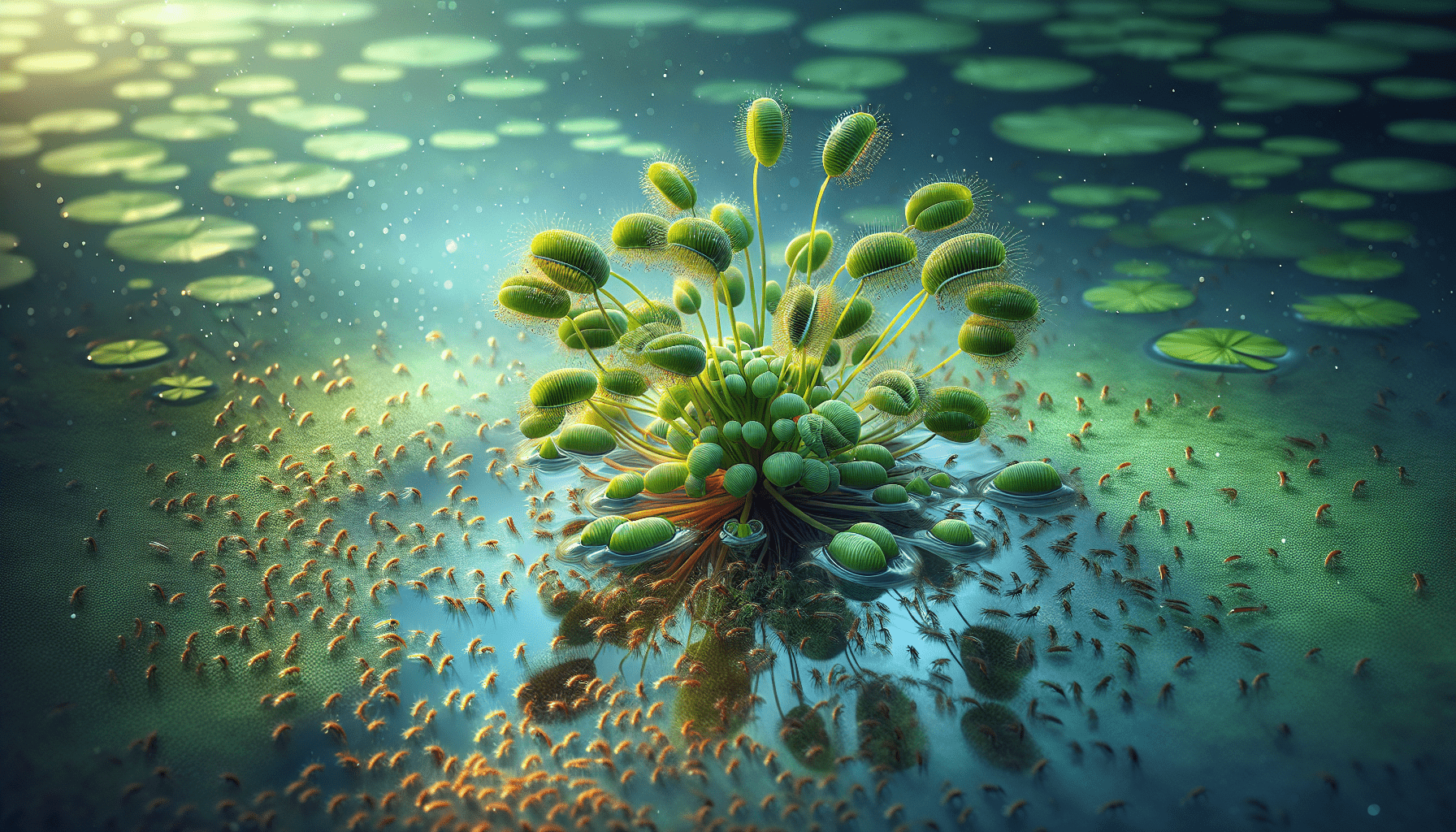

Growth and Development of Utricularia Breviscapa
Germination process
The germination process of Utricularia breviscapa usually occurs under water. The submerged seeds start to grow once they encounter favorable conditions with adequate nutrients and sunlight. These new plants form from the germinated seeds, grow stolons, and multiply, producing a new generation of plants.
Nutrient requirements
Despite flourishing in nutrient-poor aquatic environments, Utricularia breviscapa still requires basic nutrient elements like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. The lack of these nutrients in their habitat led to their evolution into carnivorous plants, filling this nutrient gap through the digestion of invertebrates trapped in their bladders.
Life cycle and reproductive mechanisms
The life cycle of Utricularia breviscapa involves both vegetative reproduction and sexual reproduction. For vegetative reproduction, the plant relies on fragmenting stolons which grow and develop into new plants. In sexual reproduction, the plant undergoes pollination followed by seed production and dispersal, and these seeds then sprout under favorable conditions.
The Unique Trapping Mechanism of Utricularia Breviscapa
Function of bladder traps
Utricularia breviscapa’s bladder traps, filled with water, serve as a crucial adaptation to their nutrient-poor environment, playing a key role in their carnivorous behavior. These bladder traps function by utilizing a vacuum mechanism to capture, suck in, and contain small invertebrates.
Target species and trapping process
The bladder traps primarily target small aquatic invertebrates such as protozoa, rotifers, and copepods. The trapping process is initiated when prey brushes against a hair trigger on the bladder, causing the trapdoor to open and rapidly suck in the organism along with surrounding water.
Impact and ecological significance of trapping
Trapping enhances the nutrient intake of Utricularia breviscapa and impacts the nutrient dynamics within the aquatic ecosystem. By capturing and digesting prey, the plant directly obtains necessary nutrients from the prey’s body, enriching its nutrient content and supporting its growth and survival in an otherwise nutrient-deficient environment.
Utricularia Breviscapa and Aquatic Biodiversity
Role within the food chain
As a carnivorous plant, Utricularia breviscapa holds a special position in the food chain. By preying on small aquatic organisms, it serves as a nutrient recycler within the ecosystem. However, it can also serve as food for a range of animals including ducks and other waterfowl.
Interactions with other aquatic species
Utricularia breviscapa interacts with other aquatic species in a variety of ways. Through predation, it affects the population dynamics of the small invertebrates on which it preys. These interactions influence the biodiversity within their respective habitats.
Influence on biodiversity in aquatic ecosystems
Utricularia breviscapa, through predation and becoming prey, directly affects the biodiversity of aquatic ecosystems. The plant’s influence extends to its environment as a whole, affecting nutrient cycles, energy flow, and the overall structure of its habitat.
Scientific Studies on Utricularia Breviscapa
Important research findings
Numerous scientific studies have been conducted on various aspects of Utricularia breviscapa. Many of these studies have shed light on its survival strategies, such as carnivory, which it employs to thrive in nutrient-poor environments and its unique growth pattern that allows it to colonize extensive areas relatively quickly.
Key scholars in the field
Notable scholars in the field of Utricularia breviscapa studies have made significant contributions to our current understanding of this species. Although many researchers have made important contributions, due to the nature of the guide no specific names are included here.
Unsolved questions and future research directions
While considerable research has been conducted on Utricularia breviscapa, many questions still remain. Future research directions may focus on refining our understanding of this plant’s trapping mechanisms, how it functions within various aquatic ecosystems, and its complete life cycle and evolutionary adaptations.
Challenges in Utricularia Breviscapa Management
Effects on aquatic ecosystems
Unchecked proliferation of Utricularia breviscapa can potentially lead to water bodies becoming choked with dense mats of these plants. This could restrict sunlight penetration, detrimentally affect oxygen levels in the water, and negatively impact other aquatic organisms.
Current weed control methods
Currently, weed control methods for managing Utricularia breviscapa populations include mechanical removal, chemical control with herbicide, or biological control through the introduction of herbivorous species. Each method has its own set of pros and cons, and its effectiveness can vary.
Challenges in weed management
Managing Utricularia breviscapa can prove challenging due to its rapid growth and propagation. In addition, some control methods can have negative impacts on other non-target organisms or disrupt the balance within the aquatic ecosystem.
The Role of Utricularia Breviscapa in Human Society
Medicinal properties and uses
Traditionally, certain species of Utricularia, including Utricularia breviscapa, are believed to possess medicinal properties. However, thorough scientific research is still lacking to confirm these potential medicinal uses.
Importance in scientific research
Utricularia breviscapa’s unique adaptations and ecological role make it an interesting subject for scientific research. Studies on this plant contribute valuable insights into the mechanisms of carnivorous plants and how organisms adapt to challenging environments.
Impact on agriculture and aquaculture
In agriculture and aquaculture, Utricularia breviscapa can be both beneficial and detrimental. While it might improve water quality by trapping and digesting small invertebrates, unchecked growth can block waterways and negatively impact other plants and animals.
Conservation Status and Threats to Utricularia Breviscapa
Current conservation status
Despite its widespread presence, there isn’t a specific global conservation status for Utricularia breviscapa. However, local regulations might exist in some regions to manage its growth, particularly in areas where it poses a threat to local biodiversity.
Major threats and survival issues
Loss of habitat due to development or pollution of water bodies is a major threat to this species. In addition, the introduction of invasive species can undermine Utricularia breviscapa populations by altering the conditions of their native habitats.
Conservation efforts and strategies
Strategies to conserve Utricularia breviscapa involve managing its growth and maintaining the quality of its aquatic habitats. These strategies can range from enacting protective legislation, to habitat restoration, to raising public awareness about the importance of conserving aquatic ecosystems.